What is Comprehension: Everything You Need to Know
Understanding how we process and interpret information is at the heart of learning, communication, and everyday problem-solving. But what is comprehension? How do we transform words on a page or spoken language into meaningful ideas and insights? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the concept of comprehension from multiple perspectives—examining its definition, historical evolution, key components, and practical applications in various fields. Whether you’re a student, educator, or lifelong learner, grasping the intricacies of comprehension is essential to improving your reading, critical thinking, and communication skills.
Introduction: The Vital Role of Comprehension
Imagine reading a complex article or listening to a detailed lecture only to find that the key ideas have slipped away. Studies suggest that effective comprehension not only boosts academic performance but also enhances everyday decision-making, problem-solving, and even social interactions. For instance, research from Reading Rockets shows that strong comprehension skills are linked to improved academic achievement and lifelong learning. This highlights the importance of understanding what is comprehension and how we can develop it.
In this article, we will cover:
- A clear, straightforward definition of what is comprehension and its essential characteristics.
- The historical and contextual background that has shaped our understanding of comprehension.
- An in-depth exploration of the key components and types of comprehension across various contexts.
- Real-world examples, case studies, and scenarios to illustrate how comprehension is applied and observed.
- The significance and benefits of developing strong comprehension skills in everyday life, education, and business.
- Common misconceptions and frequently asked questions about comprehension.
- Modern trends, research, and debates related to comprehension in today’s digital and information-driven world.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a well-rounded understanding of what is comprehension and why it plays a crucial role in both personal and professional realms.
What is Comprehension? A Straightforward Definition
At its core, comprehension is the ability to process, understand, and derive meaning from information. This skill is not merely about reading words on a page; it involves synthesizing the information, integrating it with prior knowledge, and applying it in various contexts. Here are the essential characteristics that define comprehension:
- Understanding: Comprehension involves grasping the meaning behind words, symbols, and ideas. It’s about interpreting what is being communicated.
- Integration: Effective comprehension requires integrating new information with what you already know, creating a richer and more coherent understanding.
- Retention: It also encompasses the ability to remember and recall the information later, making it useful for decision-making and problem-solving.
- Critical Analysis: Beyond surface-level understanding, comprehension involves analyzing and evaluating the content, discerning underlying themes, arguments, or biases.
- Application: Finally, true comprehension enables you to apply the knowledge gained to new situations, enhancing your ability to learn and innovate.
In essence, what is comprehension if not the active, dynamic process of making sense of the world around us?
Historical and Contextual Background of Comprehension
The concept of comprehension has evolved over centuries, deeply intertwined with the development of language, education, and cognitive psychology. Let’s take a journey through its historical milestones and contextual developments.
Ancient and Medieval Perspectives
- Early Oral Traditions: In ancient civilizations, comprehension was primarily an oral skill. Stories, laws, and cultural values were passed down through generations via storytelling. Listeners needed to comprehend and remember these narratives for cultural continuity.
- Classical Education: Greek philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle emphasized the importance of dialogue and debate. Their discussions on rhetoric and dialectics laid the groundwork for understanding how people process and internalize information.
- Medieval Manuscripts: During the medieval period, comprehension became crucial in the context of religious and philosophical texts. Monks and scholars dedicated themselves to copying, interpreting, and explaining ancient manuscripts, emphasizing careful reading and deep understanding.
Renaissance to Modern Developments
- The Renaissance: The invention of the printing press in the 15th century revolutionized the dissemination of information. With books becoming more widely available, the need for effective comprehension skills grew, spurring the development of systematic methods for reading and interpretation.
- Scientific Revolution: As scientific inquiry advanced, comprehension was no longer limited to literary texts. Scholars needed to understand complex theories, experiments, and mathematical formulas, driving innovations in critical thinking and analytical reading.
- Modern Educational Theories: In the 20th century, cognitive psychologists such as Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky explored how humans process and understand information. Their work laid the foundation for modern theories of reading comprehension, emphasizing the interaction between the reader and the text.
- Digital Age: Today, the explosion of digital information has transformed the landscape of comprehension. With vast amounts of data available online, individuals must develop advanced skills to filter, analyze, and synthesize information effectively.
This historical journey shows that what is comprehension has always been central to human development, evolving from basic oral traditions to sophisticated cognitive processes in our modern information society.
In-Depth Exploration: The Many Facets of Comprehension
To fully understand what is comprehension, it is helpful to break it down into its key components and explore its various dimensions. Below, we delve into several aspects of comprehension and how they are applied in different contexts.
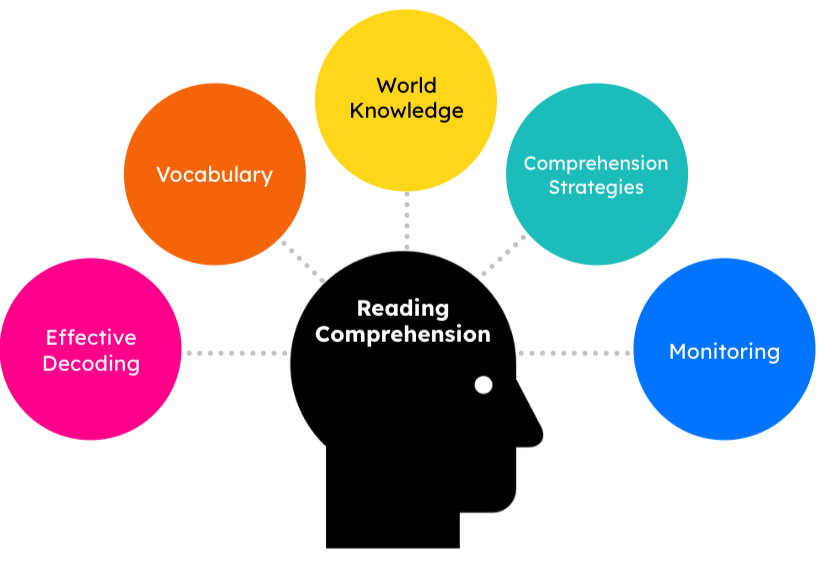
1. Reading Comprehension: Decoding and Beyond
Reading comprehension is perhaps the most familiar form of comprehension. It involves not only decoding written text but also interpreting and evaluating its meaning.
Key Elements of Reading Comprehension
- Decoding: The ability to recognize and process words and sentences.
- Literal Understanding: Grasping the explicit meaning of the text.
- Inferential Understanding: Drawing conclusions and reading between the lines based on context and prior knowledge.
- Critical Evaluation: Assessing the text’s arguments, biases, and underlying assumptions.
- Synthesis: Integrating information from multiple texts or sections of a text to form a comprehensive understanding.
Real-World Example: Academic Reading
Imagine a college student reading a dense academic article on climate change. The student must decode technical vocabulary, understand the literal facts presented, infer implications based on the data, critically evaluate the methodology, and synthesize these elements to form an overall understanding of the topic. This process exemplifies how reading comprehension goes beyond mere word recognition to involve deep cognitive engagement.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Reading Comprehension
- Active Reading: Engage with the text by asking questions, making annotations, and summarizing key points.
- Context Clues: Use surrounding words and sentences to decipher unfamiliar terms.
- Practice Regularly: Like any skill, regular practice improves reading comprehension over time.
2. Listening Comprehension: The Art of Active Listening
Listening comprehension is the ability to understand spoken language, whether in a conversation, lecture, or presentation.
Key Elements of Listening Comprehension
- Attention: Focusing on the speaker and the message being conveyed.
- Processing: Interpreting the spoken words and linking them to prior knowledge.
- Retention: Remembering key details and ideas.
- Feedback: Responding appropriately to ensure mutual understanding, often through paraphrasing or asking clarifying questions.
- Emotional Intelligence: Recognizing tone, emotion, and non-verbal cues that add depth to the spoken message.
Real-World Example: Classroom Learning
Consider a classroom where a teacher explains a complex scientific concept. Students must listen carefully, process the information in real time, and ask questions if necessary. Their ability to comprehend the lesson determines how well they can apply the concepts in exams and projects, showcasing the importance of listening comprehension in educational success.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Listening Comprehension
- Focus Fully: Minimize distractions when listening to important information.
- Take Notes: Jot down key points to reinforce retention and understanding.
- Engage Actively: Ask questions or provide feedback to clarify and confirm your understanding.
3. Visual Comprehension: Interpreting Information Beyond Words
Visual comprehension involves understanding information presented in images, graphs, videos, or other visual formats.
Key Elements of Visual Comprehension
- Observation: Carefully examining visual elements to capture details.
- Interpretation: Decoding symbols, colors, and spatial arrangements to understand the underlying message.
- Integration: Combining visual data with verbal or textual information to form a complete picture.
- Analysis: Evaluating visual elements to understand relationships, trends, and patterns.
Real-World Example: Data Visualization
In the business world, executives often rely on dashboards and infographics to make strategic decisions. A well-designed graph can communicate trends and patterns that might be lost in a table of numbers. For instance, a sales performance chart that uses color coding and clear labeling enables quick comprehension of data trends, helping leaders make informed decisions.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Visual Comprehension
- Study Visuals: Regularly analyze charts, graphs, and infographics to build your interpretative skills.
- Ask Questions: Consider what the visual elements are conveying and how they relate to the overall message.
- Combine with Text: Use captions, legends, and accompanying texts to enhance your understanding of visual information.
4. Comprehension in Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Critical thinking relies heavily on comprehension, as it involves not only understanding information but also evaluating its validity, drawing conclusions, and applying it to solve problems.
Key Elements of Critical Comprehension
- Analysis: Breaking down complex information into manageable parts.
- Evaluation: Assessing the credibility, relevance, and accuracy of the information.
- Inference: Drawing logical conclusions based on the evidence presented.
- Synthesis: Integrating diverse pieces of information to form a coherent understanding.
- Application: Using the comprehended information to make decisions or solve problems.
Real-World Example: Strategic Decision-Making in Business
Imagine a business leader reviewing market research reports, competitor analyses, and consumer trends. Their ability to comprehend and critically analyze this vast amount of data is crucial for devising effective strategies. By synthesizing insights from multiple sources, they can make informed decisions that drive business growth and innovation.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Critical Comprehension
- Question Assumptions: Don’t accept information at face value—dig deeper to understand the context and underlying assumptions.
- Practice Debates: Engaging in discussions or debates can sharpen your ability to analyze and evaluate different viewpoints.
- Use Checklists: Develop a systematic approach to evaluate the credibility and relevance of the information.
5. Digital Comprehension: Navigating the Information Age
In today’s digital world, the ability to comprehend a vast array of online content—ranging from social media posts to in-depth research articles—is more important than ever.
Key Elements of Digital Comprehension
- Source Evaluation: Assessing the reliability and credibility of online information.
- Multimodal Integration: Combining text, visuals, and interactive elements to grasp complex digital content.
- Information Filtering: Distinguishing between relevant and irrelevant data amid the information overload.
- Adaptability: Updating your comprehension strategies to keep pace with evolving digital communication styles.
Real-World Example: Online Research
A student researching climate change might encounter scholarly articles, blog posts, infographics, and videos. Their ability to critically evaluate each source, integrate the information, and extract key insights determines the quality of their research. This digital comprehension skill is essential not only for academic success but also for informed citizenship in a digital age.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Digital Comprehension
- Verify Sources: Use reputable databases, academic journals, and trusted websites.
- Engage Critically: Don’t just passively consume digital content; analyze and cross-reference the information.
- Stay Updated: As digital media evolves, continuously refine your strategies to navigate new forms of information.
Importance, Applications, and Benefits of Comprehension
Understanding what is comprehension and developing strong comprehension skills have far-reaching implications across various aspects of life. Here’s why it matters:
Academic and Educational Success
- Improved Learning: Strong comprehension skills enable students to grasp complex subjects, perform better on tests, and retain information over the long term.
- Enhanced Critical Thinking: Comprehension is foundational to analyzing texts, constructing arguments, and engaging in thoughtful discussion.
- Lifelong Learning: The ability to comprehend new information facilitates continuous personal and professional development.
Professional and Workplace Advantages
- Effective Communication: Whether it’s reading emails, understanding reports, or following presentations, comprehension ensures that information is accurately received and acted upon.
- Decision-Making: In business and management, comprehending data and trends leads to better strategic decisions.
- Innovation: Professionals who can synthesize information from various sources are better equipped to innovate and solve problems.
Personal and Social Benefits
- Informed Decision-Making: Everyday decisions—from health choices to financial planning—rely on the ability to understand and evaluate information.
- Enhanced Relationships: Good listening and comprehension skills improve interpersonal communication, leading to stronger relationships.
- Civic Engagement: A well-informed citizenry, capable of comprehending political and social issues, is essential for a healthy democracy.
Broader Societal Impact
- Educational Policy: Understanding comprehension processes helps educators design curricula that promote critical thinking and lifelong learning.
- Digital Literacy: In an age of misinformation, strong comprehension skills are crucial for discerning fact from fiction and participating meaningfully in digital spaces.
- Economic Growth: A workforce with advanced comprehension skills is better positioned to adapt to changing industries and technological advancements.
Addressing Common Misconceptions and FAQs About Comprehension
Despite its central role in learning and communication, several misconceptions about comprehension persist. Here, we clarify some common myths and answer frequently asked questions about what is comprehension.
Misconception 1: Comprehension Is the Same as Reading
Clarification:
While reading is a key component, comprehension involves much more than just decoding words. It encompasses understanding, integrating, and applying information, whether that information is written, spoken, or visual.
Misconception 2: Comprehension Is a Passive Process
Clarification:
Effective comprehension is an active, dynamic process. It requires engagement, critical analysis, and often interaction with the material through questioning and reflection.
Misconception 3: Comprehension Skills Are Innate and Cannot Be Improved
Clarification:
Although some individuals may have a natural aptitude, comprehension is a skill that can be developed and refined with practice, feedback, and targeted strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How can I improve my reading comprehension?
A: Practice active reading strategies such as annotating texts, summarizing key points, and asking questions to deepen your understanding. Regular practice and exposure to diverse texts can significantly enhance your skills.Q: Why is listening comprehension important in the workplace?
A: Effective listening comprehension ensures clear communication, reduces misunderstandings, and facilitates better collaboration and decision-making in professional settings.Q: What role does digital literacy play in comprehension?
A: Digital literacy involves the ability to critically evaluate and synthesize information from various digital sources. This is essential for navigating the vast amount of information available online.Q: Are there specific exercises to boost comprehension skills?
A: Yes. Exercises such as reading varied texts, participating in discussions, practicing summarization, and engaging in critical thinking activities can all help improve your comprehension.
Modern Relevance and Current Trends in Comprehension
In today’s rapidly changing world, the nature of comprehension is evolving to meet new challenges and opportunities.
The Digital Transformation
- Information Overload: With the exponential growth of digital content, individuals must refine their comprehension skills to filter and process information effectively.
- Multimodal Learning: Digital platforms now combine text, audio, and visuals, requiring users to integrate diverse sources of information seamlessly.
- Critical Digital Literacy: In an era of misinformation, the ability to critically assess online sources and verify facts is more important than ever.
Advances in Cognitive Science
- Neuroscientific Research: Recent studies in neuroscience have begun to map the brain regions involved in comprehension, offering insights into how learning strategies can be optimized.
- Adaptive Learning Technologies: Educational technologies that tailor content to individual comprehension levels are emerging, enhancing personalized learning experiences.
Educational Innovations
- Active Learning Models: Modern classrooms emphasize interactive and student-centered approaches, which foster deeper comprehension through discussion, collaboration, and real-world application.
- Lifelong Learning Initiatives: With rapid technological change, continuous learning and the ability to comprehend new information are becoming essential skills for career success.
Business and Professional Trends
- Data-Driven Decision Making: In the corporate world, the ability to comprehend and analyze data is critical for strategic planning and innovation.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: As industries converge, professionals must integrate knowledge from multiple fields, making advanced comprehension skills indispensable.
How to Cultivate and Enhance Your Comprehension Skills
Improving your understanding of what is comprehension can have a transformative impact on your personal, academic, and professional life. Here are actionable strategies to help you enhance your comprehension skills:
For Readers and Students
- Practice Active Reading: Engage with texts by annotating, summarizing, and asking questions.
- Expand Your Vocabulary: A robust vocabulary facilitates smoother decoding and deeper comprehension.
- Discuss and Debate: Join study groups or discussion forums to share perspectives and clarify your understanding.
- Use Comprehension Strategies: Techniques such as SQ3R (Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review) can structure your reading process and enhance retention.
For Professionals
- Focus on Listening Skills: In meetings and presentations, practice active listening—take notes and ask clarifying questions.
- Analyze Data Visually: Use graphs and charts to help break down complex information.
- Engage in Continuous Learning: Attend workshops, webinars, and professional development courses to refine your critical thinking and comprehension abilities.
- Leverage Technology: Use digital tools and apps designed to improve reading and listening comprehension.
For Educators
- Implement Interactive Learning: Design lessons that require students to apply what they’ve learned through projects, discussions, and hands-on activities.
- Provide Varied Materials: Offer texts and resources in multiple formats (print, digital, audio) to cater to diverse learning styles.
- Assess Comprehension Regularly: Use formative assessments and feedback to identify areas where students may need additional support.
- Encourage Reflective Practice: Ask students to reflect on their learning process and identify strategies that help them better understand the material.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Comprehension
In our exploration of what is comprehension, we have uncovered that it is far more than just reading or hearing words—it is an active, dynamic process that enables us to understand, analyze, and apply information across every facet of our lives. From the ancient oral traditions and early scholarly works to the modern challenges of digital literacy and information overload, comprehension remains at the heart of effective learning, communication, and decision-making.
Key Takeaways:
- Comprehension is the ability to process, integrate, and understand information, whether it’s in written, spoken, or visual form.
- Its historical evolution demonstrates its critical role in education, communication, and cultural development.
- Effective comprehension is essential for academic success, professional growth, and informed citizenship.
- Modern trends highlight the need for advanced comprehension skills to navigate the digital world and rapidly evolving information landscapes.
- Developing strong comprehension skills involves active engagement, critical thinking, and continuous practice.
Call to Action:
Reflect on your own approach to processing information. Whether you’re reading a book, listening to a podcast, or analyzing data at work, consider what strategies you can adopt to improve your comprehension. Share your experiences and tips in the comments below, and be sure to pass along this guide to anyone interested in deepening their understanding of what is comprehension. For further insights, explore resources like Edutopia and The National Reading Panel for more on enhancing comprehension skills.
Thank you for reading this comprehensive guide on what is comprehension. We hope it has provided valuable insights and practical strategies to help you become a more effective learner and communicator. Embrace the challenge, engage actively with your materials, and enjoy the journey of lifelong learning!