“What Is Electromagnetic Induction?” Everything You Need to Know
Electromagnetic induction is a cornerstone of modern technology and a fundamental principle in physics. It is the process by which a changing magnetic field produces an electric current in a conductor, powering everything from your home appliances to large-scale power generation. But what is electromagnetic induction exactly, and why is it so important? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the definition, historical evolution, key concepts, practical applications, and modern relevance of electromagnetic induction. Whether you’re a student, an engineer, or just curious about the science behind everyday technology, understanding electromagnetic induction will illuminate how energy is generated and harnessed in our world.
Introduction: Unleashing the Power of Electromagnetic Induction
Have you ever wondered how electricity is generated in power plants or how your induction stove heats your food without an open flame? These everyday marvels are made possible by electromagnetic induction. In fact, nearly 40% of the world’s electricity is produced through electromagnetic induction in generators and turbines. This phenomenon, discovered in the 19th century, revolutionized our ability to generate and control electricity, setting the stage for the modern industrial era.
In this post, we will cover:
- A clear definition: What exactly is electromagnetic induction and what are its essential properties?
- Historical context: How did scientists like Faraday and Lenz contribute to our understanding of electromagnetic induction?
- In-depth exploration: We’ll break down the underlying principles, key equations, and the mechanisms that drive electromagnetic induction.
- Real-world examples: From power generation to wireless charging and beyond, see how electromagnetic induction is applied in diverse scenarios.
- Importance and benefits: Discover how mastering this concept can lead to more efficient energy use, innovative technologies, and a deeper understanding of physical phenomena.
- Common misconceptions and FAQs: We’ll debunk myths and answer frequently asked questions to clarify any confusion.
- Modern trends: Explore the latest research and technological advancements that are evolving the applications of electromagnetic induction.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of what is electromagnetic induction and why it remains a vital element in science, engineering, and everyday life. Let’s dive in and spark your curiosity!
What Is Electromagnetic Induction? A Straightforward Definition
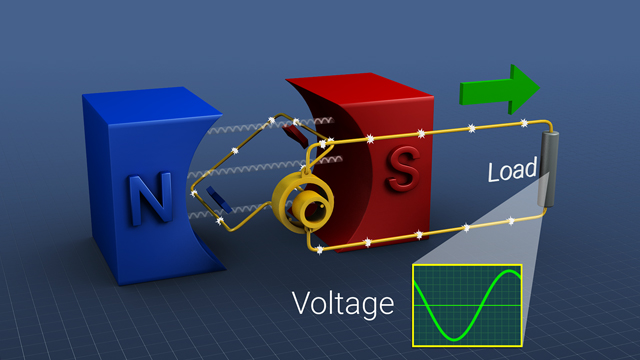
Electromagnetic induction is the process by which a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in a conductor. This phenomenon occurs when either the magnetic field within a circuit changes or when the circuit moves through a magnetic field. The induced voltage can then drive an electric current if the circuit is closed.
Essential Characteristics of Electromagnetic Induction
Induced EMF: The generation of a voltage (electromotive force) due to a change in magnetic flux.
Magnetic Flux Change: Electromagnetic induction requires a change in the magnetic field’s intensity or direction through the area of a conductor.
Relative Motion: It can result from the movement of a conductor relative to a magnetic field or from a time-varying magnetic field around a stationary conductor.
Lenz’s Law: This law states that the direction of the induced current is such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it.
Faraday’s Law: Faraday quantified the phenomenon with the equation:
where is the magnetic flux, and the negative sign indicates the direction of the induced EMF (as described by Lenz’s Law).
Understanding these characteristics is crucial for grasping how electromagnetic induction underpins the operation of electrical generators, transformers, induction motors, and many other devices.
Historical and Contextual Background
The Pioneers Who Unlocked Electromagnetic Induction
The journey to understanding electromagnetic induction is one of the most fascinating in scientific history. It began in the early 19th century with groundbreaking experiments that would eventually lead to the modern electrical revolution.
Michael Faraday: The Father of Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday’s Experiments: In 1831, Michael Faraday conducted a series of experiments that demonstrated how a changing magnetic field could produce an electric current. His experiments involved moving a magnet through a coil of wire and observing that this motion induced an electric current in the coil.
- Faraday’s Law: From these experiments, Faraday formulated what is now known as Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. His work established that the induced electromotive force is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit.
- Impact on Technology: Faraday’s discoveries laid the groundwork for modern electrical engineering. His insights made it possible to design electric generators and transformers, which are fundamental to power distribution and electrical devices.
Heinrich Lenz and the Direction of Induced Currents
- Lenz’s Law: Shortly after Faraday’s work, Heinrich Lenz introduced what is now known as Lenz’s Law. This law explains the direction of the induced current, stating that it will always oppose the change in magnetic flux that produced it. This opposition is a manifestation of the conservation of energy.
- Scientific Validation: Lenz’s Law provided a critical validation of Faraday’s experiments and helped refine the theoretical understanding of electromagnetic phenomena.
Subsequent Developments
- James Clerk Maxwell: In the latter half of the 19th century, Maxwell’s equations unified the theories of electricity and magnetism, providing a comprehensive mathematical framework that incorporated electromagnetic induction.
- Technological Milestones: The development of the electric generator, transformer, and induction motor in the late 19th and early 20th centuries transformed industries and paved the way for the widespread distribution of electrical energy.
Notable Historical Anecdotes
- Faraday’s Humble Beginnings: Faraday started as an apprentice to a bookbinder and had little formal education. His curiosity and perseverance led him to become one of the greatest experimental scientists, proving that innovation can come from unexpected places.
- Lenz’s Insight: Lenz’s formulation of the law bearing his name was a turning point in understanding that nature inherently resists changes—a principle that applies broadly in physics beyond electromagnetic induction.
These historical milestones highlight the evolution of what is electromagnetic induction from a series of experiments to a fundamental principle that drives modern technology.
In-Depth Exploration: The Many Facets of Electromagnetic Induction
To fully understand what is electromagnetic induction, we need to explore its underlying principles, practical mechanisms, and the various ways it manifests in different applications.
1. The Fundamental Principles
a. Magnetic Flux and Its Change
Magnetic Flux (ΦB): Magnetic flux is a measure of the total magnetic field passing through a given area. It is mathematically defined as:
where is the magnetic field vector and is the differential area vector.
Changing Flux: Electromagnetic induction occurs when there is a change in magnetic flux through a circuit. This change can result from:
- The movement of a magnet relative to a coil.
- The movement of a coil within a magnetic field.
- A time-varying magnetic field in a fixed coil.
b. Faraday’s Law of Induction
Mathematical Expression: Faraday’s Law quantitatively relates the rate of change of magnetic flux to the induced electromotive force (EMF):
The negative sign indicates that the induced EMF generates a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in flux (Lenz’s Law).
Practical Implications: This law is the foundation for the operation of electrical generators, where mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy through a rotating coil in a magnetic field.
c. Lenz’s Law: The Principle of Opposition
- Conservation of Energy: Lenz’s Law ensures that the induced current opposes the change in magnetic flux, thereby conserving energy. For example, if a magnet approaches a coil, the induced current will create its own magnetic field that repels the magnet.
- Real-World Manifestation: This opposition is why it takes effort to push a magnet into a coil or pull it out—an observable demonstration of electromagnetic induction at work.
2. Categories and Types of Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic induction can be categorized based on the conditions and configurations under which it occurs.
a. Self-Induction
- Definition: Self-induction occurs when a changing current in a coil induces an EMF in the same coil. This phenomenon is essential in understanding inductors, which store energy in magnetic fields.
- Example: When you quickly interrupt the current in an inductor, a high voltage spike is generated due to self-induction, which is why spark plugs in engines sometimes rely on this principle.
b. Mutual Induction
- Definition: Mutual induction is the process by which a changing current in one coil induces an EMF in a nearby second coil. This principle is the basis for transformers.
- Application: In a transformer, the primary coil’s changing current produces a varying magnetic field that induces a current in the secondary coil. This allows for the efficient transmission of electrical energy over long distances by stepping voltage up or down as needed.
c. Eddy Currents
- Definition: Eddy currents are loops of electrical current induced within conductors by a changing magnetic field. These currents flow in closed loops and can cause significant energy losses due to resistive heating.
- Mitigation: In many applications, such as in transformers and electric motors, designers use laminated magnetic cores to reduce the formation of eddy currents and minimize energy loss.
3. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Electromagnetic induction is not just a theoretical concept—it is at the heart of many modern technologies. Let’s explore several examples and case studies that illustrate its practical applications.
a. Electric Generators and Power Plants
- How Generators Work: In a typical power plant, turbines are driven by steam, water, or wind. These turbines rotate coils of wire within a strong magnetic field, inducing an EMF that generates electricity. This process is a direct application of Faraday’s Law.
- Case Study: Hydroelectric power plants, such as the Hoover Dam, rely on electromagnetic induction to convert the kinetic energy of flowing water into electrical energy. The efficient design of these generators is crucial for meeting global energy demands.
b. Transformers in Electrical Distribution
- Step-Up and Step-Down Transformers: Transformers utilize mutual induction to adjust voltage levels for efficient power transmission. A step-up transformer increases voltage for long-distance transmission, reducing energy loss, while a step-down transformer decreases voltage for safe use in homes and businesses.
- Impact: The widespread use of transformers in power grids is a testament to the importance of electromagnetic induction in modern infrastructure.
c. Induction Heating and Cooking
- Principle of Operation: Induction cooktops use electromagnetic induction to heat cooking vessels directly. When an alternating current passes through a coil beneath the cooktop, it generates a changing magnetic field that induces currents in the metal pan. These currents produce heat, warming the pan efficiently.
- Benefits: Induction cooking is highly efficient, offers rapid heating, and is considered safer and more energy-efficient compared to traditional gas or electric stoves.
d. Wireless Charging Technology
- How It Works: Wireless charging systems, such as those used for smartphones and electric toothbrushes, rely on electromagnetic induction. A charging pad generates an alternating magnetic field, which induces a current in the receiver coil within the device, charging its battery.
- Future Prospects: As wireless charging technology advances, electromagnetic induction is expected to play an even larger role in powering portable and wearable devices.
e. Medical Applications
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI machines use strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the human body. Electromagnetic induction is central to the operation of these machines, as it governs the behavior of the magnetic fields and the induced signals.
- Electromagnetic Therapy: Research into electromagnetic induction is also paving the way for innovative treatments that use controlled electromagnetic fields to stimulate tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
4. Importance, Applications, and Benefits of Electromagnetic Induction
Understanding what is electromagnetic induction is not only vital for scientists and engineers—it also has broad implications for technology, energy, and everyday life.
a. Energy Generation and Distribution
- Power Generation: Electromagnetic induction is the principle behind electric generators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. This is the foundation of modern electricity generation in power plants.
- Efficient Energy Transmission: Transformers, which operate on the principle of mutual induction, enable the efficient transmission of electrical energy over long distances by stepping voltage up or down as needed.
b. Technological Advancements
- Consumer Electronics: From induction cooktops to wireless charging devices, electromagnetic induction is embedded in many consumer products, making our lives more convenient and energy-efficient.
- Industrial Applications: In manufacturing, electromagnetic induction is used in processes such as induction heating, metal forging, and non-destructive testing, driving improvements in production speed and quality.
c. Environmental and Economic Benefits
- Sustainable Energy: By optimizing energy generation and reducing transmission losses, electromagnetic induction contributes to more sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Efficient power generation and distribution systems help lower greenhouse gas emissions, making electromagnetic induction a key player in environmental sustainability efforts.
d. Educational Value and Scientific Research
- Foundational Concept: Electromagnetic induction is a cornerstone in physics education, providing a clear example of how fundamental forces interact to produce useful energy.
- Innovative Research: Ongoing research in the fields of renewable energy, quantum computing, and advanced materials continues to build on the principles of electromagnetic induction, leading to new discoveries and technologies.
5. Addressing Common Misconceptions and FAQs
Despite its widespread application, several misconceptions about electromagnetic induction persist. Let’s clarify some common misunderstandings and address frequently asked questions.
Common Misconceptions
Misconception 1: Electromagnetic Induction Only Occurs in Power Plants.
Reality: While power plants are a major application, electromagnetic induction is also found in household appliances, medical devices, wireless chargers, and various other technologies.Misconception 2: The Process Is Too Complex for Everyday Use.
Reality: Despite its seemingly complex physics, electromagnetic induction operates seamlessly in everyday devices. The principles behind it have been refined over centuries and are now integral to numerous practical applications.Misconception 3: Induction Means Loss of Energy.
Reality: While no process is 100% efficient, electromagnetic induction is highly efficient when properly designed. Modern devices and systems minimize losses through advanced engineering and materials.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the basic equation for electromagnetic induction?
A: Faraday’s Law of Induction is given by:where is the magnetic flux and the negative sign reflects Lenz’s Law.
Q: How does electromagnetic induction relate to transformers?
A: Transformers operate on the principle of mutual induction, where a changing current in the primary coil induces a voltage in the secondary coil, allowing for voltage transformation.Q: Can electromagnetic induction occur in a static magnetic field?
A: No. A static magnetic field (one that does not change with time) will not induce an EMF. It is the change in the magnetic field that is necessary for induction.Q: Why is Lenz’s Law important?
A: Lenz’s Law determines the direction of the induced current, ensuring that the induced magnetic field opposes the change in the original magnetic flux. This principle is critical for energy conservation.Q: How is electromagnetic induction used in wireless charging?
A: Wireless chargers generate a varying magnetic field that induces a current in a receiver coil in the device, which then charges the battery.
6. Modern Relevance and Current Trends
Electromagnetic induction remains a vibrant field of study and application, influencing many aspects of modern technology and research.
a. Advances in Renewable Energy
- Wind and Hydroelectric Power: Generators that use electromagnetic induction are central to renewable energy systems. Recent innovations are improving generator efficiency and integrating smart grid technology.
- Solar Inverters: Although solar panels produce direct current (DC), inverters convert this into alternating current (AC) using principles that involve electromagnetic induction, allowing for integration into the grid.
b. Emerging Wireless Technologies
- Wireless Charging Innovations: The demand for wireless charging is driving research into more efficient induction systems. New materials and circuit designs are making wireless power transfer faster and more reliable.
- Internet of Things (IoT): As IoT devices proliferate, electromagnetic induction is increasingly used in energy harvesting and contactless power systems to keep small sensors and devices running autonomously.
c. Smart Grids and Energy Storage
- Advanced Transformers: Modern power grids are incorporating smart transformers that use electromagnetic induction to monitor and regulate power flow in real time.
- Energy Storage Systems: Inductive charging and induction-based converters are improving the efficiency of energy storage systems, which is vital for balancing supply and demand in renewable energy networks.
d. Scientific Research and Quantum Applications
- Nano-Electronics: At the nano-scale, researchers are exploring how electromagnetic induction can be harnessed to manipulate electrons in novel ways, contributing to the development of quantum computing and advanced semiconductor devices.
- Medical Technologies: Innovations in MRI technology and electromagnetic therapies continue to evolve, leveraging improved induction techniques for better imaging and treatment outcomes.
e. Educational Tools and Simulations
- Interactive Learning: Modern educational platforms utilize interactive simulations to demonstrate electromagnetic induction, helping students visualize and understand complex electromagnetic interactions.
- Online Courses and MOOCs: Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) now offer detailed modules on electromagnetism, making the concepts of electromagnetic induction accessible to a broader audience.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power and Potential of Electromagnetic Induction
In summary, understanding what is electromagnetic induction is fundamental to grasping how modern electrical systems function. From the generation of electricity in power plants to the operation of everyday devices like induction cooktops and wireless chargers, electromagnetic induction is a vital principle that drives our technological society.
Key Takeaways
- Definition and Characteristics: Electromagnetic induction is the process by which a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force in a conductor. Its essential features include the production of an induced EMF, reliance on changing magnetic flux, and the guiding principles of Faraday’s and Lenz’s laws.
- Historical Evolution: Pioneering work by Michael Faraday and Heinrich Lenz laid the groundwork for our modern understanding of electromagnetic induction, a concept that has since evolved to underpin countless technological advancements.
- Practical Applications: From electric generators and transformers to wireless charging and medical imaging, the applications of electromagnetic induction are broad and impactful.
- Modern Relevance: With ongoing advances in renewable energy, wireless technology, smart grids, and nano-electronics, electromagnetic induction continues to be at the forefront of innovation.
- Debunking Myths: Common misconceptions—such as confusion between electromagnetic induction and static magnetic fields or oversimplification of its complexity—are clarified through a deeper exploration of the underlying principles.
Call to Action
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of what is electromagnetic induction, it’s time to put this knowledge into practice:
- Explore Further: Read additional articles and research papers from reputable sources like HyperPhysics, IEEE Xplore, and MIT OpenCourseWare to deepen your understanding.
- Experiment Safely: If you’re a student or hobbyist, consider conducting simple experiments—such as moving a magnet through a coil—to observe electromagnetic induction firsthand (always follow proper safety guidelines).
- Engage with the Community: Share your questions, experiences, or experiments in the comments below or join online forums and local science clubs to discuss electromagnetic induction with fellow enthusiasts.
- Apply the Concept: Whether you’re working on a school project, a research initiative, or simply curious about how everyday devices work, let your understanding of electromagnetic induction inspire you to innovate and explore further.
We invite you to share this post with colleagues, friends, and anyone who might benefit from a deeper dive into the science behind electromagnetic induction. Your feedback and questions are invaluable—let’s continue the conversation and spark more curiosity!
Final Thoughts
Electromagnetic induction is not just a scientific principle confined to textbooks—it is a dynamic force that has transformed the way we generate, transmit, and use energy. From powering entire cities to enabling the latest advancements in wireless technology and medical imaging, the implications of electromagnetic induction are far-reaching and profound.
By understanding what is electromagnetic induction, you gain insights into the fundamental workings of our modern world. As technology continues to evolve and new challenges emerge, the principles of electromagnetic induction will undoubtedly remain at the heart of innovation and sustainable development.
Thank you for joining us on this in-depth exploration of electromagnetic induction. We hope this guide has not only answered your questions but also ignited your passion for the fascinating interplay between electricity and magnetism. Happy exploring, and here’s to a future charged with knowledge and innovation!