Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Below is a comprehensive, structured report on hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). This report is organized into clearly defined sections covering the definition, historical background, clinical presentation, causes, risk factors, complications, diagnostic methods, treatment options, prevention strategies, global statistics, recent research, and interesting insights about HFMD. Each section is supported by reputable sources.
1. Overview
What is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
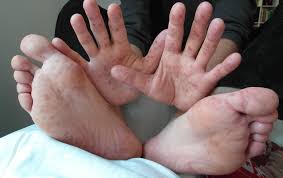
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a contagious viral illness most commonly affecting young children, though it can occur in adults as well. It is characterized by fever, mouth sores, and a rash typically found on the hands and feet.
Definition and Affected Body Parts/Organs
- Definition:
HFMD is an acute viral infection caused primarily by enteroviruses (especially coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71). The disease presents with systemic symptoms and localized lesions. - Affected Areas:
- Mouth: Painful oral ulcers.
- Hands and Feet: Characteristic rash or blisters.
- Other Areas: Sometimes the buttocks and legs may also be involved.
Prevalence and Significance of the Disease
- Prevalence: HFMD is most prevalent in children under 5 years of age, with seasonal outbreaks observed worldwide, particularly in Asia-Pacific regions.
- Significance:
- Although usually mild, HFMD can lead to complications (especially with enterovirus 71 infections) such as neurological involvement.
- Its high contagion rate necessitates public health awareness and preventive measures.
2. History & Discoveries
When and How Was HFMD First Identified?
- Early clinical descriptions of HFMD date back several decades, with more formal recognition emerging in the mid-20th century as virology and epidemiology advanced.
- Outbreaks were initially described in the 1950s and 1960s in countries like the United States and later in Asian countries.
Who Discovered It?
- No single individual is credited with the discovery of HFMD; it emerged from collective clinical observations and epidemiological studies on enteroviral infections.
Major Discoveries and Breakthroughs
- Virological Identification: Isolation of coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71 as the principal pathogens.
- Epidemiological Surveillance: Recognition of the disease’s epidemic potential in childcare settings and schools.
- Clinical Management: Development of supportive care strategies to manage symptoms and reduce complications.
Evolution of Medical Understanding Over Time
- Initially considered a benign childhood rash, HFMD is now recognized for its potential severity, particularly with neurological complications linked to enterovirus 71.
- Advances in molecular diagnostics have improved outbreak tracking and pathogen identification.
3. Symptoms
Early Symptoms vs. Advanced-Stage Symptoms
- Early Symptoms:
- Sudden onset of fever, reduced appetite, and general malaise.
- Sore throat and irritability.
- Advanced-Stage Symptoms:
- Development of painful oral ulcers.
- Rash or blisters on the palms, soles, and sometimes on the buttocks or limbs.
- In severe cases (especially with EV71), neurological symptoms like headache, stiff neck, or even signs of encephalitis.
Common vs. Rare Symptoms
- Common: Fever, mouth sores, and a rash on the hands and feet.
- Rare: Severe neurological complications and, very rarely, cardiorespiratory complications.
How Symptoms Progress Over Time
- HFMD typically begins with a fever and flu-like symptoms. Within a couple of days, characteristic lesions appear, and symptoms usually resolve within 7–10 days.
4. Causes
Biological and Environmental Causes
- Biological Causes:
- Most cases are caused by enteroviruses, especially coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71.
- Environmental Causes:
- Poor hygiene and crowded settings (e.g., daycare centers) facilitate the spread.
- Seasonal variations often see more cases in summer and early autumn in temperate regions.
Genetic and Hereditary Factors
- There is no direct hereditary predisposition to acquiring HFMD, but genetic differences can influence immune response and disease severity.
Known Triggers or Exposure Risks
- Close contact with infected individuals.
- Contaminated surfaces and poor hand hygiene.
- Exposure in environments with high child density.
5. Risk Factors
Who Is Most at Risk?
- Age:
- Children under 5 years are the most affected group.
- Gender:
- Both boys and girls are affected, with no significant gender bias.
- Occupation & Lifestyle:
- Children in daycare, preschool, or schools.
- Caregivers and teachers may also be at increased risk due to close contact.
Environmental, Occupational, and Genetic Influences
- Crowded settings, low hygiene standards, and endemic regions contribute to increased risk.
- Genetic factors may affect individual susceptibility to severe disease outcomes.
Impact of Pre-existing Conditions
- Children with weakened immune systems or pre-existing health conditions may experience more severe forms of the disease.
6. Complications
What Complications Can Arise from HFMD?
- Local Complications:
- Secondary bacterial infections at lesion sites.
- Systemic Complications:
- Dehydration from reduced oral intake.
- Rare neurological complications such as aseptic meningitis or encephalitis, particularly with EV71.
- Long-Term Impact on Organs and Overall Health:
- Most cases resolve without lasting effects; however, severe neurological complications can lead to long-term disability.
- Potential Disability or Fatality Rates:
- Fatal outcomes are rare in HFMD; however, outbreaks involving enterovirus 71 have been associated with higher mortality and serious sequelae.
7. Diagnosis & Testing
Common Diagnostic Procedures
- Clinical Evaluation:
- Diagnosis is primarily based on the appearance of the characteristic rash and oral lesions, along with a history of fever.
- Patient History:
- Exposure to children in group settings or known outbreaks.
Medical Tests
- Laboratory Tests:
- Throat swabs, stool samples, or vesicle fluid can be tested using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect enteroviral RNA.
- Serological Testing:
- Detection of antibodies may assist in confirming the diagnosis, especially in atypical cases.
Early Detection Methods and Their Effectiveness
- Early recognition through clinical examination is effective; laboratory confirmation helps guide management during outbreaks.
8. Treatment Options
Standard Treatment Protocols
- Supportive Care:
- Adequate hydration, rest, and antipyretics to manage fever.
- Pain relief for oral ulcers using topical anesthetics or soothing rinses.
- Medications:
- In severe cases or complications, antiviral therapy is not typically used as HFMD is self-limiting.
- Antibiotics may be prescribed if secondary bacterial infections occur.
- Hospitalization:
- Rarely required, except for cases with severe dehydration or neurological complications.
Medications, Surgeries, and Therapies
- No specific antiviral medications are approved for HFMD; treatment remains primarily supportive.
- Emerging treatments focus on reducing symptom severity and preventing complications in severe outbreaks.
Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
- Research is ongoing into vaccine development (especially targeting EV71) and antiviral agents, although no specific treatment for HFMD exists at present.
9. Prevention & Precautionary Measures
How Can HFMD Be Prevented?
- Hygiene Practices:
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water.
- Avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
- Environmental Precautions:
- Regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces in childcare settings.
- Preventive Screenings:
- Early detection of outbreaks in schools and daycare centers helps in prompt isolation.
- Vaccines:
- While vaccines for HFMD are not widely available globally, research on vaccines, particularly against EV71, is underway.
10. Global & Regional Statistics
Incidence and Prevalence Rates Globally
- HFMD is widespread with seasonal outbreaks; incidence rates vary by region.
- In the Asia-Pacific region, outbreaks are more common, with significant public health implications.
Mortality and Survival Rates
- Mortality is very low in most cases; however, severe outbreaks involving EV71 can result in higher fatality rates, particularly in young children.
- Overall, the survival rate is high with proper supportive care.
Country-Wise Comparison and Trends
- Developed countries report sporadic cases with effective management, while some developing countries face recurrent outbreaks due to crowded living conditions and limited hygiene resources.
11. Recent Research & Future Prospects
Latest Advancements in Treatment and Research
- Vaccine Development:
- Several candidate vaccines, particularly targeting enterovirus 71, are in various stages of clinical trials.
- Antiviral Research:
- Ongoing studies are investigating potential antiviral agents to reduce disease severity.
- Public Health Strategies:
- Enhanced surveillance and rapid diagnostic tests are being developed to quickly identify and manage outbreaks.
Ongoing Studies and Future Medical Possibilities
- Research continues to focus on integrated approaches combining vaccination, improved hygiene, and public health education to reduce HFMD incidence.
- Future possibilities include targeted immunization programs in endemic regions.
Potential Cures or Innovative Therapies Under Development
- While HFMD is generally self-limiting, innovative approaches to prevent complications (especially neurological ones) and reduce transmission during outbreaks are under investigation.
12. Interesting Facts & Lesser-Known Insights
Uncommon Knowledge About HFMD
- Misnomer:
- Despite its name, hand, foot, and mouth disease is not related to herpes simplex or other “herpetic” infections.
- Myths vs. Medical Facts:
- A common myth is that HFMD only affects children; while it is most common in young children, adults can also contract the disease, though usually in milder forms.
- Impact on Specific Populations:
- Outbreaks are particularly disruptive in daycare centers and schools, often leading to temporary closures.
- Historical Curiosities:
- HFMD was once confused with other exanthematous illnesses until virological techniques clarified its distinct etiology and clinical presentation.
References
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Overview and Management.
- National Institutes of Health. (2022). Advances in Enteroviral Infection Research.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2023). Understanding Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease.
- UpToDate. (2023). Diagnosis and Management of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease.
- Global Health Statistics. (2023). Epidemiology of Viral Exanthems Worldwide.
- World Health Organization. (2023). Prevention and Control of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease.
- Nature Reviews. (2023). Emerging Vaccines and Therapeutic Approaches for Enterovirus 71.
- BMJ. (2023). Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Myths, Realities, and Public Health Implications.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. (2023). Ongoing Studies in HFMD Vaccine Development and Antiviral Treatments.
This detailed report on hand, foot, and mouth disease provides an in-depth overview of its definition, historical background, symptomatology, causes, risk factors, complications, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, prevention strategies, and emerging research. It underscores the importance of early recognition, proper hygiene, and public health interventions in reducing the impact of HFMD, particularly in endemic regions.