Understanding Buffer Capacity: How Buffers Maintain pH Stability
Buffers are a remarkable tool in chemistry, helping maintain pH stability in solutions even when acids or bases are added. But, have you ever wondered how much acid or base can be added to a buffer before it loses its resistance? That’s where buffer capacity comes in. Let’s explore what buffer capacity is, why it’s important, and how to gauge a buffer’s effectiveness.
What Is Buffer Capacity?
Buffer capacity measures a buffer’s ability to resist changes in pH when a strong acid or strong base is added. In simpler terms, it indicates how much acid or base a buffer can absorb before it starts to experience a significant pH change.
Key Concepts Recap
- Buffers are solutions containing a weak acid and its conjugate base (or vice versa) that resist pH changes.
- Buffers are not indestructible; adding too much acid or base will eventually overwhelm them.
- Buffer capacity helps quantify the resilience of a buffer.
Describing Buffer Capacity
According to the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, the pH of a buffer depends on the ratio of the concentrations of the conjugate base to the acid [A−]/[HA]. The buffer capacity is determined by the absolute magnitudes of these concentrations. Higher concentrations of the weak acid and its conjugate base result in a buffer with a higher capacity, meaning it can better resist pH changes.
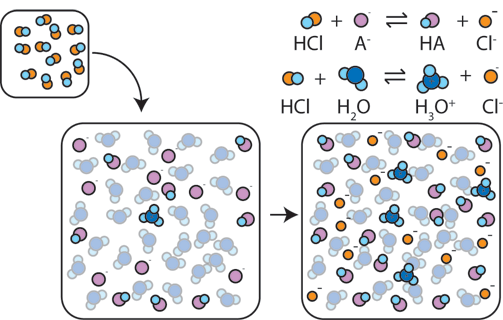
Image From ChemCollective
What Magnitude Means in Buffering
Consider two buffers:
- Buffer 1: Contains 5M acetic acid and 5M sodium acetate.
- Buffer 2: Contains 0.05M acetic acid and 0.05M sodium acetate.
Even though both buffers have the same [A−]/[HA] ratio and thus the same pH, Buffer 1 has a higher buffer capacity because it contains more moles of the acid and its conjugate base. Buffer 1 can resist greater changes in pH when an acid or base is added compared to Buffer 2.
Example Problem: Comparing Buffer Capacities
Problem Statement:
Consider two buffer systems:
- Buffer A: 5M acetic acid and 5M sodium acetate.
- Buffer B: 0.05M acetic acid and 0.05M sodium acetate.
Both buffers have an initial pH of 4.74. When HCl is added:
- Buffer A’s pH remains unchanged.
- Buffer B’s pH drops to 4.56.
Question: Which buffer has the better buffering capacity and why?
Answer: Buffer A has the better buffering capacity because its high concentrations of acetic acid and sodium acetate make it more resistant to pH changes. The large number of moles in Buffer A allows it to absorb added HCl with minimal pH change.
How to Identify Stronger Buffers
When determining buffer capacity:
- Examine concentrations: Higher concentrations of both the acid and its conjugate base result in a stronger buffer.
- Evaluate volume and molarity changes: Lowering either volume or concentration reduces the buffer’s ability to resist pH changes.
Example Scenario
Scenario:
A student prepares a buffer using 250 mL of 0.100M acetic acid and 500 mL of 0.440M sodium acetate. Due to a mistake, the student uses 0.050M acetic acid and 250 mL of sodium acetate.
Impact: The moles of both the acid and its conjugate base are halved, reducing the buffer capacity.
Practice Problem Tip
Questions on buffer capacity often require a qualitative approach—understanding and explaining changes without heavy calculations. Focus on changes in moles and their impact on buffer performance.
Why Buffer Capacity Matters
Buffers are essential in:
- Biological systems: Maintaining stable pH in blood and cellular fluids.
- Industrial processes: Ensuring consistent pH levels for reactions.
- Laboratory settings: Controlling pH during experiments.
A buffer’s capacity ensures stability within a given range, making it a crucial component in countless chemical applications.
Quick Recap
- Buffer capacity measures how much acid/base can be added before a buffer’s pH significantly changes.
- Higher concentrations of the weak acid and conjugate base increase buffer capacity.
- Buffer problems often involve comparing molarities, volumes, and their effects on pH resistance.







