Economics in the Global Age
Introduction
Economic globalization has fundamentally transformed the way the world operates, fostering interconnectedness and interdependence among global economies. This trend, often referred to as Economics in the Global Age, is characterized by the expansion of international trade, investment, and financial flows, as well as the rise of multinational corporations and transnational economic systems. From the end of the Cold War to the modern-day knowledge economy, the global economic landscape has undergone profound changes, creating opportunities and challenges for countries, industries, and individuals alike.
This comprehensive exploration of Economics in the Global Age examines the causes and consequences of economic globalization, the rise of free market policies, post-industrial economies, and the growing influence of multinational corporations. Understanding these dynamics is essential for navigating the complexities of the modern global economy and addressing the debates surrounding its benefits and drawbacks.
The Rise of Free Market Economics
Post-Cold War Economic Policies
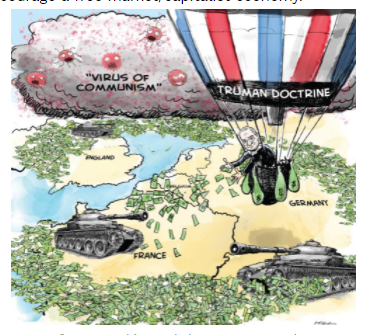
During and after the Cold War, many nations embraced free market economic policies as a counterpoint to communism. A free market economy prioritizes privately-owned businesses and properties with minimal government intervention. The United States, under the Truman Doctrine, provided monetary aid to countries like Greece and Turkey to support free market systems and prevent the spread of communism. This policy underscored America’s commitment to fostering capitalist economies worldwide.
Economic Liberalization
Economic liberalization emerged as a key trend in the post-Cold War era. This approach involves reducing governmental control over markets to encourage private enterprise and economic growth. Several world leaders spearheaded these policies, including:
Margaret Thatcher (UK): Known as the “Iron Lady,” Thatcher implemented policies that reduced government spending and deregulated industries, aiming to curb inflation.
Ronald Reagan (USA): Reaganomics, or supply-side economics, focused on lowering taxes and reducing unemployment while controlling inflation.
Deng Xiaoping (China): Deng’s economic reforms transformed China into a more socialist-oriented market economy, emphasizing privatization and tax reforms.
Augusto Pinochet (Chile): Pinochet’s “Miracle of Chile” involved privatizing state-owned companies and stabilizing inflation.
These leaders exemplify the global shift toward free market policies that have defined Economics in the Global Age.
Post-Industrial Economies
The Transition from Manufacturing
The United States, once a global leader in manufacturing, experienced a significant economic shift from the 1960s onward. By the 1980s, many industrial jobs had been outsourced or automated, leading to the decline of manufacturing hubs in cities like Detroit, Pittsburgh, and Toledo—collectively known as the “Rust Belt.” This transition marked the rise of post-industrial economies, which rely on services, knowledge, and technology rather than manufacturing.
The Knowledge Economy
Modern economies, particularly in More Developed Countries (MDCs), are increasingly based on knowledge and information. A knowledge economy thrives on communication technology, innovation, and globalization. Notable examples include:
United States: Silicon Valley epitomizes the knowledge economy, with companies like Apple designing products in California while outsourcing manufacturing to countries like China.
Japan: Known for its technological advancements and export-oriented industries.
Finland: A leader in education and technology, contributing significantly to the global knowledge economy.
These economies demonstrate the shift from industrial production to high-value activities such as research, design, and technological innovation.
Multinational Corporations in the Global Economy
The Role of Multinational Corporations
Multinational corporations (MNCs) play a pivotal role in Economics in the Global Age. These entities operate on a global scale, often headquartered in one country while conducting business across multiple regions. Examples of MNCs include Exxon, Nestle, and Nissan. They leverage global markets to maximize profits, driving economic globalization.
Transnational Impact
MNCs not only influence economies but also cultures. For instance, McDonald’s represents the phenomenon of “McDonaldization,” which involves the spread of Western-style fast food and the values of efficiency, predictability, and standardization. While this trend has introduced convenience and economic growth, it has also led to cultural homogenization and the erosion of local food traditions.
Outsourcing and Global Supply Chains
MNCs often outsource manufacturing to regions with lower labor costs, such as:
Asia: Countries like Vietnam, Bangladesh, and China serve as hubs for manufacturing and industrial production.
Latin America: Nations like Mexico and Honduras have become key players in global supply chains.
This interconnected system highlights the dual nature of globalization, where economic growth in one region may lead to exploitation or inequality in another.
Economic Globalization and Its Impacts
Benefits of Economic Globalization
Economic globalization has brought numerous advantages, including:
Increased Trade: Global markets allow countries to specialize in their strengths, boosting efficiency and productivity.
Economic Growth: Access to international markets and investments fosters development in emerging economies.
Cultural Exchange: The integration of economies promotes cross-cultural understanding and collaboration.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its benefits, economic globalization has faced significant criticism:
Income Inequality: The wealth generated by globalization often remains concentrated among a small elite, exacerbating economic disparities.
Environmental Degradation: Industrial activities associated with globalization contribute to pollution, deforestation, and climate change.
Cultural Erosion: The spread of global brands and products can undermine local traditions and identities.
The Future of Economics in the Global Age
As the world continues to evolve, Economics in the Global Age will face new challenges and opportunities. Technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, have the potential to revolutionize industries and redefine economic systems. However, addressing issues like income inequality, environmental sustainability, and cultural preservation will be critical to ensuring a balanced and equitable global economy.
Through innovation, collaboration, and thoughtful policy-making, nations and businesses can navigate the complexities of economic globalization, fostering a future that benefits all.
FAQs on Economics in the Global Age
1. What is meant by the “global age” in economics? The “global age” refers to the era of heightened globalization, characterized by interconnected economies, cross-border trade, and global financial systems enabled by technological advancements and liberalized trade policies.
2. How does globalization affect economies? Globalization boosts economic growth by increasing trade, foreign direct investment, and access to global markets. However, it also creates challenges such as income inequality and vulnerability to global crises.
3. What are the main drivers of economic globalization? Key drivers include technological advancements, trade liberalization, multinational corporations, improved transportation, and international organizations fostering economic cooperation.
4. How does free trade impact global economies? Free trade promotes efficiency, competition, and access to a variety of goods and services. However, it can also lead to job losses in industries unable to compete globally.
5. What is the role of multinational corporations in the global economy? Multinational corporations drive globalization by operating across borders, transferring technology, and creating jobs. They also influence policy-making and local economies.
6. How has technology reshaped global economics? Technology accelerates globalization by enabling e-commerce, automating industries, and improving communication and logistics, making markets more accessible and efficient.
7. What is the impact of globalization on developing countries? Globalization provides opportunities for growth, technology transfer, and access to global markets. However, it can also lead to exploitation, dependency, and environmental degradation.
8. How do global supply chains work? Global supply chains involve the production and distribution of goods across multiple countries, optimizing costs but increasing exposure to geopolitical and logistical risks.
9. What is the relationship between globalization and inequality? Globalization has reduced poverty in some regions but widened income and wealth disparities both within and between nations, requiring inclusive policies to address.
10. How do international trade agreements shape the global economy? Trade agreements like NAFTA and the EU reduce tariffs and barriers, fostering economic integration and growth, but they can also face criticism for favoring larger economies.
11. What is the role of the World Trade Organization (WTO)? The WTO regulates international trade, resolves disputes, and promotes fair competition among member nations to facilitate global economic stability.
12. How does foreign direct investment (FDI) impact economies? FDI brings capital, technology, and jobs to host countries, boosting growth. However, it may also lead to profit repatriation and local industry dependency.
13. What is the role of financial markets in the global economy? Financial markets enable capital flow, investment, and risk-sharing across borders, supporting economic development and stability.
14. How do global economic crises spread? Economic crises spread through interconnected financial systems, trade dependencies, and investor behavior, as seen in events like the 2008 financial crisis.
15. How does globalization affect labor markets? Globalization creates job opportunities in emerging markets but can lead to wage stagnation and job displacement in developed economies due to outsourcing.
16. What is the significance of emerging markets in the global economy? Emerging markets like China, India, and Brazil drive global growth with their expanding consumer bases, industrialization, and innovation.
17. How does e-commerce influence global trade? E-commerce simplifies cross-border transactions, broadens market access for businesses, and enhances consumer choice but raises concerns about data privacy and taxation.
18. What are the economic effects of international migration? Migration contributes to labor market flexibility, skill transfer, and remittances but can also strain public services and raise cultural integration challenges.
19. How does globalization affect environmental sustainability? Globalization increases resource consumption and emissions but also fosters environmental cooperation and the spread of green technologies.
20. What is the role of international financial institutions? Institutions like the IMF and World Bank provide financial aid, policy advice, and development support to stabilize and grow global economies.
21. How do currency exchange rates impact global trade? Exchange rates influence export competitiveness, import costs, and investment flows, affecting trade balances and economic stability.
22. What is the role of innovation in the global economy? Innovation drives productivity, creates new markets, and enhances competitiveness, fueling economic growth in the global age.
23. How does global taxation affect economies? Global taxation policies address issues like tax evasion and profit shifting by multinationals, promoting fair tax systems and government revenue.
24. What are the economic implications of climate change? Climate change affects agriculture, infrastructure, and health, increasing costs and risks while driving investment in green technologies and resilience measures.
25. How do trade tariffs impact the global economy? Tariffs protect domestic industries but can increase costs for consumers, reduce trade volumes, and spark retaliatory measures between nations.
26. How does globalization influence cultural exchange? Globalization fosters cultural exchange, enhancing diversity and understanding, but also raises concerns about cultural homogenization and identity loss.
27. What is the impact of global tourism on economies? Tourism generates income, creates jobs, and promotes cultural exchange, but it can also strain resources and cause environmental degradation.
28. How do central banks affect global economics? Central banks influence global economics through monetary policies, currency stabilization, and responses to economic crises.
29. What is the significance of digital currencies in the global economy? Digital currencies like Bitcoin offer decentralized financial systems and fast transactions, but they raise regulatory and security challenges.
30. How does globalization affect education? Globalization expands access to education through international institutions and online platforms, promoting skill development for global job markets.
31. What is the role of remittances in the global economy? Remittances support families and local economies in developing countries, contributing to poverty reduction and economic stability.
32. How do trade sanctions influence global economics? Sanctions restrict trade and financial activities, affecting targeted nations’ economies and sometimes leading to broader global impacts.
33. How does globalization impact small businesses? Small businesses gain access to international markets but face challenges from competition, regulatory complexities, and supply chain dependencies.
34. What is the impact of intellectual property (IP) on global economics? Strong IP protection encourages innovation and investment but raises debates about access to technology and medicines in developing nations.
35. How do sovereign wealth funds affect global economics? Sovereign wealth funds invest national savings in global markets, stabilizing economies and generating returns but influencing geopolitical dynamics.
36. How does urbanization influence global economics? Urbanization drives economic growth by concentrating industries and innovation but creates challenges like housing shortages and infrastructure demands.
37. How does globalization influence food security? Global trade improves food availability but also exposes nations to supply chain disruptions and price volatility.
38. What is the impact of global trade on healthcare? Trade improves access to medicines and medical technology but raises concerns about affordability and dependency on imports.
39. How does globalization affect regional trade agreements? Globalization encourages regional trade agreements to enhance economic integration and competitiveness within regions.
40. How do pandemics impact global economics? Pandemics disrupt trade, labor markets, and investment flows, necessitating coordinated global responses and resilience planning.
41. What is the relationship between globalization and inflation? Globalization affects inflation by influencing production costs, labor markets, and global supply chains, often leading to lower consumer prices.
42. How does global economic integration influence innovation? Integration fosters competition and collaboration, accelerating innovation and the spread of new technologies.
43. What is the role of global financial hubs? Financial hubs like New York, London, and Hong Kong facilitate international banking, investment, and trade, shaping global economic trends.
44. How does globalization impact income redistribution? Globalization increases wealth but often exacerbates income inequality, requiring redistributive policies to balance benefits.
45. How do global recessions affect economies? Recessions reduce trade, investment, and employment, with ripple effects across interconnected economies.
46. How do trade deficits impact the global economy? Trade deficits reflect imbalances in imports and exports, affecting currency value, debt levels, and economic stability.
47. How does globalization affect intellectual capital? Globalization enhances knowledge exchange, skill development, and innovation but also leads to brain drain in developing countries.
48. What is the role of entrepreneurship in the global economy? Entrepreneurship drives economic growth, creates jobs, and fosters innovation, playing a pivotal role in global competitiveness.
49. How does globalization impact economic sovereignty? Globalization challenges sovereignty by increasing reliance on international trade, regulations, and organizations, limiting independent decision-making.
50. What is the future of globalization in economics? The future depends on balancing integration with sustainability, addressing inequality, and leveraging technology to foster inclusive growth.







