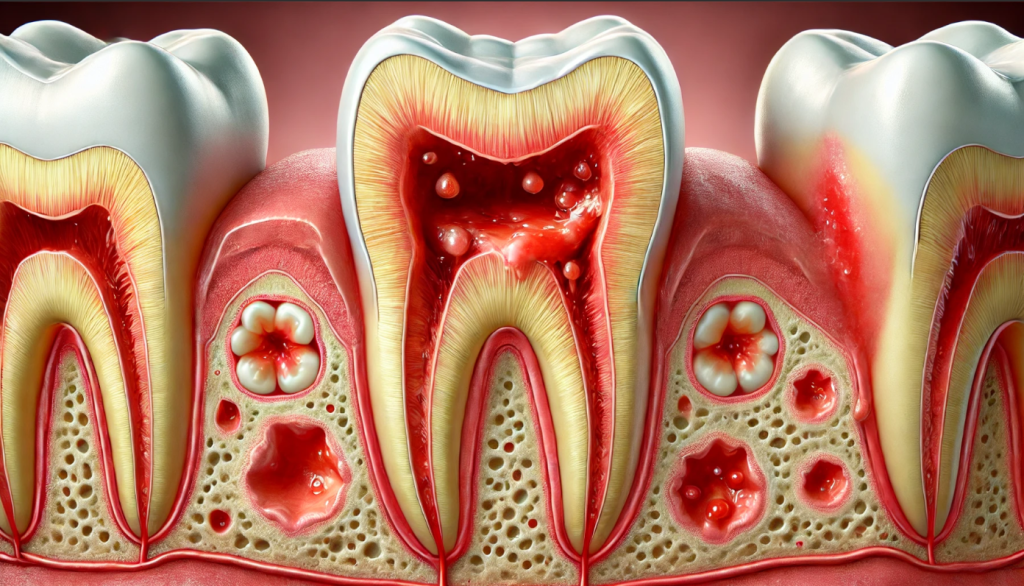
Dental abscess
A dental abscess is a painful and potentially serious condition where pus accumulates in a tooth, the gums, or the surrounding bone due to bacterial infection. This localized infection can cause significant discomfort and, if left untreated, may spread to other areas of the body and lead to serious health complications.
Types of Dental Abscesses:
- Periapical Abscess: Occurs at the tip of the tooth’s root, often resulting from untreated tooth decay or a cracked tooth that allows bacteria to enter the tooth’s pulp.
- Periodontal Abscess: Develops in the gum tissue surrounding a tooth. It is often associated with severe gum disease (periodontitis) but can also occur due to an injury to the gums.
Symptoms of a Dental Abscess:
Common symptoms of a dental abscess may include:
- Intense, throbbing pain that can appear suddenly and gradually worsen. This pain may be felt in the affected tooth or gum and can radiate to the ear, jaw, or neck.
- Swelling and redness of the face or gums.
- Tenderness and possible discoloration or loosening of the affected tooth.
- Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures.
- Bad breath or an unpleasant taste due to the pus.
- Difficulty sleeping or worsened pain when lying down.
- In some cases, a fever or a general feeling of being unwell.
- Difficulty opening the mouth, swallowing, or breathing (in severe cases).
What to Do if You Have a Dental Abscess:
If you suspect a dental abscess, it’s crucial to see a dentist as soon as possible. While waiting for an appointment, you can manage symptoms by:
- Pain relief: Ibuprofen is preferred, but paracetamol can be used if ibuprofen is not suitable. Avoid giving aspirin to children under 16.
- Dietary modifications: Avoid hot, cold, or very sweet foods and drinks, as they may exacerbate the pain.
- Oral hygiene: Use a soft toothbrush and temporarily avoid flossing near the affected area.
Treatment Options:
The goal of treatment for a dental abscess is to eliminate the infection and relieve symptoms. Treatment options may include:
- Draining the abscess: An incision may be made to drain the pus.
- Root canal treatment: Involves removing the infected pulp from within the tooth and sealing it to prevent future infections.
- Tooth extraction: If a root canal is not possible, the affected tooth may need to be removed.
- Antibiotics: While not routinely prescribed, antibiotics may be used if the infection has spread or is particularly severe.
Causes of Dental Abscesses:
Dental abscesses are primarily caused by bacterial infections, which can arise from:
- Poor oral hygiene: Failure to brush and floss regularly can lead to plaque build-up, tooth decay, and gum disease.
- Dietary factors: A diet high in sugary and starchy foods can promote bacterial growth.
- Dental trauma or surgery: Injury or surgery may create openings for bacteria to enter.
- Weakened immune system: Conditions like diabetes or certain medications can increase the risk of infection.
Preventing Dental Abscesses:
To minimize your risk of developing a dental abscess, it’s essential to maintain good oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste for at least two minutes each time.
- Floss daily or use an interdental brush to clean between teeth and below the gumline.
- Limit sugary and starchy foods and drinks, especially between meals or close to bedtime.
- Regular dental check-ups: Your dentist can identify potential issues early and offer tailored advice for maintaining oral health.
When to Seek Emergency Help:
Immediate medical attention is necessary if:
- You experience severe swelling that makes it difficult to breathe, swallow, or open your mouth.
- Your symptoms worsen, or you develop a high fever or feel generally very unwell.
- There is no improvement after initial dental treatment.
Final Thoughts:
Dental abscesses are not just painful; they can lead to serious complications if untreated. Prompt dental care, adherence to a healthy oral care routine, and awareness of symptoms can significantly reduce the risk of severe outcomes. If you notice any signs of an abscess, seek dental advice without delay to avoid complications and ensure proper treatment.