Advanced Password Generator
Check out our Conversion Tools
Check out our Calculator
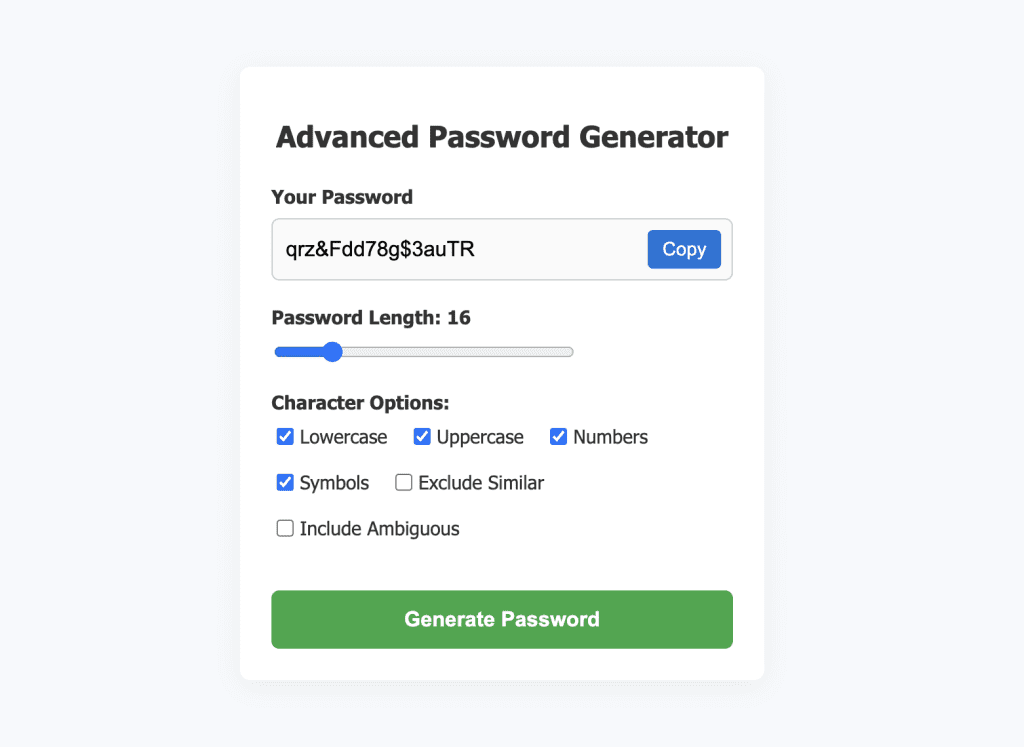
How to Generate a Random Password
Creating a strong, random password is crucial for securing your digital accounts and personal information. Our password generator simplifies this process, enabling you to produce highly secure passwords with just a click of the “Generate Password” button. Here’s a detailed guide on how it works and why strong passwords are essential.
Using the Password Generator
Simple Generation Process:
- One-Click Generation: Simply press the “Generate Password” button to create a new password instantly.
- Cryptographic Security: The generator employs robust cryptographic algorithms to produce random numbers. These numbers are then mapped to symbols based on your specified preferences, resulting in a randomly generated password tailored to your needs.
Privacy Assurance:
- Exclusive Visibility: The generated password is visible only to you. Each time you click the button, a new password is created, and the page refreshes.
- No Server Storage: Our server does not store any of the passwords you generate. Once you close the page, the password disappears, ensuring that only you have access to it.
Secure Transmission:
- Encrypted Connection: To safeguard your password from potential network sniffing, the generator uses HTTPS. Specifically, it leverages encryption and authentication with TLS 1.2, ECDHE_RSA with P-256 for key exchange, and AES_128_GCM for encryption.
- Verification: You can verify the secure connection in your browser to ensure that your password is transmitted safely.
Customization Options:
- Symbol Selection: Different websites and applications have varying password requirements. Our generator allows you to customize your password by including or excluding:
- Numbers (0-9)
- Uppercase Letters (A-Z)
- Symbols (!@#$%&*?^ )
- Potentially Ambiguous Characters (e.g., {}/'”`~,;:.<>)\ )
- Default Inclusion: Lowercase letters (a-z) are included by default to ensure a base level of complexity.
- Symbol Selection: Different websites and applications have varying password requirements. Our generator allows you to customize your password by including or excluding:
Why a Strong Password is Essential
Having a strong password protects you in two primary scenarios:
Preventing Unauthorized Access:
- Automated Attacks: Attackers use automated tools to guess passwords by attempting numerous combinations rapidly. Strong, randomly generated passwords significantly increase the time and effort required to crack them.
- Increased Security: A robust password makes it exponentially harder for attackers to succeed, often requiring years of dedicated computing power to breach.
Mitigating Data Breaches:
- Hashing Algorithms: Reputable websites store passwords using one-way hashing algorithms (e.g., SHA256, SHA512). Even if a breach occurs, hackers obtain hashed passwords, not plain text.
- Resistance to Cracking: Strong, random passwords resist dictionary attacks, where attackers use dictionaries of common or previously breached passwords to guess credentials.
- Unique Passwords: Using a unique, strong password for each service ensures that a breach in one does not compromise your other accounts.

Tips for Creating Strong Passwords
While using our password generator is a great start, consider the following additional tips to enhance your password security:
Password Length:
- Longer is Stronger: The length of your password is a critical factor in its strength. For example:
- 4 Characters: Only 456,976 possible combinations with lowercase letters—easily cracked.
- 6 Characters: 11,881,376 combinations—better but still vulnerable.
- 10 Characters: 95,428,956,661,682,176 combinations—extremely secure.
- Recommendation: Aim for passwords between 12 and 16 characters. Our generator supports even longer passwords for maximum security.
- Longer is Stronger: The length of your password is a critical factor in its strength. For example:
Diverse Symbols:
- Variety Enhances Security: Incorporating uppercase letters, numbers, and special characters increases the number of possible combinations.
- Example: A 4-character password with lowercase, uppercase, and numbers has 14,776,336 possible combinations, vastly improving security over using only lowercase letters.
- Support for Multiple Symbols: Our generator includes all Latin letters (both cases), numbers, and 29 special characters to maximize password complexity.
Avoid Common Patterns:
- No Repetition or Sequences: Do not use repeating characters, keyboard patterns (like “abcd”), or sequential numbers (like “1234”).
- Steer Clear of Personal Information: Avoid using names, dates of birth, anniversaries, phone numbers, or any information that could be easily guessed or discovered.
- No Dictionary Words: Avoid using actual words or easily guessable phrases to prevent dictionary attacks.
Memorable Yet Secure:
- Avoid Predictable Substitutions: While mixing words and symbols (e.g., “br0wn^threes.are^the.c00lest!”) can create long passwords, they may still be vulnerable to advanced dictionary attacks.
- Random Generation Preferred: For maximum security, use the random password generator instead of manually creating passwords.
Additional Password Security Tips
To further enhance the security of your passwords, adhere to these best practices:
Do Not Share Passwords:
- Keep your passwords confidential and avoid sharing them with anyone.
Remember Passwords When Possible:
- Try to memorize your passwords instead of storing them, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Secure Storage Solutions:
- If you must store passwords, use reputable password managers that encrypt your data. Avoid insecure methods like writing them on paper or saving them in easily accessible files.
Unique Passwords for Each Service:
- Use different passwords for different accounts to prevent a breach in one service from affecting others.
Use Reputable Password Managers:
- Ensure that any password storage software you use is from a trusted source and has a strong security track record.
Secure Login Environments:
- Avoid logging into your accounts from public or unsecured networks. Public Wi-Fi can be a significant security risk.
Avoid Cloud Storage for Critical Passwords:
- Do not store sensitive passwords on cloud services unless they are part of a secure password manager with strong encryption.
Be Aware of Your Surroundings:
- Ensure that no cameras are recording your screen when entering passwords, especially in public or shared spaces.
Balancing Security and Convenience
Security in password management is about finding the right balance between protection and usability. While highly secure passwords are essential, they should not impede your ability to access your accounts efficiently. Using a strong, randomly generated password is a critical step in safeguarding your online presence, but it should be part of a comprehensive security strategy that includes other measures like two-factor authentication and regular security updates.
By leveraging our password generator and following these best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your personal and financial information from potential threats.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Password Generators
1. What is a password generator? A password generator is a tool or software that creates strong, random passwords for users. These passwords typically include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters to enhance security and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
2. Why should I use a password generator instead of creating my own passwords? Using a password generator ensures that your passwords are truly random and complex, making them harder for attackers to guess or crack. Manually created passwords often follow predictable patterns, which can be vulnerable to brute-force or dictionary attacks.
3. How does a password generator ensure password security? Password generators use cryptographic algorithms to produce random sequences of characters. This randomness, combined with the inclusion of various character types (uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols), ensures high entropy and reduces the likelihood of password compromise.
4. Are password generators safe to use online? Reputable online password generators use secure methods to generate passwords and often employ encryption protocols (like HTTPS) to protect data during transmission. However, it’s essential to choose trusted and well-reviewed generators to ensure your passwords remain secure.
5. Can I customize the passwords generated by a password generator? Yes, most password generators allow you to customize various aspects of the generated passwords, such as length, inclusion of specific character types (e.g., symbols, numbers), and exclusion of ambiguous characters to meet specific security requirements.
6. Do password generators store my generated passwords? Trusted password generators typically do not store any generated passwords. They are designed to generate passwords on-the-fly and ensure that only you have access to them. Always verify the privacy policy of the tool you are using to confirm this behavior.
7. How long should a password generated by a password generator be? For optimal security, it’s recommended to use passwords that are at least 12 to 16 characters long. Longer passwords exponentially increase the number of possible combinations, making them significantly harder to crack.
8. Can password generators create passwords that meet specific criteria for different websites? Yes, many password generators offer customization options to meet the specific password requirements of various websites, such as minimum length, required character types, and restrictions on certain symbols.
9. What is the difference between online and offline password generators? Online password generators operate through web browsers and require an internet connection, while offline generators are software applications that run locally on your device without needing internet access. Offline generators can offer enhanced security by eliminating potential online threats.
10. Are there any risks associated with using a password generator? While password generators are generally safe, potential risks include using untrusted tools that might store or transmit your passwords insecurely. To mitigate these risks, use reputable generators and consider offline options for added security.
11. How do password managers integrate with password generators? Many password managers include built-in password generators. They allow you to create strong, random passwords and securely store them within the manager, making it easy to use unique passwords for each of your accounts without remembering them all.
12. Can I use a password generator to update my existing passwords? Absolutely. Regularly updating your passwords with new, randomly generated ones enhances your account security. Password generators make this process quick and ensure that each new password is strong and unique.
13. Do password generators support the creation of passphrases? Yes, some password generators offer the option to create passphrases—longer sequences of random words or a combination of words and characters. Passphrases can be easier to remember while still providing strong security.
14. How do password generators compare to biometric authentication methods? Password generators and biometric authentication serve different purposes. While password generators create strong passwords to secure your accounts, biometric methods (like fingerprint or facial recognition) provide an additional layer of security. Combining both can significantly enhance overall account protection.
15. Are there open-source password generators available? Yes, there are several open-source password generators available. Open-source tools allow the community to inspect and verify the code, ensuring transparency and trustworthiness. Examples include Bitwarden, KeePassXC, and pwgen.
16. Can I generate passwords for multiple accounts at once using a password generator? While most password generators create one password at a time, some advanced tools and password managers allow you to generate and manage multiple passwords simultaneously, streamlining the process of securing multiple accounts.
17. What should I do if I lose a password generated by a password generator? If you lose a generated password, you will typically need to use the account’s password recovery options, such as resetting the password via your email. To prevent loss, consider using a secure password manager to store and organize your generated passwords safely.
18. How often should I change my passwords using a password generator? It’s recommended to change your passwords periodically, such as every 3 to 6 months, especially for sensitive accounts like banking or email. Using a password generator makes this process easier and ensures that each new password is strong and unique.
19. Can password generators help with compliance to security standards? Yes, password generators can help you comply with various security standards and policies by creating passwords that meet specific criteria, such as minimum length, complexity, and the inclusion of diverse character types required by industry regulations.
20. Are there mobile apps that function as password generators? Yes, many mobile applications offer password generation features. These apps often integrate with password managers to provide on-the-go access to strong, random passwords, ensuring you can securely create and manage passwords from your smartphone or tablet.
Educational Resources
- Official guidelines from the National Institute of Standards and Technology on digital identity and password creation standards.
Additional Resources
- A service that allows you to check if your passwords have been exposed in data breaches, helping you identify compromised passwords.
- Provides practical tips on creating and managing strong passwords to keep your accounts secure.
- A tool by Google that checks your passwords against known data breaches and provides security recommendations.
Mozilla Firefox Password Generator
- A built-in password generator within the Firefox browser that helps you create strong passwords when signing up for new accounts.
Best Practices and Guidelines
Creating Strong Passwords – NIST
- Detailed guidelines from NIST on creating and managing strong passwords as part of digital identity management.
Password Policy Recommendations
- Microsoft’s updated recommendations for password policies to enhance security and usability.
Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) Password Guidance
- Comprehensive guidance from CISA on creating, managing, and protecting passwords effectively.
Security Tools and Libraries
OpenSSL Random Number Generator
- A powerful library for generating cryptographically secure random numbers, often used in password generators.
- A module in Python for generating secure random numbers suitable for password generation.
- Java’s class for generating cryptographically strong random numbers for use in secure password generation.
Interesting Facts About Secure Passwords
Creating and maintaining secure passwords is a cornerstone of digital security. Here are some fascinating and lesser-known facts about secure passwords that highlight their importance, evolution, and best practices:
1. The Origin of Passwords Dates Back to Ancient Times
- Historical Roots: The concept of passwords isn’t modern. Ancient civilizations, such as the Greeks, used secret phrases to gain access to military camps. A famous example is the Spartan password “Molon Labe” (“Come and take them”) during the Battle of Thermopylae.
2. Short Passwords Are Easier to Crack Than You Think
- Brute-Force Vulnerability: A password with just 8 characters, using a mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols, can be cracked in minutes using modern brute-force techniques. This underscores the need for longer, more complex passwords.
3. Password Strength Is Measured by Entropy
- Entropy Explained: Entropy in password security refers to the randomness and unpredictability of a password. Higher entropy means more possible combinations, making the password harder to guess or crack.
4. The Most Common Passwords Are Shockingly Simple
- Top Offenders: Lists of compromised passwords reveal that many people use simple and easily guessable passwords like “123456,” “password,” or “qwerty.” These are among the most frequently hacked passwords.
5. Passwords Can Be Biometric and Beyond
- Beyond Traditional Passwords: Modern authentication methods include biometrics (like fingerprints and facial recognition) and hardware tokens, which can complement or replace traditional password-based systems for enhanced security.
6. Password Reuse Is a Major Security Risk
- Single Point of Failure: Using the same password across multiple sites means that a breach on one platform can compromise all your accounts. Unique passwords for each service are essential to mitigate this risk.
7. The Introduction of Password Managers Revolutionized Security
- Convenience Meets Security: Password managers securely store and generate complex passwords, eliminating the need to remember multiple passwords and encouraging the use of stronger, unique credentials for each account.
8. Password Policies Have Evolved Over Time
- From Complexity to Length: Earlier password policies emphasized complexity (mix of characters), but recent guidelines, such as those from NIST, prioritize length and discourage frequent mandatory changes unless there’s a security breach.
9. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) Enhances Password Security
- Adding Layers: 2FA requires two forms of verification (something you know, like a password, and something you have, like a smartphone), significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if a password is compromised.
10. Passphrases Are Becoming More Popular
- Memorable Security: Instead of complex strings, passphrases use a series of random words (e.g., “BlueFishMountain7!”) that are easier to remember and can be just as secure when sufficiently long and random.
11. The First Computer Password Was Used in the 1960s
- Early Adoption: The Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS) at MIT, developed in the early 1960s, is credited with introducing the first computer password system to protect user accounts.
12. Social Engineering Is a Common Password Compromise Technique
- Human Factor: Attackers often exploit human psychology through phishing, pretexting, or other social engineering tactics to trick individuals into revealing their passwords, highlighting the importance of user awareness and training.
13. Password Cracking Tools Have Become More Sophisticated
- Advanced Techniques: Tools like Hashcat and John the Ripper use GPU acceleration and optimized algorithms to crack passwords faster than ever, emphasizing the need for stronger password practices.
14. The Use of Special Characters Can Significantly Increase Password Security
- Character Diversity: Incorporating symbols, numbers, and varying cases increases the complexity and entropy of a password, making it more resistant to guessing and brute-force attacks.
15. Password Expiry Policies Are Being Re-Evaluated
- Policy Shifts: Traditional policies mandated regular password changes, but research shows that forced changes can lead to weaker passwords. Modern guidelines suggest changing passwords only when there is evidence of compromise.
16. Quantum Computing Could Impact Password Security
- Future Threats: Quantum computers have the potential to break current encryption methods, including those protecting passwords. This possibility is driving research into quantum-resistant algorithms to future-proof password security.
17. Some Systems Use Password Salting to Enhance Security
- Salting Explained: Salting involves adding a unique, random string to each password before hashing, making it significantly harder for attackers to use precomputed tables (rainbow tables) to crack passwords.
18. Passwords Are Often the Weakest Link in Security
- Security Hierarchy: Despite advancements in security technologies, passwords remain a primary target for attackers due to their pivotal role in authentication processes.
19. The Longest Password Ever Used in a Security Breach
- Record Lengths: Some breaches have exposed extremely long passwords (over 100 characters), which, while secure, highlight the importance of balancing security with usability.
20. Biometric Data Is Not a Replacement for Passwords
- Complementary Use: While biometrics offer enhanced security, they are not infallible and are best used in conjunction with strong passwords rather than as a complete replacement.
21. Password Managers Can Generate Passwords with Up to 100 Characters
- Unprecedented Lengths: Some password managers allow the creation of exceptionally long passwords, providing unparalleled security for highly sensitive accounts.
22. The Cost of a Password Breach Can Be Enormous
- Financial Impact: Data breaches involving passwords can cost companies millions in fines, legal fees, and reputational damage, emphasizing the need for robust password security measures.
23. Password Complexity Requirements Can Sometimes Backfire
- User Frustration: Overly complex requirements can lead to user frustration, resulting in insecure practices like writing passwords down or using predictable patterns, undermining security efforts.
24. AI and Machine Learning Are Enhancing Password Security
- Smart Detection: AI algorithms are being used to detect unusual login patterns and potential breaches, enabling more proactive and dynamic password security measures.
25. Cultural Factors Influence Password Choices
- Global Variations: Password preferences and practices can vary significantly across different cultures and regions, affecting how password security strategies are implemented globally.