What Is Electric Potential? Everything You Need to Know
Electric potential is a fundamental concept in physics and electrical engineering, forming the backbone of our understanding of electric fields, circuits, and energy transfer. But what is electric potential exactly, and why is it so important? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the definition of electric potential, trace its historical development, and break down its key components. We’ll examine real-world examples, discuss its applications across various fields, and debunk common misconceptions. Whether you’re a student, a professional in the sciences, or simply curious about the forces that power our modern world, understanding electric potential can illuminate the way we harness and use energy.
Introduction: The Spark Behind Electric Potential
Imagine a world where energy flowed as freely as water, powering everything from your smartphone to entire cities. Have you ever wondered what makes this possible? The answer lies in the invisible forces and potentials that govern electrical energy. What is electric potential? This intriguing concept explains how electric charges interact, store energy, and create electric fields that drive modern technology.
In this post, we will cover:
- A clear definition: What exactly is electric potential and what are its key properties?
- Historical context: How have scientists’ understanding and measurement of electric potential evolved over time?
- In-depth exploration: A detailed look at the principles of electric potential, its mathematical formulation, and its relationship to other electrical concepts.
- Real-world examples: Practical scenarios and case studies that illustrate the role of electric potential in everyday life and advanced technology.
- Common misconceptions and FAQs: Clarifying myths and answering frequently asked questions.
- Modern relevance: Discussing recent developments, research, and how electric potential is shaping current and future technologies.
By the end of this article, you will have a solid grasp of what is electric potential and its significance in science, technology, and our daily lives. Let’s spark your curiosity and dive into the electrifying world of electric potential!
What Is Electric Potential? A Straightforward Definition
Electric potential is defined as the amount of electric potential energy per unit charge at a specific point in an electric field. In simpler terms, it represents the work needed to move a positive test charge from a reference point (usually infinity) to that point, without any acceleration.
Essential Characteristics of Electric Potential
- Measured in Volts (V): One volt is equal to one joule per coulomb (1 V = 1 J/C). This unit expresses how much potential energy is available to each unit of electric charge.
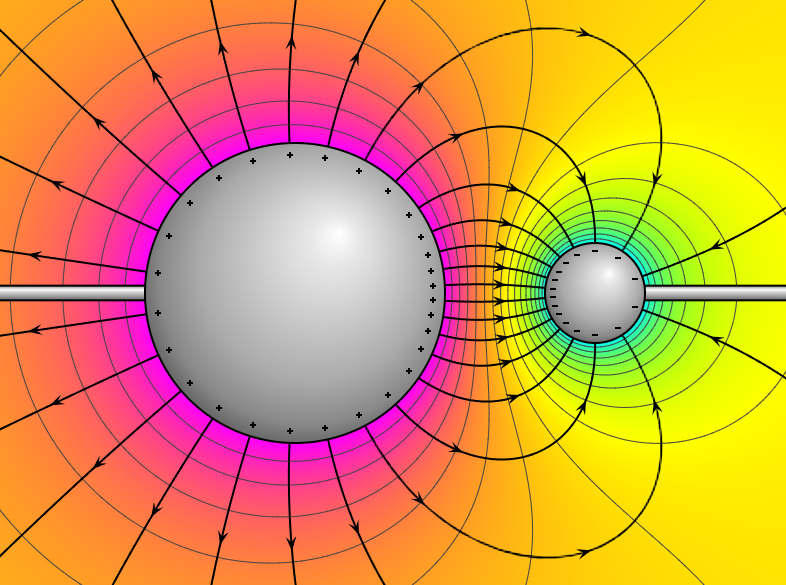
- Scalar Quantity: Unlike electric field, which is a vector, electric potential has magnitude but no direction.
- Relative Nature: Electric potential is always measured relative to a reference point. Often, the reference is chosen to be at infinity where the potential is defined as zero.
- Work and Energy: It is a measure of the work done per unit charge in bringing a test charge from a reference point to a particular point in the field.
Understanding electric potential helps us grasp how energy is stored and transferred in electric fields, and it plays a crucial role in designing circuits and electrical systems.
Historical and Contextual Background
Early Developments and Discoveries
The concept of electric potential emerged from the broader study of electricity and magnetism in the 18th and 19th centuries. Pioneering scientists laid the groundwork for our modern understanding of electric potential through experiments and theoretical insights.
Pioneers in Electricity
- Benjamin Franklin: In the mid-1700s, Franklin’s experiments with lightning and static electricity led him to propose the concept of positive and negative charges. His work laid an early foundation for thinking about how charges interact.
- Charles-Augustin de Coulomb: Coulomb’s work in the late 1700s quantified the force between charged particles, establishing the inverse-square law of electrostatic force. His studies indirectly paved the way for understanding how work is done in electric fields.
- Alessandro Volta: In 1800, Volta invented the battery (Voltaic pile), providing a steady source of electric charge. His work was instrumental in demonstrating that electricity could be stored and harnessed, a concept inherently linked to electric potential.
Theoretical Milestones
- Michael Faraday: Faraday’s experiments in the early 19th century led to the development of the field theory of electricity. His insights into electric fields and induction were crucial in conceptualizing electric potential as a field property.
- James Clerk Maxwell: Maxwell’s equations, formulated in the mid-1800s, provided a comprehensive mathematical framework for electromagnetism. These equations include the relationship between electric potential, electric fields, and charge distributions, solidifying the concept in physics.
Historical Anecdotes
- Faraday’s Lines of Force: Faraday visualized electric fields using “lines of force,” a concept that helped scientists later understand how electric potential is distributed in space.
- Maxwell’s Unification: Maxwell’s work in unifying electricity and magnetism into a single theory not only advanced our understanding of electric potential but also paved the way for the development of modern technologies like radio, television, and even the internet.
These historical milestones show how our understanding of what is electric potential evolved from simple observations of static electricity to a robust, mathematical description of electric fields and energy.
In-Depth Exploration: The Many Facets of Electric Potential
To fully appreciate what is electric potential, we need to examine its various aspects and see how it applies in different contexts. Below, we break down key points, attributes, and categories related to electric potential.
1. Mathematical Foundations of Electric Potential
Understanding the mathematics behind electric potential is crucial for grasping its practical applications.
a. The Formula for Electric Potential
The electric potential (V) at a point in space due to a point charge (Q) is given by the equation:
where:
- is Coulomb’s constant (),
- is the charge,
- is the distance from the charge.
This formula shows that the electric potential decreases as you move further away from the charge.
b. Electric Potential in Continuous Charge Distributions
For more complex systems where charge is distributed over a region (like a charged rod, sphere, or plane), the electric potential is determined by integrating the contributions of each infinitesimal charge element:
This integral takes into account the contributions of all charge elements at varying distances .
c. Relationship with Electric Field
The electric field (E) is related to electric potential by the gradient (or rate of change) of the potential:
This equation tells us that the electric field points in the direction of the greatest decrease in electric potential. The negative sign indicates that the field points from regions of higher potential to lower potential.
2. Types and Categories of Electric Potential
Electric potential can be examined from several perspectives, each offering insight into its behavior and applications.
a. Static vs. Dynamic Electric Potential
- Static Electric Potential: In static (or electrostatic) situations, charges are stationary, and the electric potential is constant over time. This is the simplest case, often encountered in introductory physics.
- Dynamic Electric Potential: In dynamic scenarios, such as in alternating current (AC) circuits, the electric potential varies with time. Here, potential differences change periodically, requiring more complex analysis involving time-dependent equations.
b. Potential Difference (Voltage)
While electric potential refers to the potential energy per unit charge at a specific point, the potential difference (often called voltage) is the difference in electric potential between two points:
Voltage is what drives current in an electrical circuit, as charges move from a higher potential to a lower potential.
c. Absolute vs. Relative Potential
- Absolute Potential: Theoretically, absolute electric potential is the potential at a point relative to a point at infinity, where it is assumed to be zero.
- Relative Potential: In practice, we often measure electric potential relative to a common reference point (such as the ground in electrical circuits). This relative measurement is what we commonly refer to as voltage.
3. Real-World Examples and Applications
Electric potential is not just an abstract concept—it has practical applications in everyday life and advanced technology.
a. Batteries and Power Supplies
- How Batteries Work: A battery creates a potential difference between its terminals through chemical reactions. This potential difference drives the flow of electrons through a circuit, powering devices like flashlights, smartphones, and cars.
- Voltage Ratings: The voltage of a battery indicates its electric potential. For example, a standard AA battery typically has a voltage of about 1.5 V, while a car battery usually provides 12 V.
b. Capacitors and Energy Storage
- Storing Energy: Capacitors store energy in the form of electric potential energy. When a capacitor is charged, it holds an electric potential difference across its plates, which can be released when needed.
- Applications: Capacitors are used in electronic circuits for filtering, energy storage, and power smoothing in devices such as computers, televisions, and power supplies.
c. Electrostatic Precipitators
- Air Pollution Control: In industrial settings, electrostatic precipitators use high electric potentials to charge particles in exhaust gases. These charged particles are then attracted to oppositely charged plates, effectively removing pollutants from the air.
- Environmental Impact: This application of electric potential helps reduce air pollution and improves environmental quality.
d. Medical Applications
- Electrocardiograms (ECG): ECG machines measure the electric potential differences generated by the heart’s activity. These readings are crucial for diagnosing and monitoring heart conditions.
- Medical Imaging: Techniques like electrical impedance tomography rely on differences in electric potential to create images of the internal body structure.
4. Importance and Benefits of Understanding Electric Potential
Grasping what is electric potential offers numerous benefits, both in scientific research and everyday technology.
a. Advancements in Technology
- Electronics and Circuit Design: Knowledge of electric potential is fundamental for designing efficient circuits, optimizing power distribution, and ensuring the safety and performance of electrical devices.
- Renewable Energy Systems: In solar panels and wind turbines, electric potential is harnessed to convert natural energy into usable electrical energy, contributing to sustainable power solutions.
b. Educational and Scientific Research
- Physics and Engineering Education: A solid understanding of electric potential is essential for students and professionals in the fields of physics, electrical engineering, and applied sciences.
- Research and Innovation: Electric potential plays a critical role in emerging technologies, such as nanotechnology, semiconductor devices, and quantum computing.
c. Everyday Applications
- Household Electronics: From smartphones to kitchen appliances, electric potential is at the heart of the technology we use daily.
- Safety and Maintenance: Understanding the principles of electric potential helps in maintaining and troubleshooting electrical systems, reducing hazards like short circuits and electrical shocks.
5. Addressing Common Misconceptions and FAQs
Despite its importance, several misconceptions about electric potential persist. Let’s clarify some common misunderstandings and answer frequently asked questions.
Common Misconceptions
Misconception 1: Electric Potential Is the Same as Electric Current.
Reality: Electric potential is the energy per unit charge (voltage), while electric current is the flow of charge (measured in amperes). They are related but distinct concepts.Misconception 2: Higher Voltage Always Means More Dangerous.
Reality: While higher voltage can be dangerous, it is the combination of voltage and current that determines the hazard. Proper insulation and safety measures can mitigate risks even at high voltages.Misconception 3: Electric Potential Is Only Relevant in High-Tech Industries.
Reality: Electric potential is a fundamental concept that applies to everyday devices, household wiring, and even natural phenomena like lightning.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the unit of electric potential?
A: Electric potential is measured in volts (V), where 1 volt is equivalent to 1 joule per coulomb (1 V = 1 J/C).Q: How does electric potential relate to energy?
A: Electric potential represents the work done per unit charge. When a charge moves through a potential difference, the work done on the charge is equal to the product of the potential difference and the charge.Q: Why is electric potential considered a scalar quantity?
A: Unlike electric fields, which have both magnitude and direction, electric potential only has a magnitude, making it a scalar quantity.Q: Can electric potential exist in the absence of an electric field?
A: No. Electric potential is intrinsically linked to the electric field; a variation in potential across space creates an electric field.
6. Modern Relevance and Current Trends
The study of what is electric potential remains at the forefront of scientific and technological advancements. Let’s explore some modern trends and developments.
a. Advances in Semiconductor Technology
- Microelectronics: As electronic devices continue to shrink, managing electric potential at the micro- and nano-scale has become critical for improving performance and reducing power consumption in semiconductors.
- Transistor Design: Innovations in transistor design, such as FinFETs and other advanced structures, rely on precise control of electric potential to regulate current flow and enhance speed.
b. Renewable Energy and Smart Grids
- Solar Power: Electric potential is a key factor in the operation of photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electrical energy.
- Smart Grid Technology: Modern power grids use sensors and control systems to monitor and adjust electric potential across the network, optimizing energy distribution and reducing losses.
c. Emerging Research in Quantum Technologies
- Quantum Computing: In quantum devices, electric potential plays a role in manipulating quantum bits (qubits) and controlling electron behavior at the atomic level.
- Nano-scale Devices: Research into nano-electronics and molecular electronics often focuses on how electric potential influences electron transport in extremely small systems.
d. Educational Innovations
- Interactive Simulations: Digital tools and simulations help students visualize electric potential, making abstract concepts more accessible and engaging.
- Online Courses: Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) and virtual laboratories offer hands-on learning experiences in electromagnetism, reinforcing the principles of electric potential.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Electric Potential
In summary, understanding what is electric potential is fundamental for grasping how electric energy is stored, transferred, and utilized. Electric potential not only underpins the operation of everyday electrical devices but also drives innovation in fields ranging from renewable energy to quantum computing.
Key Takeaways
- Definition and Characteristics: Electric potential is the energy per unit charge, measured in volts, and represents the work required to move a charge within an electric field.
- Historical Evolution: From early experiments by pioneers like Franklin and Coulomb to modern applications in semiconductor technology, the concept of electric potential has evolved significantly.
- Practical Applications: Electric potential is crucial in batteries, capacitors, medical devices, and industrial applications, making it a cornerstone of modern technology.
- Modern Relevance: Ongoing advancements in technology and research continue to expand our understanding of electric potential, influencing everything from sustainable energy systems to cutting-edge quantum devices.
- Debunking Myths: Misconceptions—such as confusing electric potential with current or overestimating its dangers—are clarified by recognizing its role as a fundamental, manageable property of electric fields.
Call to Action
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of what is electric potential, here are some ways to put this knowledge into practice:
- Explore Further: Read more about electromagnetism and its applications on reputable sites such as HyperPhysics and IEEE Xplore.
- Experiment Safely: If you’re a student or hobbyist, consider conducting simple experiments (with proper safety measures) to observe electric potential in action, such as building a basic circuit with a battery and LED.
- Engage with the Community: Share your insights or ask questions in the comments below. Join online forums or local science clubs to discuss and deepen your understanding of electric potential.
- Apply the Knowledge: Whether you’re troubleshooting a circuit, designing a new device, or simply curious about how your smartphone works, let your understanding of electric potential guide you in exploring the fascinating world of electricity.
We invite you to share this post with anyone who might benefit from a deeper dive into the science of electric potential. Your feedback and questions are always welcome—let’s keep the conversation going!
Final Thoughts
Electric potential is more than just a theoretical construct; it is a practical tool that has powered human progress for centuries. From the early days of static electricity to the sophisticated electronic devices of today, the principles of electric potential continue to shape our world. As technology advances and our energy needs evolve, a clear understanding of electric potential will remain essential for innovation and sustainable development.
Thank you for joining us on this in-depth exploration of what is electric potential. We hope that this guide has not only answered your questions but also sparked your curiosity to learn more about the wonders of electricity and its role in our modern lives.
Happy exploring, and here’s to a future powered by knowledge and innovation!