Periodic Waves: Understanding the Fundamentals
What Are Periodic Waves?
Periodic waves are waves that repeat a continuous pattern over multiple cycles. These waves are characterized by their wavelength, frequency, period, amplitude, and overall shape. Understanding periodic waves lays the foundation for analyzing a variety of wave phenomena in physics, including sound, light, and water waves.
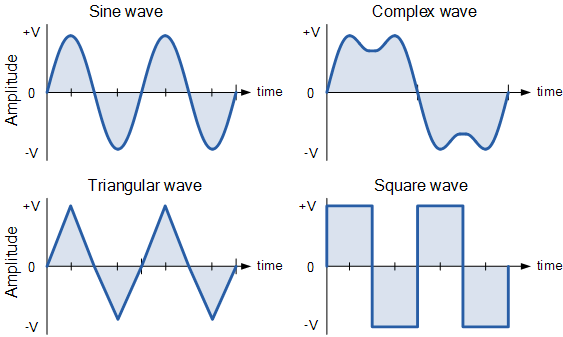
Key Features of Periodic Waves
- Repetition: A periodic wave repeats its motion at regular intervals, known as the period.
- Continuous Pattern: The shape of the wave remains consistent across cycles.
- Classifications: Periodic waves can be either transverse or longitudinal, depending on the direction of particle displacement relative to wave propagation.
Properties of Periodic Waves
To fully grasp periodic waves, let’s break down their core properties:
Period (T):
- The time it takes for one full cycle to complete.
- Measured in seconds (s).
Frequency (f):
- The number of cycles completed per second.
- Measured in Hertz (Hz).
- Related to the period by .
Wavelength (λ):
- The distance between two consecutive points in phase, such as two crests or troughs.
- Measured in meters (m).
Amplitude (A):
- The maximum displacement from the rest position.
- Represents the wave’s energy; higher amplitude = higher energy.
Wave Speed (v):
- The distance traveled by the wave per unit of time.
- Related to wavelength and frequency by
Wave Shape:
- Described by its waveform, typically represented as a sine or cosine function.
Wave Equation
The behavior of periodic waves can be described mathematically using wave equations. These equations express wave properties as functions of time and position.
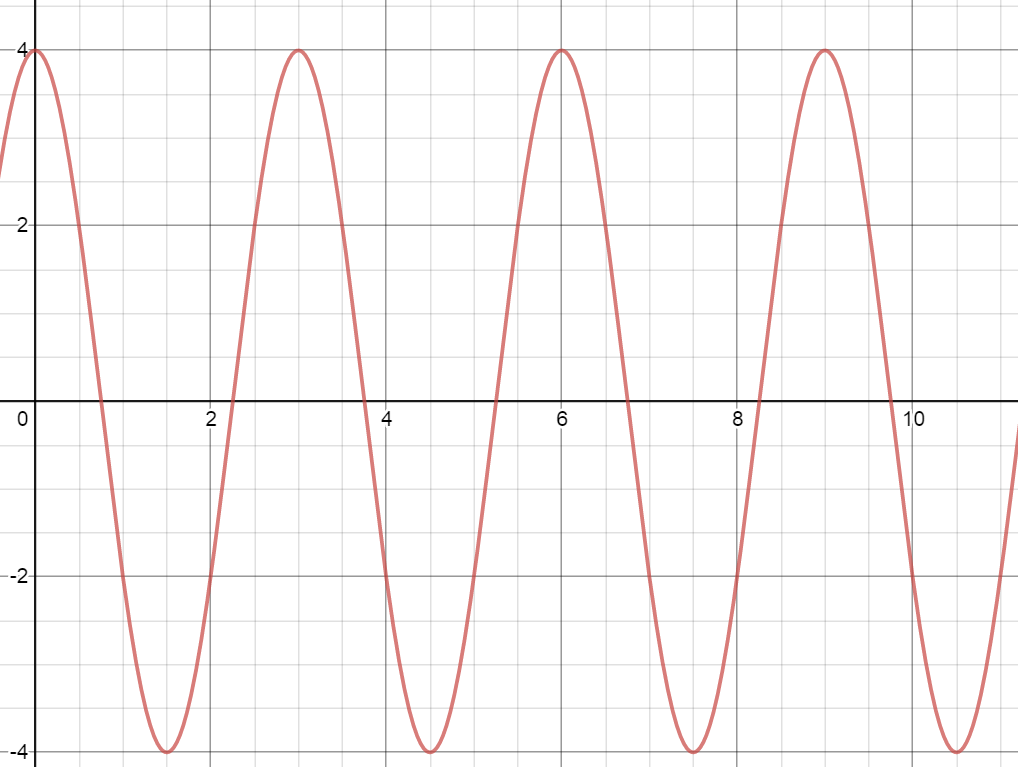
As a Function of Time
Where:
- : Amplitude
- : Frequency
- : Time
As a Function of Position
Where:
- : Amplitude
- : Wavelength
- : Position
Angular Frequency ()
The angular frequency relates to the period and frequency:
Example Problem: Deriving the Wave Equation
Consider a wave with the following properties:
- Amplitude () = 4 cm
- Wavelength () = 3 m
Step 1: Write the equation for position:
Step 2: Substitute values:
This equation describes the wave’s behavior at any point along its path.
The Physics Behind the Wave Equation
The general form of the wave equation is:
∂t2
Where:
- : Displacement of the wave
- : Time
- : Space
- : Speed of the wave
Key Insights:
- The equation describes the relationship between displacement, time, and space.
- It applies to a variety of waves, including sound, light, and water waves.
- The solutions to the equation, known as wave functions, reveal the wave’s shape and behavior.
Classification of Periodic Waves
Transverse Waves:
- Displacement is perpendicular to wave propagation.
- Examples: Water waves, light waves.
Longitudinal Waves:
- Displacement is parallel to wave propagation.
- Examples: Sound waves, seismic waves.
Applications of Periodic Waves
Periodic waves are integral to understanding various real-world phenomena:
Sound Waves:
- Mechanical, longitudinal waves.
- Used in communication and music.
Light Waves:
- Electromagnetic, transverse waves.
- Enable vision and optical technologies.
Water Waves:
- Mechanical, transverse waves.
- Studied for oceanography and renewable energy.
Seismic Waves:
- Mechanical waves traveling through Earth’s crust.
- Critical for understanding earthquakes and geophysics.
Practice Problems
Problem 1: Frequency of a Tuning Fork
The frequency of the tuning fork is approximately:
- A) 0.0039 Hz
- B) 0.020 Hz
- C) 2.55 Hz
- D) 50 Hz
- E) 256 Hz
Answer: E
Problem 2: Amplitude of a Wave
The amplitude of the wave is:
- A) 4 cm
- B) 5 cm
- C) 8 cm
- D) 10 cm
- E) 16 cm
Answer: A
Problem 3: Speed of a Wave
The speed of the wave is:
- A) 4 cm/s
- B) 25 cm/s
- C) 50 cm/s
- D) 100 cm/s
- E) 200 cm/s
Answer: C
Problem 4: Longest Wavelength
The length of the longest wavelength shown is:
- A) 0.5 m
- B) 0.75 m
- C) 1 m
- D) 2 m
- E) 4 m
Answer: E
Conclusion
Periodic waves are a cornerstone of wave mechanics, explaining phenomena across sound, light, and water systems. By understanding their properties, equations, and classifications, you gain valuable insights into their behavior and applications in science and technology.
Ready to explore more? Dive into interactive tutorials and practice problems on SlyAcademy.com to deepen your understanding of waves and their impact on our world!







