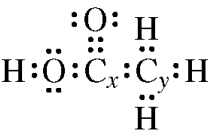2.7 VSEPR and Bond Hybridization
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory
VSEPR theory (Valence-Shell Electron-Pair-Repulsion) allows us to predict the geometry of molecules by minimizing electron-electron repulsion. The theory is based on Coulombic repulsion between electrons, helping us understand the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
What Should I Know for the AP Exam?
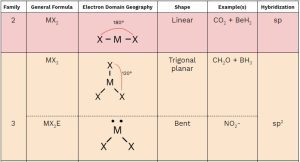
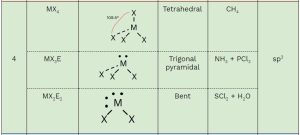
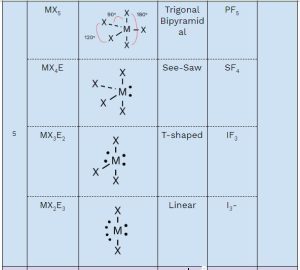
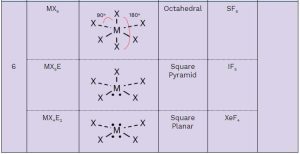
You should memorize the table below, as it will help you answer many questions about molecular geometry on the exam. Once you practice, these questions will become free points! 🥳
Here’s a breakdown of each column:
- Family: The number of groups (atoms + lone pairs) around the central atom (M).
- General Formula:
- M: Central atom
- X: Attached atoms
- E: Lone pairs
- Electron Domain Geometry: Describes the arrangement of electrons (bonding and lone pairs) around the central atom.
- Shape: The molecular geometry you need to memorize.
- Hybridization: You only need to memorize the hybridization of families 2, 3, and 4.
Sigma (σ) and Pi (π) Bonds
- Sigma (σ) bonds: Covalent bonds where electrons are shared along the internuclear axis. Hybrid orbitals form σ bonds, and they are stronger than π bonds.
- Pi (π) bonds: Covalent bonds where orbitals overlap perpendicularly to the internuclear axis. These are formed by unhybridized orbitals.
You don’t need to know these definitions by heart, but here’s what you should remember:
- Single bond: 1 σ bond
- Double bond: 1 σ bond and 1 π bond
- Triple bond: 1 σ bond and 2 π bonds
Key Points:
- The more π bonds in a molecule, the higher the bond energy and the shorter the bond length.
Examples: Count the σ and π Bonds
Let’s analyze the number of σ and π bonds in these two structures:
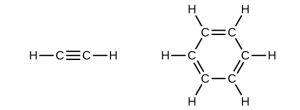
In the left molecule, there is 1 triple bond and 2 single bonds. The triple bond has 1 σ bond and 2 π bonds, while each single bond has 1 σ bond.
Total: 3 σ bonds, 2 π bonds.In the right molecule, there are 3 double bonds and 9 single bonds. Each double bond has 1 σ bond and 1 π bond, while each single bond has 1 σ bond.
Total: 12 σ bonds, 3 π bonds.
Hybridization
Hybridization is the process by which atomic orbitals fuse to form new, hybrid orbitals, which influences molecular geometry and bonding properties. Hybridization builds on the valence bond theory 💥.
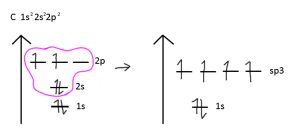
There are five main types of hybridization, but you will be tested on sp³, sp², sp, sp³d, and sp³d². During hybridization, orbitals combine to fill subshells and reach a lower energy state.
For example, in CH₄ (methane), carbon’s 2p and 2s orbitals hybridize to form four sp³ orbitals. These sp³ orbitals can make four σ bonds, which would not have been possible without hybridization.
AP Free-Response Questions
2007 Exam – Questions #6a-d
- (a) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot diagram for IF₃.
- (b) Based on your diagram, predict the molecular geometry of IF₃.
- (c) The bonds in SO₂ are the same length. Draw the Lewis diagram for SO₂ and explain why.
- (d) Identify the hybridization of sulfur in SO₂.
2010 Exam – Questions #5a-c
| Compound | Formula | Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram |
|---|---|---|
| Ethanethiol | CH₃CH₂SH | H H H—C—C—S—H H H |
| Ethane | CH₃CH₃ | H H H—C—C—H H H |
| Ethanol | CH₃CH₂OH | H H H—C—C—O—H H H |
| Ethyne | C₂H₂ | H—C≡C—H |
Given a table of molecules:
- (a) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot diagram for ethyne (C₂H₂).
- (b) Which molecule has the shortest carbon-to-carbon bond? Explain.
- (c) Identify the geometry for carbon x and carbon y in ethanoic acid (CH₃COOH).

AP FRQ Scoring Guidelines
2007 Exam – #6a-d
- (a) Draw the Lewis structure for IF₃ (shown below). You can use dots or lines to represent bonds.
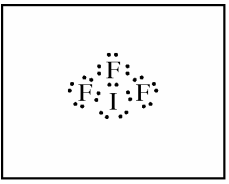
(b) The molecular geometry of IF₃ is T-shaped.
- Even if your drawing in part (a) is incorrect, you can still earn credit for part (b) if your geometry is consistent.
(c) For SO₂, both bonds are equal due to resonance.
Draw the resonance structures and mention that both sulfur-oxygen bonds are double bonds.(d) The sulfur atom in SO₂ has an sp² hybridization.
2010 Exam – #5a-c
- (a) Draw the Lewis structure for ethyne (C₂H₂):

(b) Ethyne has the shortest C-to-C bond due to the triple bond, which is shorter than a single bond.
(c) The geometry for carbon x (in the carboxyl group) is trigonal planar, and the geometry for carbon y (in the methyl group) is tetrahedral.