What Is An Anagram: Everything You Need to Know About This Intriguing Word Play
Have you ever stared at a word, rearranged its letters in your mind, and discovered a completely different word that sparks curiosity or humor? If so, you’ve encountered one of the oldest and most playful forms of linguistic creativity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what is an anagram—delving into its definition, historical roots, methods of creation, various types, real-world applications, common misconceptions, and its modern-day relevance. Whether you’re a wordplay enthusiast, a language lover, or someone simply looking to enhance their mental agility, this post has something for you.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Fascination with Anagrams
- Defining Anagrams: What Is an Anagram?
- Historical Background: The Origins and Evolution of Anagrams
- How Anagrams Work: A Deep Dive into the Mechanics
- Categories and Types of Anagrams
- The Importance and Applications of Anagrams
- Common Misconceptions and Frequently Asked Questions
- Modern Relevance and Current Trends
- Conclusion: Embracing the Art of Wordplay
1. Introduction: The Fascination with Anagrams
Imagine unlocking hidden meanings in everyday words or even secret messages embedded within famous texts. Anagrams have a way of capturing our imagination by revealing the playful side of language. From ancient philosophers to modern-day puzzle enthusiasts, the art of rearranging letters to form new words has sparked intrigue and delight for centuries.
Did you know? In the 16th century, anagrams were so popular that they were used as a form of intellectual competition among scholars and poets. Today, they appear in everything from cryptic crosswords to popular mobile apps, proving that the appeal of anagrams is truly timeless.
In this article, we will explore:
- What is an anagram? – A straightforward definition and explanation.
- Historical and cultural significance – Discover the origins and evolution of anagrams over time.
- Mechanics and examples – Learn how to create anagrams and see examples that illustrate their fun and function.
- Applications and benefits – Understand why anagrams matter in education, literature, cryptography, and even business branding.
- Misconceptions and FAQs – Get answers to common questions and clear up any misunderstandings.
- Modern relevance – Explore how digital technology is revolutionizing the way we create and enjoy anagrams.
By the end of this post, you’ll have a deep appreciation for this fascinating form of wordplay and plenty of ideas on how to incorporate anagrams into your own language adventures.
2. Defining Anagrams: What Is an Anagram?
At its core, an anagram is a word, phrase, or name formed by rearranging the letters of another word, phrase, or name. The essential characteristics that define an anagram include:
- Letter Rearrangement: Every letter of the original word must be used, and no new letters are added.
- Meaningful Transformation: The resulting word or phrase should ideally convey a meaning or evoke an idea, even if it’s just a playful twist.
- Integrity of Components: While the order changes, the frequency and identity of each letter remain constant.
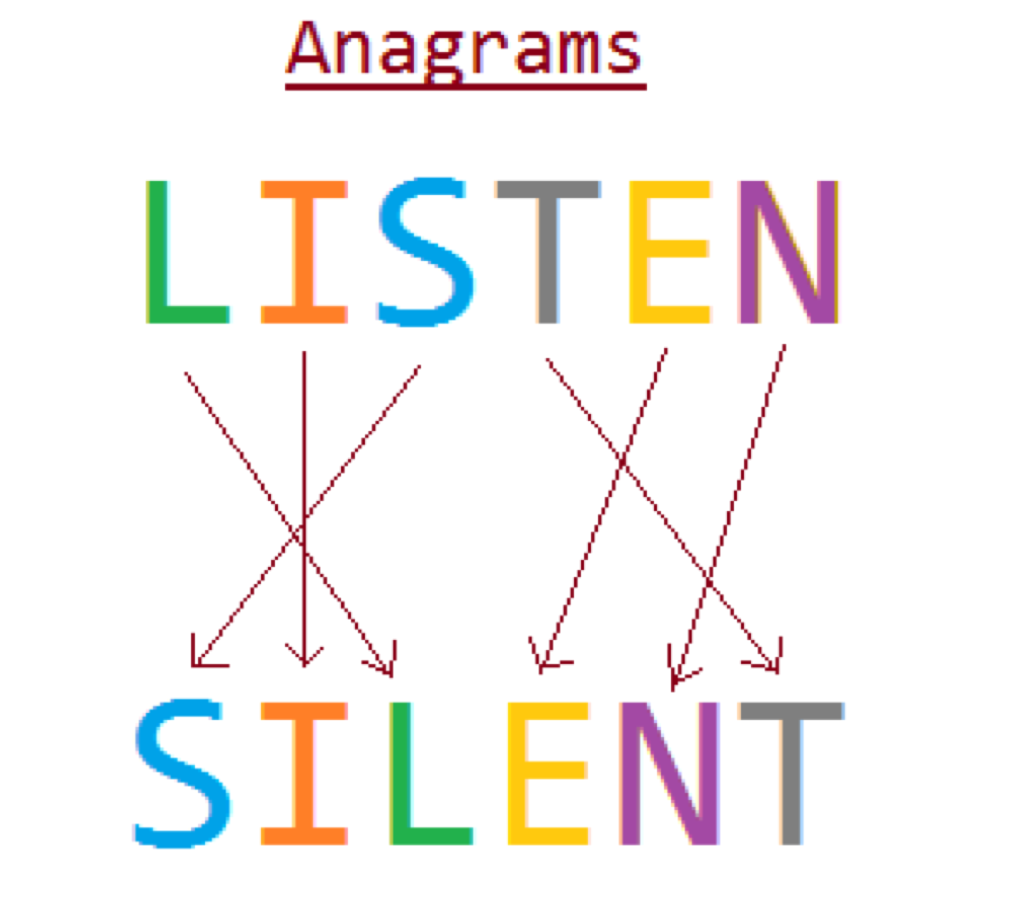
For example, the word “listen” can be rearranged to form “silent”, showcasing how the same letters can yield a completely different yet related concept. This interplay between form and meaning is what makes anagrams a delightful challenge for the mind.
Key Characteristics:
- Exact Letter Usage: All letters from the original must be present in the new arrangement.
- Order Variation: The sequence of letters is the only change.
- Potential for Hidden Meaning: Anagrams can reveal hidden messages or create puns.
In essence, asking “what is an anagram” invites us to explore the clever ways in which letters can be reshuffled to create new layers of meaning, humor, or even secret codes.
3. Historical Background: The Origins and Evolution of Anagrams
Anagrams are not a modern invention. Their roots stretch back thousands of years, with significant cultural and intellectual contributions throughout history.
Ancient Beginnings
- Greece and Rome: The concept of rearranging letters dates back to ancient civilizations. The Greeks and Romans used anagrams not only as a form of entertainment but also as a tool for divination and cryptography. Historical texts suggest that philosophers and mystics believed that rearranging letters could reveal hidden truths about the universe.
- Religious and Mystical Texts: In medieval Europe, anagrams were often found in religious texts and manuscripts. Scholars believed that the true meanings of sacred words could be unlocked through careful letter rearrangement, contributing to theological debates and mystical practices.
Renaissance and the Golden Age of Anagrams
- Literary Competitions: During the Renaissance, anagrams gained popularity among poets, writers, and intellectuals. It became a common pastime to challenge peers by creating clever anagrams from famous names or phrases. Notably, authors like William Shakespeare are rumored to have enjoyed wordplay, with some scholars even suggesting that anagrammatic techniques influenced his writing.
- Political Intrigue: Anagrams were sometimes used as covert communication tools during times of political tension. By rearranging letters in significant names or messages, conspirators could hide their true intentions, making anagrams an early form of cryptography.
Modern Day Evolution
- Puzzle Craze: The 20th century saw an explosion in the popularity of word puzzles, with anagrams playing a central role in crosswords, word scrambles, and other brain teasers. Magazines, newspapers, and later the internet provided a vast platform for anagram enthusiasts.
- Digital Revolution: Today, anagram generators and mobile apps have made the creation and sharing of anagrams easier than ever. With just a few clicks, anyone can generate thousands of combinations, opening up a world of linguistic experimentation.
The historical journey of anagrams reflects humanity’s enduring fascination with language. Understanding this evolution helps us appreciate how anagrams have not only entertained but also influenced cultural and intellectual movements over the centuries.
4. How Anagrams Work: A Deep Dive into the Mechanics
4.1 Step-by-Step Process
Creating an anagram may seem like a simple rearrangement of letters, but there’s a delightful complexity to the process. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the steps involved:
Start with a Base Word or Phrase: Choose a word or phrase that you’d like to transform. For example, let’s consider the word “conversation.”
List All the Letters: Write down each letter of the word to ensure that no letter is missed.
C, O, N, V, E, R, S, A, T, I, O, NMix and Match: Begin rearranging the letters. You might do this manually on paper, use letter tiles, or employ a digital tool. The goal is to form new words or phrases while using all the letters exactly once.
Check for Meaning: Not every rearrangement will result in a meaningful word or phrase. In our example, “conversation” can be transformed into “voices rant on,” which is both playful and contextually relevant.
Refine and Experiment: Sometimes the first attempt might not yield a coherent result. Experiment with different groupings and orders until you find an arrangement that satisfies your goal.
Validate the Anagram: Ensure that every letter from the original word is accounted for, and that no extraneous letters have been introduced. The final product should be a perfect permutation of the original.
4.2 Popular Examples
Let’s explore some classic and fun examples of anagrams:
“Listen” → “Silent”
This is one of the most famous anagrams. The transformation from “listen” to “silent” not only rearranges the letters but also offers a clever commentary on the nature of communication.“The Eyes” → “They See”
A neat trick that highlights how closely related words can be rearranged to reveal a hidden observation.“Astronomer” → “Moon Starer”
An anagram that humorously connects an astronomer’s role with the act of gazing at the stars.“Dormitory” → “Dirty Room”
A playful rearrangement that turns a mundane space into a humorous observation about its state.
4.3 Tools and Techniques
While traditional pen-and-paper methods are still cherished by many, modern technology offers several tools to assist in creating anagrams:
- Online Anagram Generators: Websites like Wordsmith Anagram allow users to input a word or phrase and receive a list of potential anagrams.
- Mobile Apps: There are numerous smartphone apps available that can instantly shuffle letters and generate anagrams, making the process accessible anywhere.
- Programming Algorithms: For those with coding skills, writing an algorithm to generate all possible permutations can be an enlightening challenge that combines computer science with linguistic art.
Using these tools not only speeds up the process but also introduces a level of precision and creativity that can inspire further exploration into the world of anagrams.
5. Categories and Types of Anagrams
Anagrams come in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. Let’s break down the different categories:
5.1 Simple vs. Complex Anagrams
Simple Anagrams:
These involve straightforward rearrangements where a single word is transformed into another single word or a short phrase. Examples include:- “Debit Card” → “Bad Credit”
- “Funeral” → “Real Fun”
Complex Anagrams:
These are more intricate, often involving multiple words or longer phrases. They may require additional creativity to maintain coherence and meaning. For example, the phrase “The Morse Code” can be reimagined as “Here Come Dots,” which cleverly references the method of Morse code communication.
5.2 Partial vs. Complete Anagrams
Partial Anagrams:
Sometimes, only a portion of the original letters is rearranged to form a new word, leaving behind a part of the original intact. This type is common in puzzles where only a fragment of a word or phrase is used to generate a clue.Complete Anagrams:
In this case, every letter from the original word or phrase must be used exactly once in the final output. This is the classical definition of an anagram and is typically what puzzles and competitions demand.
5.3 Anagram Puzzles in Popular Culture
Anagrams are not limited to word puzzles—they have also made their way into literature, music, and even advertising:
Literature:
Authors have long used anagrams as pseudonyms or as hidden signatures within their works. The use of anagrams can serve as an intellectual challenge for readers who enjoy deciphering hidden messages.Music and Entertainment:
Bands and artists sometimes rearrange letters in their names or song titles to create memorable, playful variations that engage their audience.Branding and Advertising:
Clever marketing campaigns occasionally incorporate anagrams to create catchy slogans or to disguise secret product names until the big reveal.
Understanding these categories can deepen your appreciation for the art of anagramming and open your eyes to the many ways that rearranging letters can lead to unexpected discoveries.
6. The Importance and Applications of Anagrams
Anagrams are more than just a playful diversion—they hold significant value in various fields and have a wide range of applications.
6.1 Cognitive Benefits and Mental Exercise
Engaging with anagrams is a proven method to sharpen the mind and improve mental agility. Here are some of the cognitive benefits:
- Enhanced Vocabulary:
Regular exposure to anagrams can expand your word bank, helping you recognize and remember new words. - Improved Pattern Recognition:
The process of identifying and rearranging letters improves your ability to detect patterns—a skill that is useful in both academic and everyday problem-solving. - Boosted Creativity:
Experimenting with different letter combinations encourages creative thinking and can lead to innovative solutions in unrelated fields. - Memory and Focus:
The challenge of keeping track of each letter in a complex anagram helps improve working memory and concentration.
6.2 Anagrams in Literature and Cryptography
- Literary Devices:
Throughout history, anagrams have been used as a literary tool to add layers of meaning to texts. Authors have embedded anagrams as secret messages, hidden dedications, or playful signatures in their manuscripts. - Cryptography:
In times of war and political intrigue, anagrams have served as a rudimentary form of encryption. By rearranging letters in sensitive messages, senders could obscure the true meaning from unintended readers. This historical use underscores the timeless human desire to protect information through clever linguistic tricks.
6.3 Business, Branding, and Entertainment
- Brand Naming:
Businesses often search for unique, memorable names that resonate with consumers. Anagrams can offer an innovative way to reimagine existing words or phrases, resulting in brand names that stand out. - Advertising Slogans:
In a crowded market, a clever anagram in a slogan or marketing campaign can capture attention and create buzz around a product or service. - Entertainment and Games:
Beyond traditional puzzles, anagrams play a central role in board games (like Scrabble and Boggle) and digital games, engaging players in fun, educational challenges.
The applications of anagrams span from the purely recreational to the highly practical. Whether it’s exercising your brain, crafting a memorable brand, or unlocking the secrets of a historical document, understanding what is an anagram and how it works can provide unexpected benefits in your everyday life.
7. Common Misconceptions and Frequently Asked Questions
Despite their popularity, there are a few common misunderstandings about anagrams. Let’s address these misconceptions head-on and answer some frequently asked questions.
7.1 Myth vs. Reality: Clearing Up the Confusion
Myth: Anagrams Are Just Random Jumbles of Letters.
Reality: Anagrams require precision and creativity. Every letter must be accounted for, and the end result often carries a deliberate meaning or hidden message.Myth: All Anagrams Are Equally Difficult.
Reality: The difficulty of creating an anagram can vary greatly depending on the complexity of the original word or phrase and the intended outcome. Simple anagrams might be easily solved, while more intricate ones can challenge even seasoned word enthusiasts.Myth: Anagrams Are Outdated and Only Relevant in Puzzles.
Reality: While anagrams are a staple in word puzzles, their applications extend far beyond. They play a role in cryptography, literature, branding, and even computer programming, proving their enduring relevance.
7.2 FAQ Section: Quick Answers to “What Is an Anagram?”
Q1: What exactly is an anagram?
A1: An anagram is a word, phrase, or name formed by rearranging the letters of another, using every original letter exactly once.
Q2: Can any word be turned into an anagram?
A2: In theory, yes. However, not every rearrangement will result in a meaningful or recognizable word or phrase. The challenge lies in finding a combination that makes sense.
Q3: Are there tools available to help generate anagrams?
A3: Absolutely. Numerous online generators, mobile apps, and even programming libraries can assist in creating anagrams. These tools are particularly useful for exploring complex or long phrases.
Q4: How can anagrams benefit my brain?
A4: Engaging in anagram puzzles enhances vocabulary, improves pattern recognition, boosts creativity, and sharpens memory and focus.
Q5: Are anagrams used in any professional fields?
A5: Yes, anagrams have historical significance in cryptography, are used in literary works, and even influence modern branding and advertising strategies.
8. Modern Relevance and Current Trends
In today’s digital age, the concept of what is an anagram continues to evolve, finding new applications and resonating with contemporary audiences.
8.1 Technological Advances: From Paper to Apps
Online Tools and Software:
The advent of the internet has revolutionized the way we approach anagrams. Websites such as Wordsmith Anagram allow users to generate countless permutations with just a click. These tools not only make the process accessible but also provide inspiration for creative minds.Mobile Applications:
With a growing number of word-based games and educational apps, anagram solvers have become a common feature on smartphones and tablets. These apps often include challenges, leaderboards, and community features that make learning and practicing anagrams both fun and competitive.Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
Recent advances in AI have led to sophisticated language processing algorithms that can generate and solve anagrams almost instantaneously. This technology has applications in everything from code-breaking to enhancing language learning platforms.
8.2 Contemporary Uses in Social Media and Pop Culture
Social Media Engagement:
Platforms like Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok have seen a surge in language-based challenges, including daily anagram puzzles. These challenges not only engage users but also foster a community of puzzle solvers who share tips and creative insights.Pop Culture References:
Modern literature, television shows, and movies often include clever wordplay that incorporates anagrams. Whether it’s a hidden clue in a mystery novel or a witty tagline in a film, anagrams add an extra layer of intrigue that audiences love to decipher.Educational Trends:
Educators are increasingly incorporating anagrams into classroom activities to encourage creative thinking and problem-solving. By engaging students in playful language exercises, teachers can make learning more interactive and enjoyable.
8.3 Future Prospects
As technology and language continue to evolve, the future of anagrams looks bright:
Enhanced Learning Tools:
With virtual reality and augmented reality technologies on the rise, imagine a future where students can interact with 3D anagrams that float in space, making learning both immersive and memorable.Cross-Disciplinary Applications:
The principles behind anagrams—pattern recognition, creative rearrangement, and logical problem-solving—can be applied to fields such as data science, bioinformatics, and even art. As we see more interdisciplinary approaches to education and innovation, the skills honed by solving anagrams may prove invaluable.
9. Conclusion: Embracing the Art of Wordplay
In this extensive exploration of what is an anagram, we have journeyed through its definition, historical significance, methods of creation, varied categories, and modern applications. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
Definition:
An anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of another, using every letter exactly once to potentially reveal hidden meanings or playful messages.Historical Significance:
From ancient Greece and Rome to Renaissance literary circles and modern digital platforms, anagrams have been a part of human culture for centuries.Mechanics and Creativity:
The process of creating anagrams involves a careful balance of precision and creativity. Whether through traditional pen-and-paper methods or sophisticated digital tools, the art of rearranging letters continues to challenge and delight us.Applications and Benefits:
Beyond recreational puzzles, anagrams enhance cognitive abilities, enrich literature and cryptography, and even influence modern branding and business strategies.Modern Relevance:
The digital age has breathed new life into anagrams, making them more accessible, engaging, and applicable to a range of disciplines from social media to advanced AI.
Final Thoughts and Call-to-Action
Understanding what is an anagram opens up a world of linguistic innovation and playful creativity. Whether you’re looking to challenge your mind, add a clever twist to your writing, or simply enjoy a fun word puzzle, anagrams offer endless possibilities.
We’d love to hear from you!
- Have you ever created or encountered a memorable anagram?
- What are your favorite examples of wordplay?
- How do you incorporate puzzles like anagrams into your daily routine?
Feel free to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. If you found this guide helpful, consider sharing it with fellow language enthusiasts and exploring further resources on wordplay and cryptic puzzles. For more fascinating insights into language and creative writing, check out our related articles on linguistic puzzles and cryptography basics.
Embrace the art of anagramming, and let your imagination rearrange the world—one letter at a time!
Additional Resources and Further Reading
Online Anagram Solvers:
Wordsmith Anagram
Anagram Solver by The Word FinderBooks on Wordplay and Linguistics:
- Word Play: A Curious Dictionary of Language Oddities by Chris Shuker
- Anagrams: A Collection of Word Puzzles by Peter Adlington
Educational Articles and Tutorials: