What Is Empathy? Everything You Need to Know
Introduction
Imagine a world where you not only understood another person’s feelings but truly felt them as if they were your own. In our increasingly interconnected society, the ability to connect with others on an emotional level is more valuable than ever. Yet, you might find yourself wondering, what is empathy? Despite being a term we use daily, empathy is a complex and multifaceted concept that touches every aspect of human interaction—from personal relationships and education to leadership and global diplomacy.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore:
- A clear, straightforward definition of what is empathy?
- The essential characteristics and dimensions of empathy, including cognitive and emotional empathy.
- The historical and contextual background that has shaped our understanding of empathy.
- In-depth exploration of empathy in various contexts—personal, professional, cultural, and even digital.
- Real-world examples, case studies, and scenarios illustrating how empathy is applied in everyday life.
- The importance and benefits of empathy in fostering healthy relationships, effective leadership, and a more compassionate society.
- Common misconceptions and frequently asked questions (FAQs) to help clarify what empathy truly means.
- Modern relevance and current trends in empathy research and practice, including debates on how empathy might be evolving in today’s world.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a thorough understanding of what is empathy? and why it is essential not only for personal well-being but also for building stronger, more resilient communities. Whether you’re a student, educator, business leader, or simply someone looking to deepen your connections with others, this guide is designed to equip you with the insights and practical tips you need to harness the transformative power of empathy.
A Straightforward Definition: What Is Empathy?
Core Definition
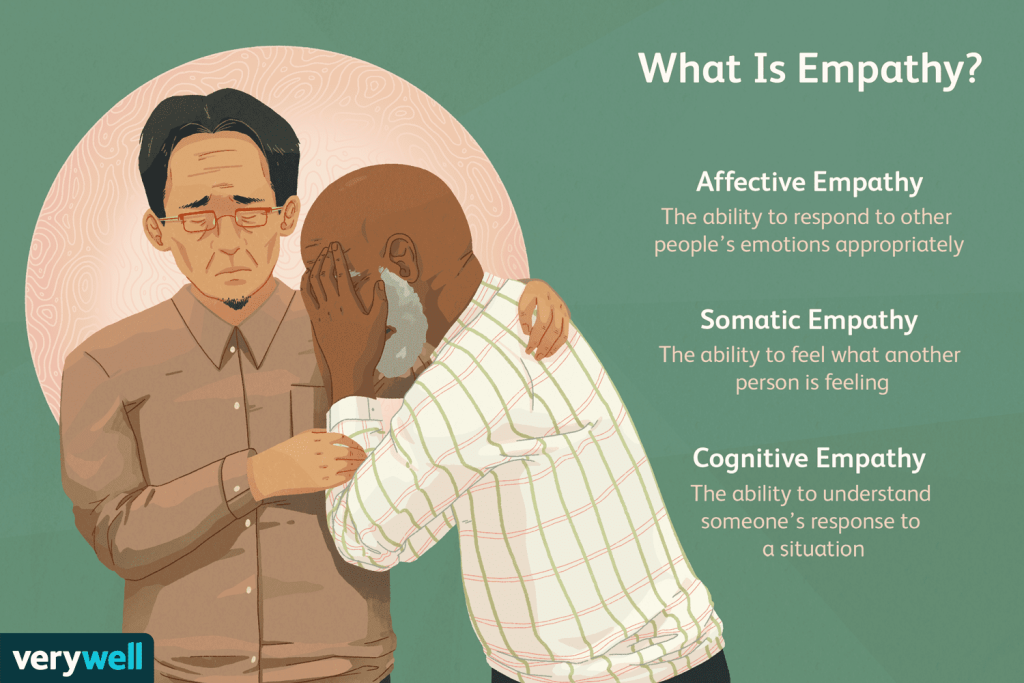
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person. It is the capacity to place oneself in someone else’s shoes, to see the world from their perspective, and to resonate with their emotional experience. Empathy goes beyond mere sympathy; while sympathy involves feeling pity or sorrow for someone else, empathy involves an emotional and cognitive connection with the other person’s experiences.
Essential Characteristics of Empathy
Emotional Empathy:
- This refers to the ability to actually feel the emotions of another person. When you see someone in distress and you feel their sadness, that is emotional empathy.
Cognitive Empathy:
- This involves understanding another person’s perspective or mental state. It’s the intellectual ability to comprehend what someone else might be thinking or feeling, even if you do not share those emotions yourself.
Compassionate Empathy (also known as Empathic Concern):
- This form of empathy combines both emotional and cognitive aspects and motivates an individual to help someone in distress. It is the drive to take action to alleviate another’s suffering.
Perspective-Taking:
- A critical component of empathy is the capacity to adopt another’s viewpoint. This means not only understanding their emotions but also appreciating the context that shapes those feelings.
Non-Judgmental Attitude:
- Empathy involves accepting another person’s feelings without criticism. It requires an open mind and a willingness to understand, even if you might not agree with their perspective.
In essence, what is empathy? It is a multifaceted ability that encompasses feeling, understanding, and acting upon the emotional experiences of others—a vital skill that underpins human connection and social cohesion.
Historical and Contextual Background
Understanding what is empathy? necessitates exploring its evolution over time and its role in various cultures and disciplines.
Ancient Philosophical Roots
Greek and Roman Thought:
Early philosophers, including Plato and Aristotle, discussed concepts related to empathy long before the term itself was coined. Aristotle’s notion of philia (friendship) and the importance of understanding others’ experiences laid the groundwork for later studies of empathy.Eastern Philosophies:
In many Eastern traditions, such as Buddhism and Hinduism, empathy is intrinsic to the practice of compassion and interconnectedness. The Buddhist concept of karuṇā (compassion) and the emphasis on ahimsa (non-violence) highlight the importance of understanding and sharing in the suffering of others.
The Emergence of Empathy in Modern Psychology
19th Century Beginnings:
The scientific study of empathy began in the 19th century with researchers like Theodor Lipps, who introduced the idea of Einfühlung (feeling into) as a way to understand art and human behavior.20th Century Developments:
In the 20th century, psychologists such as Carl Rogers and Martin Hoffman further developed the concept of empathy, integrating it into theories of personality, counseling, and moral development. Their work highlighted empathy as a critical factor in effective communication, therapy, and social interactions.
Empathy in Contemporary Society
Digital Age and Globalization:
Today, empathy is more important than ever in a globalized and digitally connected world. With social media enabling rapid communication across cultures, understanding and practicing empathy has become essential for fostering tolerance and inclusivity.Cultural Shifts:
Modern debates on gender, race, and social justice have brought empathy into the spotlight. As societies grapple with complex issues of diversity and inequality, empathy is recognized as a key ingredient in bridging divides and promoting social harmony.
Notable Historical Anecdotes
Empathy in Literature and Art:
Throughout history, literature and art have been powerful mediums for conveying empathy. The works of writers like Leo Tolstoy and Jane Austen, and the paintings of artists like Rembrandt, evoke deep emotional responses that illustrate the power of empathetic understanding.Social Movements:
Empathy has played a central role in numerous social and political movements. For instance, the civil rights movement in the United States was driven by leaders who appealed to the empathy of the broader public, calling for understanding and equality.
The historical evolution of empathy—from ancient philosophies to modern psychological research—provides a rich context for understanding what is empathy? and underscores its enduring importance in human society.
In-Depth Exploration / Main Body
Now that we have defined and contextualized what is empathy?, let’s delve deeper into its various dimensions, applications, and transformative power in different domains.
1. Dimensions of Empathy
a) Emotional Empathy
Description:
Emotional empathy is the ability to share and feel the emotions of another person. This form of empathy enables you to experience others’ joy, sadness, or pain as if it were your own.Real-World Example:
When a friend is grieving, emotional empathy allows you to feel their sorrow, prompting a compassionate response. This shared emotion can foster deeper connections and mutual support.
b) Cognitive Empathy
Description:
Cognitive empathy is the ability to understand another person’s perspective or mental state without necessarily sharing their emotions. It involves intellectual insight into someone else’s experiences and thoughts.Real-World Example:
In a workplace setting, a manager who practices cognitive empathy might understand why an employee is stressed due to a heavy workload, even if they do not feel the stress themselves. This understanding can lead to more effective problem-solving and support.
c) Compassionate Empathy (Empathic Concern)
Description:
Compassionate empathy combines emotional and cognitive empathy to not only understand and share someone’s feelings but also to take action to help alleviate their suffering.Real-World Example:
Volunteers at a crisis center often exhibit compassionate empathy by listening to distressed individuals and taking steps to offer practical assistance and emotional support.
d) The Role of Perspective-Taking
Description:
Perspective-taking is a key element of cognitive empathy. It involves stepping into another person’s shoes to understand their viewpoint, even if you don’t share the same emotions.Real-World Example:
In conflict resolution, mediators use perspective-taking to help disputing parties understand each other’s positions, paving the way for mutually beneficial solutions.
2. How Empathy Enhances Communication
a) Building Strong Relationships
Personal Relationships:
Empathy is foundational for deep, meaningful relationships. It allows people to connect on a level that fosters trust, understanding, and mutual support.Professional Relationships:
In the workplace, empathetic communication can lead to better teamwork, increased employee satisfaction, and more effective leadership.
b) Conflict Resolution and Negotiation
De-Escalating Tensions:
By understanding and acknowledging the feelings and perspectives of others, empathy can help defuse conflicts before they escalate.Facilitating Dialogue:
Empathy encourages open, honest conversations where all parties feel heard. This can lead to more sustainable and amicable resolutions.
c) Enhancing Persuasion and Influence
Effective Public Speaking:
Speakers who demonstrate empathy—by connecting with their audience on an emotional and intellectual level—are often more persuasive. Their messages resonate more deeply, leading to greater engagement and influence.Marketing and Branding:
Companies that communicate with empathy in their advertising and customer service build stronger, more loyal relationships with their customers.
3. Empathy in Education and Personal Growth
a) Academic Success
Learning Environment:
Empathy in educational settings creates a supportive, inclusive atmosphere where students feel valued and understood. Teachers who practice empathy can better address individual learning needs and foster a positive classroom environment.Peer Support:
Empathy among students encourages collaborative learning and helps build a community of mutual respect and assistance.
b) Personal Development
Self-Awareness:
Developing empathy enhances self-awareness by encouraging individuals to reflect on their own emotions and reactions. This introspection is a key part of personal growth.Emotional Intelligence:
Empathy is a core component of emotional intelligence, which is crucial for navigating life’s challenges, building resilience, and achieving personal fulfillment.
4. Empathy in Leadership and Organizational Culture
a) Ethical and Effective Leadership
Trust and Credibility:
Leaders who exhibit empathy earn the trust and respect of their teams. They are seen as approachable, understanding, and capable of making fair decisions.Motivation and Engagement:
An empathetic leader can inspire and motivate employees by acknowledging their challenges and supporting their professional and personal growth.
b) Fostering Inclusive Organizational Culture
Workplace Diversity:
Empathy plays a critical role in creating an inclusive environment where diverse perspectives are valued. This leads to improved collaboration and innovation.Conflict Management:
In organizations, empathetic communication is key to resolving conflicts and maintaining a harmonious work environment. Leaders who understand and validate employees’ feelings can more effectively manage disputes.
5. Empathy in Society and Global Communities
a) Social Justice and Human Rights
Advocacy and Activism:
Empathy drives social justice movements by helping individuals understand the struggles and injustices faced by others. This understanding motivates collective action for change.Building Bridges:
Empathy facilitates dialogue between different social, cultural, and political groups, fostering understanding and cooperation in diverse communities.
b) Cultural Exchange and Global Understanding
Intercultural Communication:
In our globalized world, empathy is essential for navigating cultural differences. It enables us to appreciate diverse perspectives and bridge cultural divides.Global Citizenship:
Empathy is a cornerstone of global citizenship, encouraging individuals to act with compassion and responsibility toward people around the world.
Addressing Common Misconceptions and FAQs
Even though empathy is widely recognized as a positive quality, there are several misconceptions that can obscure its true meaning and application. Let’s address some of these common misunderstandings.
Common Misconceptions
- Misconception 1: Empathy Is Innate and Cannot Be Learned
- Clarification:
While some individuals may have a natural inclination toward empathy, it is a skill that can be developed and strengthened through practice, reflection, and education.
- Clarification:
- Misconception 2: Empathy Is the Same as Sympathy
- Clarification:
Sympathy involves feeling pity or sorrow for someone else’s misfortune, whereas empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another. Empathy requires both emotional and cognitive engagement.
- Clarification:
- Misconception 3: Too Much Empathy Can Be a Weakness
- Clarification:
While excessive emotional involvement can sometimes lead to burnout, empathy, when balanced with healthy boundaries, is a powerful asset in personal and professional relationships.
- Clarification:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
FAQ 1: What is empathy in simple terms?
Answer:
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person. It involves both feeling what someone else is feeling (emotional empathy) and understanding their perspective (cognitive empathy).
FAQ 2: Why is empathy important?
Answer:
Empathy is crucial for effective communication, strong relationships, and social harmony. It fosters trust, helps resolve conflicts, and promotes a deeper understanding of others, which is essential in both personal and professional settings.
FAQ 3: How can I develop more empathy?
Answer:
You can cultivate empathy through practices such as active listening, mindfulness, self-reflection, and seeking out diverse perspectives. Engaging in conversations with people from different backgrounds also helps broaden your understanding.
FAQ 4: Can empathy be measured or quantified?
Answer:
While empathy is largely qualitative, researchers use various psychological scales and assessments to measure aspects of empathy. However, its true value is often best observed through its impact on relationships and social interactions.
FAQ 5: Is empathy the same as compassion?
Answer:
Not exactly. While empathy involves understanding and sharing the feelings of others, compassion goes a step further by motivating actions to alleviate their suffering. Both are interrelated and essential for effective social interaction.
Modern Relevance and Current Trends
1. Empathy in the Digital Age
Virtual Connections:
In a world dominated by digital communication, empathy is more critical than ever. Online interactions can sometimes lack the nuance of face-to-face conversations, making it essential to be mindful and empathetic in our digital communications.Social Media and Mental Health:
Studies show that empathetic interactions on social media can improve mental health and foster a supportive online community. Digital empathy involves thoughtful responses, active listening in online forums, and respectful engagement.
2. The Role of Empathy in Leadership and Business
Ethical Leadership:
Leaders who practice empathy can build more cohesive teams, improve employee satisfaction, and drive better business outcomes. Companies are increasingly recognizing that empathy is a key trait in successful leadership.Customer Relations:
Businesses that demonstrate empathy in customer service and engagement build trust and loyalty. Empathetic communication helps resolve conflicts and enhances overall customer experience.
3. Empathy in Education and Personal Development
Inclusive Education:
Modern educational systems are incorporating empathy training into their curricula. Programs that teach emotional intelligence and social skills are vital in creating a more inclusive and supportive learning environment.Lifelong Learning:
As part of personal development, cultivating empathy is considered essential for emotional well-being, resilience, and effective interpersonal communication.
4. Research and Technological Advances
Neuroscience of Empathy:
Advances in neuroscience are uncovering how empathy is processed in the brain, leading to better understanding and new approaches to fostering empathy through education and therapy.AI and Empathetic Technology:
There is growing interest in developing artificial intelligence that can recognize and respond to human emotions empathetically. While still in its early stages, empathetic AI could revolutionize customer service, mental health support, and human-computer interaction.
5. Global and Cultural Shifts
Intercultural Empathy:
In an increasingly interconnected world, empathy is crucial for bridging cultural divides and fostering global understanding. Cross-cultural empathy enables us to appreciate diverse perspectives and work collaboratively across borders.Social Justice and Activism:
Empathy is a driving force behind many social justice movements. By understanding and sharing the experiences of marginalized communities, individuals and organizations can advocate more effectively for change.
Practical Tips for Cultivating Empathy
Whether you’re looking to enhance your personal relationships, become a more effective leader, or simply improve your communication skills, here are some practical strategies to help you develop and nurture empathy.
1. Active Listening
Focus Fully on the Speaker:
Practice giving your full attention when someone is speaking. Avoid interrupting and reflect on what is being said before responding.Ask Clarifying Questions:
Show that you are engaged by asking questions that delve deeper into the speaker’s thoughts and feelings.
2. Practice Mindfulness and Reflection
Mindfulness Meditation:
Regular mindfulness meditation can help you become more aware of your own emotions and more attuned to the feelings of others.Reflective Journaling:
Keeping a journal about your daily interactions and your emotional responses can foster self-awareness and empathy.
3. Engage with Diverse Perspectives
Read Widely:
Explore literature, news, and media from different cultures and viewpoints. This exposure can broaden your understanding and help you empathize with experiences different from your own.Participate in Community Activities:
Engage in social or volunteer activities that allow you to connect with people from diverse backgrounds.
4. Develop Emotional Intelligence
Learn to Identify Emotions:
Enhance your ability to recognize emotions in yourself and others. Tools like emotional intelligence assessments can be helpful.Practice Empathic Responses:
When someone shares their feelings, respond in a way that acknowledges their experience. Phrases like “That sounds really challenging” or “I can see why you feel that way” can go a long way.
5. Leverage Technology Thoughtfully
Digital Empathy:
When interacting online, be mindful of tone and context. Use respectful language, and consider the impact of your words on others in digital communications.Use Empathy-Building Apps:
Consider apps and online courses designed to enhance emotional intelligence and empathy, such as those offered by platforms like Coursera or Udemy.
Conclusion
Summarizing the Key Points
Definition:
What is empathy? It is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person. Empathy involves both emotional resonance and cognitive understanding, making it a key element in effective communication and social interaction.Core Characteristics:
Empathy is defined by emotional and cognitive dimensions, which allow us to connect with others on a deep level. It is characterized by active listening, perspective-taking, and a compassionate, non-judgmental approach.Historical Evolution:
From ancient philosophical discussions to modern psychological research, the understanding of empathy has evolved significantly. Cultural shifts and technological advances have further enriched our comprehension of empathy.Applications and Benefits:
Empathy enhances personal relationships, improves leadership and teamwork, fosters inclusive communication, and drives social justice and cultural understanding. Its benefits extend from individual well-being to global harmony.Modern Trends:
In today’s digital age, empathy is more important than ever. The integration of empathy in AI, education, and global communication reflects its evolving role in a connected, multicultural world.
Reinforcing the Importance
Understanding what is empathy? is essential for building meaningful relationships, effective leadership, and a more compassionate society. Empathy is not just a personal trait—it is a critical skill that fosters trust, reduces conflict, and promotes mutual understanding across all areas of life.
Call to Action
Explore Further:
Dive deeper into the science and practice of empathy by reading academic articles, watching TED Talks on emotional intelligence, or taking online courses on empathy and communication. Resources like the Greater Good Science Center and Coursera offer excellent insights.Share Your Experiences:
Have you experienced a moment of deep empathy that changed your perspective? Share your stories and insights in the comments below or on social media using the hashtag #WhatIsEmpathy. Your experiences can inspire others to cultivate empathy in their own lives.Engage with the Community:
Join discussion groups, online forums, or local workshops focused on emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills. Engaging with a community that values empathy can provide support, new ideas, and practical strategies for everyday interactions.Practice Daily:
Make a conscious effort to practice empathy in your daily interactions. Whether it’s through active listening, reflective journaling, or simply being kind to others, small steps can lead to significant personal and social transformation.Stay Informed:
Subscribe to newsletters, follow thought leaders, and stay updated with the latest research on empathy. Understanding the evolving nature of empathy in a digital and globalized world will help you remain adaptable and open-minded.
By embracing and cultivating empathy, you empower yourself to connect more deeply with others, lead with compassion, and contribute to a more understanding and inclusive world. Understanding what is empathy? is not just about learning a concept—it’s about transforming how you interact with the world, one empathetic moment at a time.
Additional Resources
Books and Academic Texts
- Empathy: Why It Matters, and How to Get It by Roman Krznaric – An exploration of empathy’s role in personal growth and societal change.
- The Empathy Exams by Leslie Jamison – A collection of essays that delve into the complexities of empathy and its impact on human relationships.
- Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More Than IQ by Daniel Goleman – Offers insights into how empathy is a crucial component of emotional intelligence.
Online Educational Platforms
- Coursera – Courses on emotional intelligence, empathy, and interpersonal communication.
- edX – Provides courses that explore the psychology of empathy and social interaction.
- Khan Academy – While primarily focused on academic subjects, offers content related to personal development and social skills.
Websites and Blogs
- Greater Good Science Center – Research-based insights into empathy, compassion, and emotional well-being.
- Psychology Today – Articles and blog posts that discuss the science of empathy and practical tips for cultivating it.
Research Journals and Publications
- Journal of Personality and Social Psychology – Features studies on empathy and interpersonal relationships.
- Emotion Review – Offers articles on the latest research in emotional intelligence and empathetic behavior.
Digital Tools and Apps
- Mindfulness Apps (Headspace, Calm) – These apps provide guided meditations that can help you develop a more empathetic and mindful outlook.
- Empathy Building Exercises – Online platforms and workshops that offer practical exercises and scenarios to enhance your empathetic skills.
Community Forums and Discussion Groups
- Reddit: r/empathy – Engage with a community of people interested in discussing and practicing empathy.
- Stack Exchange: Psychology – A Q&A forum for in-depth discussions on the science and practice of empathy.
By leveraging these resources, you can deepen your understanding of what is empathy? and continue to cultivate this vital skill for personal growth, professional success, and positive societal change.
Final Thoughts
From transforming personal relationships to shaping effective leadership and fostering global understanding, empathy is a cornerstone of human connection. Understanding what is empathy? equips you with the tools to navigate the complexities of emotional and social interactions with clarity and compassion. Whether in your personal life, professional endeavors, or broader societal engagement, the ability to empathize is indispensable.
Embrace the journey of cultivating empathy, share your experiences, and contribute to a more compassionate world—one empathetic moment at a time.


 4.1 Attribution Theory and Person Perception: Why We Judge People the Way We Do (Even When We’re Totally Wrong) Let’s be honest. We’ve all
4.1 Attribution Theory and Person Perception: Why We Judge People the Way We Do (Even When We’re Totally Wrong) Let’s be honest. We’ve all



