Unit 2.2: The Gravitational Field in AP Physics 1
Understanding Gravitational Fields and Weight ⬇️
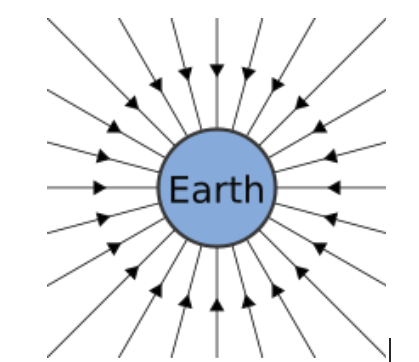
The gravitational field is a region around a massive object where other objects experience a force due to gravity. On Earth, this field exerts a downward force on all objects, commonly referred to as their weight.
Key Formula:
The gravitational force on an object can be calculated using:
where:
is the force due to gravity (weight)
is the mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
is the acceleration due to gravity (on Earth,
, but
can be used for simplification on the AP Physics 1 exam)
SI Units:
- Weight: Newtons (N)
- Mass: Kilograms (kg)
Weight vs. Mass
It’s crucial to differentiate between weight and mass:
- Mass is the measure of the amount of matter in an object and remains constant regardless of location.
- Weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object, which varies depending on the gravitational field strength.
Example: An object will weigh less on the Moon than on Earth due to the Moon’s weaker gravitational field.
Key Concepts
- Gravitational Field (
): Region around a massive object where a force of attraction acts on other masses. The strength of this field depends on the mass of the object and its distance from other objects. - The gravitational constant (
) relates the gravitational force between two objects to their masses and the distance between them:
Example Problems and Solutions
Example Problem 1: Calculating Gravitational Force
Problem: A 5.00-kg object is placed on a frictionless table. Determine the gravitational force on the object due to Earth’s gravity (
).
Solution:
Using the formula
:
The gravitational force on the object is 49 N.
Example Problem 2: Gravitational Force on a Different Planet
Problem: A 10.0 g sample of material is placed on Planet X, which has a mass of
and a radius of
. The acceleration due to gravity on Planet X is
. Calculate the gravitational force on the sample.
Solution:
- Convert mass to kilograms:
- Calculate the gravitational force using
:
The gravitational force on the sample is 0.09 N.
Example Problem 3: Weight of an Object
Problem: A textbook has a mass of 2.00 kg. Calculate its weight on Earth (
) and convert the weight to pounds.
Solution:
- Calculate weight in newtons:
- Convert newtons to pounds (1 N = 0.225 pounds):
The textbook’s weight is 19.6 N or 4.42 pounds.
Practical Applications of Gravitational Fields
- Understanding weight differences on various planets: Objects weigh less on the Moon than on Earth due to the Moon’s lower gravitational field strength.
- Space travel and celestial mechanics: The concept of gravitational fields is essential for calculating spacecraft trajectories and planetary orbits.







