Understanding and Managing Male Breast Enlargement: Gynecomastia vs. Chest Fat
Male breast enlargement, colloquially known as “man boobs,” can be caused by a variety of factors, including fat accumulation, hormonal imbalances, and certain medical conditions. This condition often leads to self-consciousness and can impact a man’s confidence and mental well-being.
Gynecomastia vs. Pseudogynecomastia (Chest Fat)
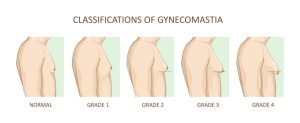
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue in men due to an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen levels. When testosterone levels decrease or estrogen levels increase, breast tissue responds by growing, leading to male breast enlargement.
Pseudogynecomastia (chest fat), on the other hand, occurs due to excess fat accumulation on the chest and is not related to hormonal imbalances. It is commonly seen in overweight individuals and can be resolved by reducing overall body fat.
Key Differences Between Gynecomastia and Chest Fat
Causes:
- Gynecomastia: Hormonal imbalances during puberty, aging, genetic factors, certain medications, recreational drug use, and steroid use.
- Chest Fat: Primarily caused by excess body fat and weight gain.
Symptoms:
- Gynecomastia: Firm, glandular tissue beneath and around the nipples, often resulting in a more feminine breast-like appearance. Puffy and swollen nipples are common. Sometimes, a hard lump may form under the nipple.
- Chest Fat: Soft, saggy tissue with excess skin. It resembles a fatty chest rather than firm breast tissue.
Self-Examination Tips:
- Check for lumps under the nipple area. Gynecomastia often presents with a firm lump, whereas chest fat feels softer and less defined.
- Puffy, erect nipples can be a sign of gynecomastia.
- If unsure, a medical consultation and ultrasound scan can confirm the diagnosis.
Managing Gynecomastia and Chest Fat
For Chest Fat:
- Diet and Exercise: Reducing overall body fat is key. Focus on a balanced, low-calorie diet rich in lean proteins, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Strength Training and Cardio: Engage in chest-specific exercises, such as push-ups, planks, and bench presses, while incorporating full-body workouts to boost metabolism and fat loss.
- Avoid Quick Fixes: Steer clear of unregulated pills and creams as they may cause harmful side effects.
For Gynecomastia:
- Hormonal Balance: In teenagers, gynecomastia often resolves as hormones stabilize. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a nutritious diet can help.
- Eliminate Triggers: If the condition is related to medication or recreational drug use, stopping these substances can reduce symptoms. Always consult a healthcare professional before making changes.
- Medical Intervention: In persistent cases, male breast surgery, such as liposuction or glandular tissue removal (mastectomy), may be recommended. Consulting an experienced cosmetic surgeon is crucial for optimal results.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you suspect gynecomastia, especially if you feel a hard lump beneath the nipple or experience significant discomfort, it’s important to consult a doctor. In rare cases, male breast enlargement can indicate breast cancer.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between chest fat and gynecomastia is essential to determine the appropriate course of action. While chest fat can often be reduced through lifestyle changes, gynecomastia may require medical intervention. If considering surgery, ensure you choose a reputable clinic with qualified specialists for safe and effective treatment.