Interference and Diffraction: The Wave Nature of Light
Light’s ability to interfere and diffract demonstrates its wave-like nature, offering deep insights into physics. When waves meet in phase (crest aligns with crest), they produce constructive interference. Conversely, when waves meet out of phase (crest aligns with trough), destructive interference occurs. These patterns can be explored through phenomena like diffraction and Young’s Double-Slit Experiment.
Understanding Interference
Interference occurs when two or more waves overlap, combining their amplitudes in different ways. This can either amplify or diminish the resultant wave, depending on their phase relationship.
Key Types of Interference
Constructive Interference
- Occurs when waves meet in phase.
- Results in a wave with a greater amplitude.
- Path difference:
Destructive Interference
- Occurs when waves meet out of phase.
- Results in a smaller amplitude or complete cancellation.
- Path difference:
Important Notes:
- Constructive interference amplifies wave intensity, whereas destructive interference reduces it.
- This phenomenon applies to various wave types, including sound, water, and light waves.
Thomas Young’s Double-Slit Experiment
The Double-Slit Experiment is a landmark study proving the wave nature of light. It demonstrates how light diffracts and interferes.
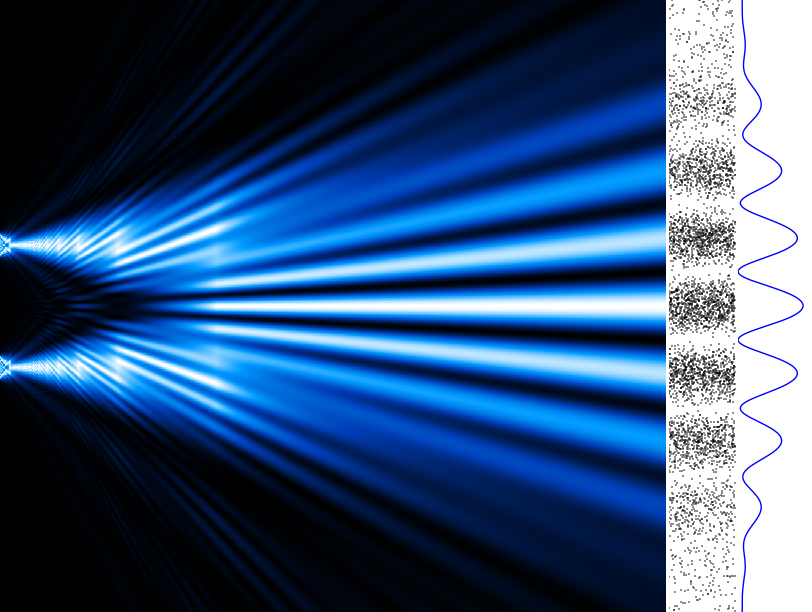
The Setup
Young directed coherent monochromatic light through two narrow, closely spaced slits. Instead of forming two distinct bright spots on the screen, the light created a series of alternating bright and dark fringes due to interference.
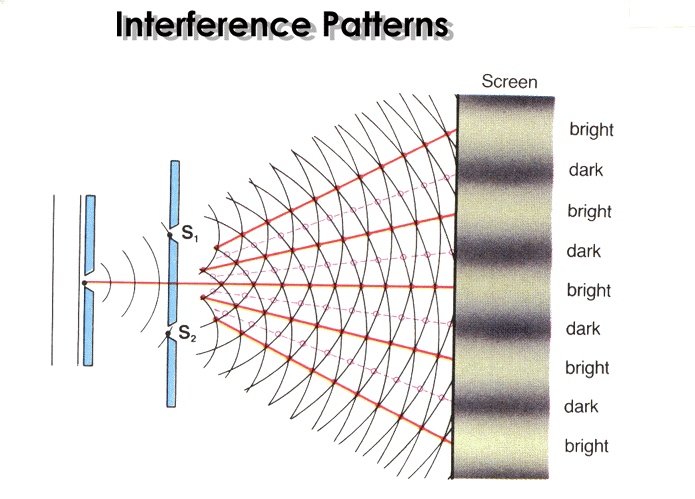
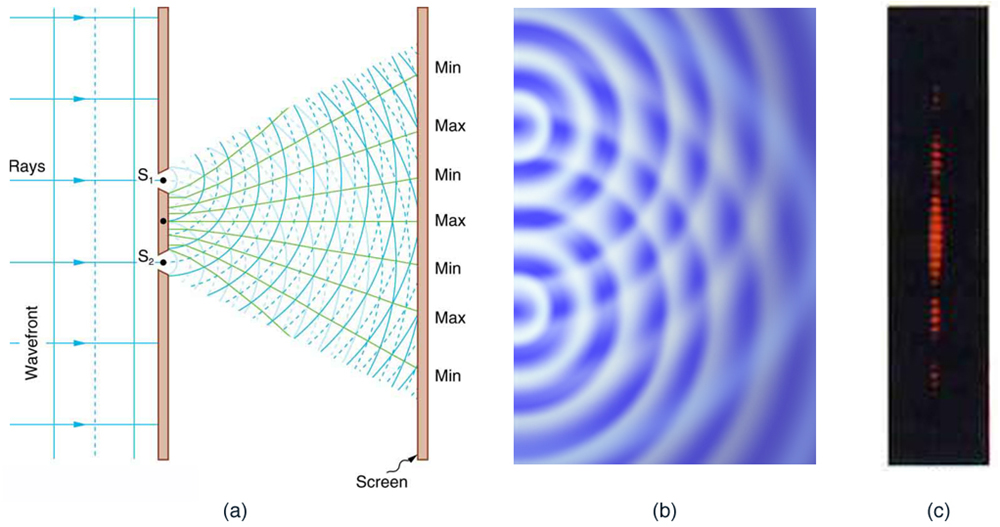
Observations
- Bright Fringes: Points of constructive interference, where waves align in phase.
- Dark Fringes: Points of destructive interference, where waves align out of phase.
Key Equations for Fringes
Constructive Interference (Bright Fringes):
Destructive Interference (Dark Fringes):
Where:
- : Distance between slits.
- : Angle from the central axis to the fringe.
- : Wavelength of light.
Fringe Spacing Equation
For small angles ( ):
Where:
- : Fringe spacing.
- : Distance from slits to the screen.
Diffraction: Light’s Ability to Bend
Diffraction occurs when waves encounter an obstacle or slit, causing them to bend and spread. This phenomenon is most noticeable when the slit width is comparable to the wavelength.
Key Insights on Diffraction
- Light diffracts through small openings, forming patterns of bright and dark spots due to interference.
- The degree of diffraction depends on wavelength and slit size.
- Diffraction explains why sound can bend around corners while light cannot.
Thin Film Interference
Thin film interference arises when light reflects off the top and bottom surfaces of a thin material, such as soap bubbles or oil films. This creates colorful patterns due to varying path lengths and phase changes.
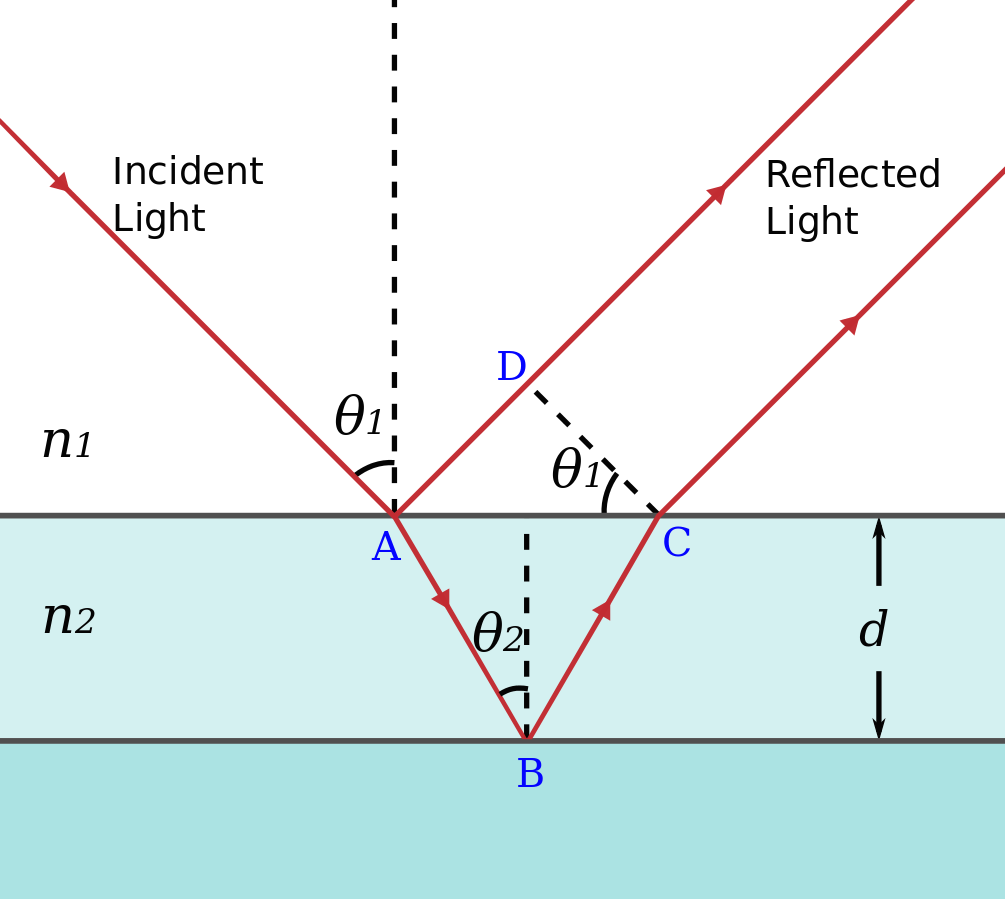
How It Works
- Light reflects off the top surface of the film (phase change occurs if ).
- Light reflects off the bottom surface and refracts out.
- The two reflected waves interfere.
Image Source: Physics.stackexchange.com
Key Equations
Destructive Interference:
Constructive Interference:
Where:
- : Thickness of the film.
- : Wavelength in the material.
Applications of Interference and Diffraction
Optical Instruments:
Interference patterns are critical for devices like interferometers and diffraction gratings.Thin Films:
Used in anti-reflective coatings, lenses, and solar panels.Everyday Examples:
- The iridescence of soap bubbles.
- Patterns on CDs and DVDs.
Practice Problems
Two waves approach a point and overlap. What happens to their shapes as they leave the point?
Answer: They continue unaffected (Principle of Superposition).In a double-slit experiment, decreasing the slit separation will:
Answer: Increase fringe spacing.Doubling the slit separation requires the screen distance to:
Answer: Be doubled to maintain the same fringe spacing.







