A Complete Guide to PPC Ad Targeting Options
Running a successful Pay-Per-Click (PPC) campaign today requires more than just placing ads online; it’s about delivering your message to the right audience with precision. Whether your goal is to attract local shoppers or engage a global audience, mastering PPC ad targeting is essential to maximizing your return on investment (ROI).
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the myriad of PPC ad targeting options available on platforms like Google Ads and Microsoft Ads. We’ll delve into each targeting method, offering detailed explanations, practical examples, and best practices to help you fine-tune your campaigns for optimal performance.
Understanding PPC Ad Targeting
PPC ad targeting is the process of defining specific criteria to display your ads to a particular group of people. Effective targeting ensures that your ads reach users who are most likely to be interested in your products or services, thereby increasing the chances of conversion and maximizing your advertising budget.
Why is PPC Ad Targeting Important?
- Relevance: Ensures your ads are shown to users interested in your offerings.
- Cost-Efficiency: Reduces wasted spend by avoiding irrelevant audiences.
- Higher ROI: Increases the likelihood of conversions, improving your return on investment.
- Competitive Advantage: Helps you stand out by reaching niche or specific audiences.
Search Targeting
Search targeting is the cornerstone of PPC campaigns on platforms like Google Ads and Microsoft Ads. It allows advertisers to reach users who are actively searching for specific products, services, or information.
Keywords and Match Types
Keywords are the terms or phrases that users enter into search engines. Bidding on relevant keywords ensures your ads appear alongside search results that are pertinent to your business.
Match Types Explained
Broad Match:
- Definition: Shows your ad for searches that include misspellings, synonyms, related searches, and other variations.
- Pros: Maximum reach.
- Cons: Can attract irrelevant traffic.
- Example: Keyword “running shoes” may trigger ads for “buy sneakers” or “jogging footwear.”
Phrase Match:
- Definition: Shows your ad for searches that include the exact phrase or close variations with additional words before or after.
- Pros: More control than broad match.
- Cons: Limited reach compared to broad match.
- Example: Keyword “running shoes” may trigger ads for “best running shoes” or “running shoes for men.”
Exact Match:
- Definition: Shows your ad only when the exact keyword or close variants are searched.
- Pros: Highest control and relevance.
- Cons: Lowest reach.
- Example: Keyword “running shoes” will only trigger ads for “running shoes” or minor variations like “running shoe.”
Negative Keywords:
- Definition: Keywords that prevent your ads from showing for specific searches.
- Pros: Improves relevance and reduces wasted spend.
- Cons: Requires ongoing management.
- Example: Adding “free” as a negative keyword to prevent ads from showing for “free running shoes.”
Best Practices for Keyword Targeting
- Conduct Thorough Keyword Research: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to identify relevant keywords with high search volume and low competition.
- Utilize Long-Tail Keywords: These are longer, more specific phrases that typically have lower competition and higher conversion rates.
- Regularly Update Your Keyword List: Remove underperforming keywords and add new ones based on performance data.
- Monitor Quality Score: Ensure your keywords maintain a high Quality Score by optimizing ad relevance, landing page experience, and expected click-through rate (CTR).
Dynamic Search Ads (DSA)
Dynamic Search Ads are an automated ad format that uses your website content to match user searches with relevant ads. DSAs are particularly useful for filling keyword gaps and ensuring comprehensive coverage without exhaustive keyword lists.
How DSAs Work
- Website Crawling: Google scans your website to understand its structure and content.
- Ad Generation: Based on user queries, Google dynamically generates ad headlines and landing pages.
- Keyword Gap Filling: DSAs can target searches that you haven’t explicitly bid on, capturing additional traffic.
Benefits of Using DSAs
- Time-Saving: Reduces the need for extensive keyword research and management.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Ensures no relevant search queries are missed.
- Flexibility: Automatically updates ads based on website changes.
Best Practices for DSAs
- Optimize Website Content: Ensure your website is well-structured with clear headings and relevant content to improve DSA performance.
- Use Page Feeds: Specify which pages to include or exclude, ensuring ads are relevant and high-quality.
- Combine with Traditional Campaigns: Use DSAs to complement existing keyword-based campaigns, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
Location Targeting
Location targeting allows you to display your ads to users in specific geographic locations, ranging from entire countries to specific cities or even a radius around a particular address.
Types of Location Targeting
- Country-Level Targeting: Reach users in entire countries.
- Region/State Targeting: Focus on specific states or regions within a country.
- City or Postal Code Targeting: Target users in specific cities or postal codes.
- Radius Targeting: Define a radius around a specific location to capture local audiences.
Benefits of Location Targeting
- Relevance: Tailor your ads to local events, weather, or trends.
- Cost-Efficiency: Avoid spending on regions that are not profitable or relevant.
- Enhanced Personalization: Customize ad messaging based on local preferences or languages.
Best Practices for Location Targeting
- Analyze Performance by Location: Use platform analytics to identify high-performing regions and allocate budgets accordingly.
- Exclude Irrelevant Locations: Prevent ads from showing in locations where you don’t serve or want to avoid.
- Customize Ad Copy: Reflect local culture, language, or references to increase engagement.
- Use Location Extensions: Enhance your ads with additional information like address, phone number, or a map.
Device Targeting
Device targeting enables you to display ads on specific devices such as desktops, tablets, or mobile phones. This is crucial as user behavior and engagement can vary significantly across different devices.
Types of Device Targeting
- Desktop: Users on laptops or desktop computers.
- Mobile: Users on smartphones.
- Tablet: Users on tablet devices.
- Operating Systems: Target based on the device’s operating system (e.g., iOS, Android, Windows).
Benefits of Device Targeting
- Optimized User Experience: Ensure your ads and landing pages are tailored for the device being used.
- Bid Adjustments: Increase or decrease bids based on device performance.
- Enhanced Engagement: Cater to the unique behaviors of users on different devices.
Best Practices for Device Targeting
- Analyze Device Performance: Review metrics like CTR, conversion rate, and cost per conversion by device.
- Optimize Landing Pages: Ensure mobile landing pages are fast-loading and user-friendly.
- Adjust Bids Accordingly: Allocate more budget to devices that perform better.
- Use Responsive Ads: Ensure your ads display correctly across all device types.
Audience Targeting
Audience targeting allows you to segment users based on various attributes, behaviors, and interests. This method enhances the relevance of your ads by reaching users who are more likely to engage with your offerings.
In-Market Audiences
In-Market Audiences are users actively researching or considering purchasing a product or service similar to what you offer. These users are deemed ready to make a purchase, making them highly valuable for advertisers.
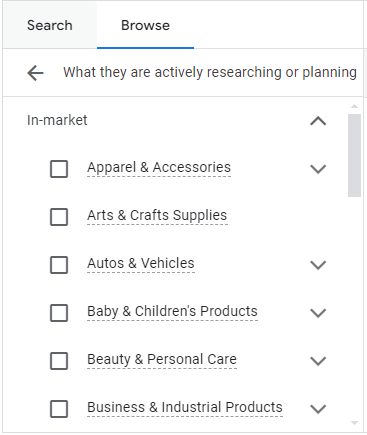
Examples of In-Market Audiences
- Automotive: Users searching for cars, car rentals, or auto insurance.
- Travel: Users planning trips, booking flights, or seeking travel deals.
- Home Improvement: Users looking for remodeling services, appliances, or furniture.
Benefits of In-Market Targeting
- High Intent: Users are closer to making a purchase decision.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Increased likelihood of conversions due to purchase intent.
- Efficient Budget Allocation: Focus spending on users most likely to convert.
Best Practices for In-Market Targeting
- Combine with Remarketing: Re-engage users who have previously interacted with your site.
- Use in Conjunction with Other Audiences: Layer in-market audiences with demographic or behavioral segments for more precise targeting.
- Regularly Update Audiences: Ensure your in-market segments are up-to-date with current user behaviors and trends.
Affinity Audiences
Affinity Audiences are users who have demonstrated a strong interest or passion for a particular topic, hobby, or lifestyle. These audiences are ideal for building brand awareness and reaching a broader audience.
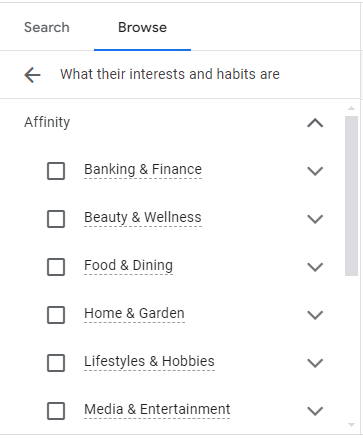
Examples of Affinity Audiences
- Fitness Enthusiasts: Users interested in health, exercise, and wellness.
- Tech Savvy: Users passionate about technology, gadgets, and innovations.
- Foodies: Users who enjoy cooking, dining out, and exploring cuisines.
Benefits of Affinity Targeting
- Broad Reach: Ideal for brand awareness campaigns targeting large groups.
- Engagement: Users are likely to engage with content related to their interests.
- Long-Term Relationships: Build a loyal audience over time.
Best Practices for Affinity Targeting
- Align Interests with Offerings: Ensure the affinity audience’s interests align with your product or service.
- Customize Ad Creative: Use visuals and messaging that resonate with the audience’s interests.
- Monitor Performance: Track engagement metrics to assess the effectiveness of affinity targeting.
Remarketing
Remarketing allows you to re-engage users who have previously visited your website or interacted with your brand. It’s a powerful way to remind potential customers of your offerings and encourage them to complete a purchase or take another desired action.
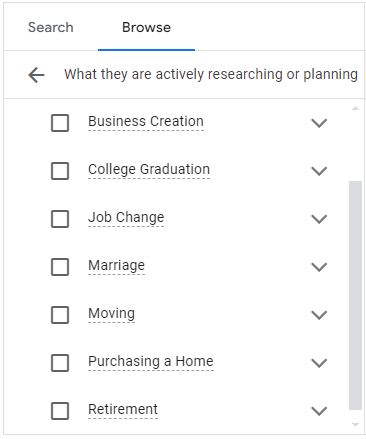
Types of Remarketing
Standard Remarketing:
- Definition: Shows ads to previous visitors as they browse other sites on the Google Display Network.
- Use Case: Remind users of products they viewed but didn’t purchase.
Dynamic Remarketing:
- Definition: Shows personalized ads featuring the specific products or services users viewed on your site.
- Use Case: Encourage users to return and complete their purchase with tailored product ads.
Remarketing Lists for Search Ads (RLSA):
- Definition: Customizes search ads for users who have previously visited your site when they perform subsequent searches.
- Use Case: Target users with specific search queries based on their past interactions with your site.
Benefits of Remarketing
- Increased Conversion Rates: Re-engage interested users who are more likely to convert.
- Cost-Effective: Lower cost per conversion compared to cold audiences.
- Personalization: Deliver highly relevant ads based on user behavior.
Best Practices for Remarketing
- Segment Your Audiences: Create distinct remarketing lists based on user behavior (e.g., cart abandoners, past purchasers).
- Frequency Capping: Limit the number of times a user sees your ad to avoid ad fatigue.
- Exclude Converted Users: Prevent showing ads to users who have already converted to save budget.
- Use Compelling Creative: Design eye-catching ads with clear calls-to-action to entice users back.
Custom Audiences
Custom Audiences enable you to define and target users based on specific criteria tailored to your business needs. This flexibility allows for highly granular targeting, ensuring your ads reach precisely the right people.
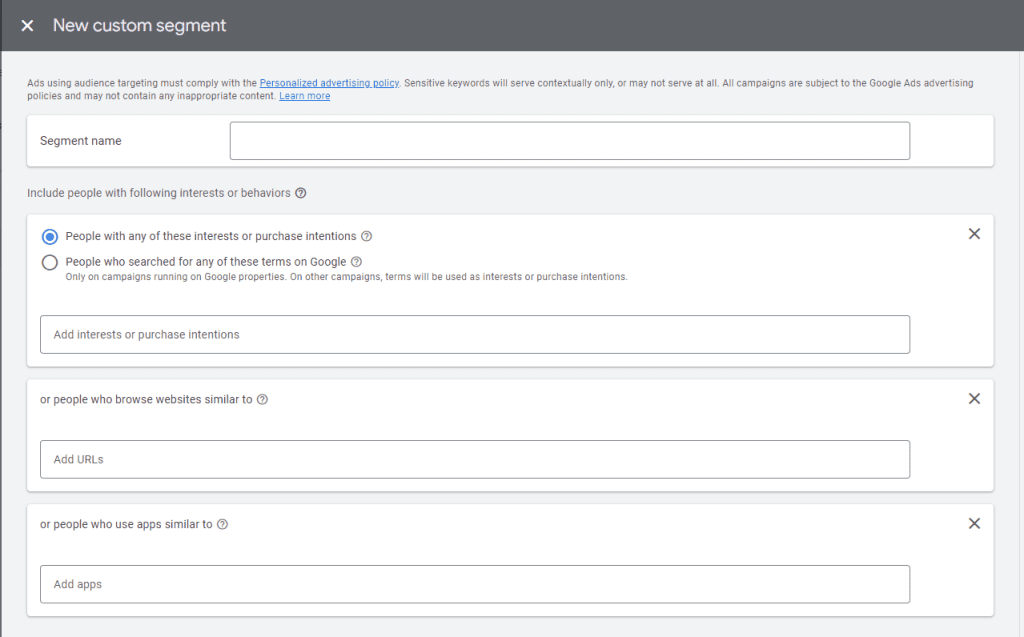
Types of Custom Audiences
Custom Intent Audiences:
- Definition: Users who are actively researching or have shown intent related to your products or services.
- Use Case: Target users searching for specific solutions you offer.
Custom Affinity Audiences:
- Definition: Users with a unique combination of interests tailored to your brand.
- Use Case: Reach niche segments with specific interests relevant to your offerings.
Customer Match:
- Definition: Upload your own customer lists (emails, phone numbers) to target or exclude existing customers.
- Use Case: Re-engage loyal customers or prevent existing customers from seeing acquisition ads.
Benefits of Custom Audience Targeting
- Highly Relevant: Tailor audiences based on unique business criteria.
- Enhanced Personalization: Deliver personalized ad experiences to specific user segments.
- Improved ROI: Focus on audiences with the highest potential for conversion.
Best Practices for Custom Audience Targeting
- Ensure Data Accuracy: Use clean and updated customer data to create effective custom audiences.
- Respect Privacy Regulations: Comply with data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA when using customer data.
- Combine with Other Targeting Methods: Layer custom audiences with demographic or behavioral targeting for enhanced precision.
- Regularly Refresh Audiences: Update custom audience lists to reflect current customer data and behaviors.
Combined Segments
Combined Segments allow you to create more refined audience groups by combining multiple audience criteria. This method uses logical operators like AND and OR to intersect or union different audience segments, enabling highly specific targeting.
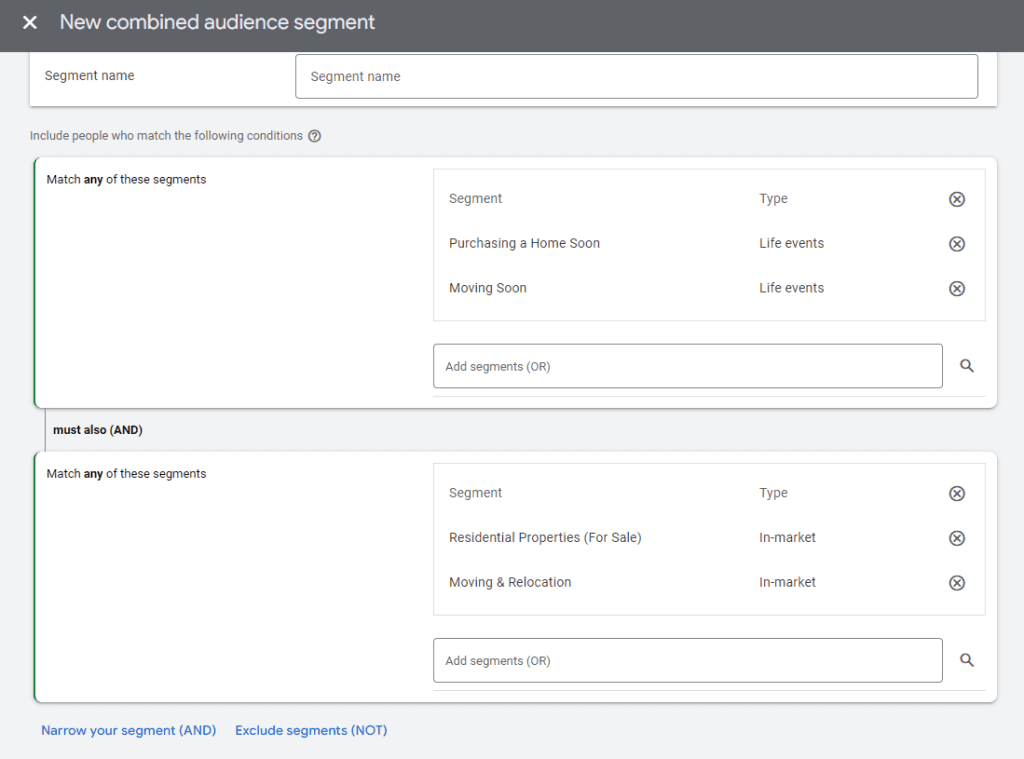
Examples of Combined Segments
- AND Combination: Users who are both “In-Market for Travel” AND “Have shown interest in Luxury Resorts.”
- OR Combination: Users who are either “Fitness Enthusiasts” OR “Health Conscious.”
Benefits of Combined Segments
- Precision Targeting: Reach users who meet multiple criteria, enhancing relevance.
- Flexibility: Customize audience definitions to align with complex marketing strategies.
- Improved Campaign Performance: Higher engagement and conversion rates due to highly relevant audience targeting.
Best Practices for Combined Segments
- Start Simple: Begin with combining two audience criteria and expand as you gather more data.
- Test Different Combinations: Experiment with various audience combinations to identify what works best.
- Monitor Performance Metrics: Track the performance of combined segments to ensure they meet your campaign goals.
- Avoid Over-Complication: Ensure that combined segments don’t become too narrow, limiting your reach excessively.
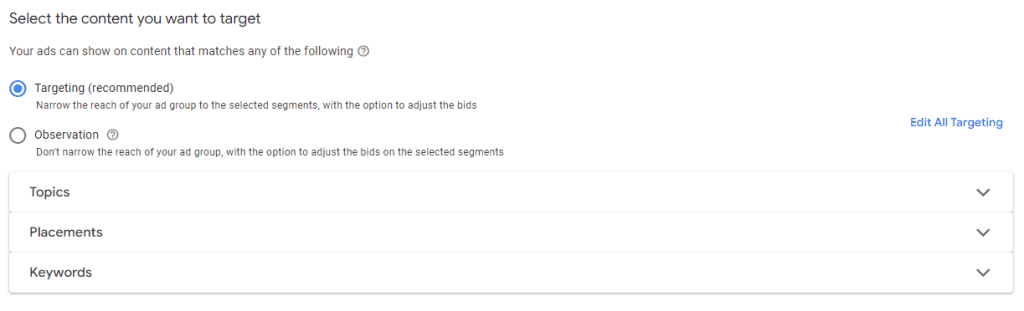
Display Targeting
Display targeting allows advertisers to reach users across the Google Display Network (GDN) through various targeting options based on content, audience, and placement. The Display Network comprises millions of websites, apps, and videos, providing extensive reach for your campaigns.
Contextual Targeting
Contextual Targeting focuses on the content of the webpage or platform where the ad will appear. This method ensures that your ads are relevant to the context of the content the user is engaging with.
Key Components of Contextual Targeting
Topics:
- Definition: Categorize content based on specific subjects or themes.
- Example: Choosing topics like “Gardening,” “Technology,” or “Health” to display ads on related content.
Keywords:
- Definition: Select keywords that align with the content of the webpages where ads will appear.
- Example: Using keywords like “fitness equipment” to display ads on pages discussing exercise gear.
Placements:
- Definition: Choose specific websites, apps, or YouTube channels where you want your ads to appear.
- Example: Targeting ads to appear on “TechCrunch” or a popular cooking app.
Benefits of Contextual Targeting
- High Relevance: Ads appear alongside related content, increasing the likelihood of engagement.
- Brand Safety: Ensures ads are displayed in appropriate environments aligned with your brand values.
- Broader Reach: Access to a wide range of content categories and topics.
Best Practices for Contextual Targeting
- Select Relevant Topics and Keywords: Ensure that your chosen topics and keywords closely match your product or service.
- Monitor Ad Placements: Regularly review where your ads are appearing to maintain brand safety and relevance.
- Use Negative Keywords: Exclude irrelevant topics or keywords to refine targeting.
- Leverage Automated Targeting: Utilize Google’s machine learning to optimize contextual targeting based on performance data.
Topic Targeting
Topic Targeting is a subset of contextual targeting that allows advertisers to choose specific topics to display their ads alongside related content. It categorizes content into predefined topics, making it easier to align your ads with relevant subjects.
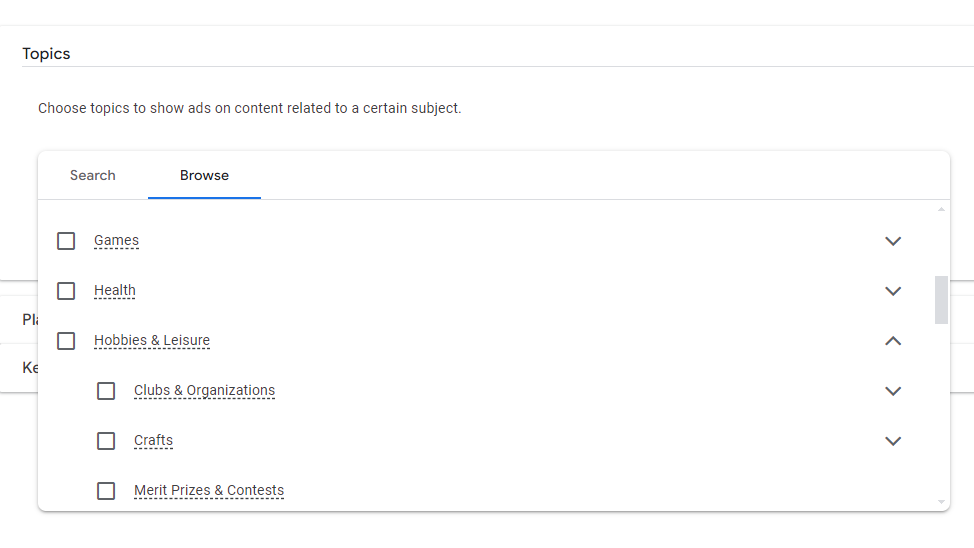
Examples of Topic Targeting
- Technology: Targeting content related to software, gadgets, and IT services.
- Health & Fitness: Displaying ads on pages about wellness, exercise routines, and nutrition.
- Finance: Placing ads on content discussing banking, investments, and financial planning.
Benefits of Topic Targeting
- Wide Reach: Access to a vast array of content topics, increasing ad exposure.
- Ease of Use: Simplifies the targeting process by categorizing content into manageable topics.
- Enhanced Relevance: Ensures ads are shown in contexts that resonate with your audience’s interests.
Best Practices for Topic Targeting
- Choose Relevant Topics: Select topics that closely align with your product or service to maximize relevance.
- Combine with Other Targeting Methods: Layer topic targeting with demographic or audience targeting for more precise reach.
- Regularly Update Topics: Adjust your topic selections based on campaign performance and changing market trends.
- Exclude Irrelevant Topics: Prevent ads from appearing alongside content that doesn’t align with your brand or offerings.
Placement Targeting
Placement Targeting allows advertisers to specify exact websites, apps, or YouTube channels where they want their ads to appear. This method provides granular control over ad placements, ensuring your ads are displayed in environments that best suit your campaign objectives.
Types of Placements
Websites:
- Definition: Choose specific websites within the GDN to display your ads.
- Example: Targeting your ads on “Forbes” or “National Geographic.”
Apps:
- Definition: Select particular mobile or desktop apps to show your ads.
- Example: Displaying ads within popular gaming or productivity apps.
YouTube Channels:
- Definition: Target ads on specific YouTube channels or videos.
- Example: Placing ads on a popular beauty vlog or a tech review channel.
Benefits of Placement Targeting
- High Control: Precisely choose where your ads appear, enhancing relevance and effectiveness.
- Brand Alignment: Ensure ads are displayed alongside content that aligns with your brand values and messaging.
- Performance Optimization: Focus on high-performing placements to maximize ROI.
Best Practices for Placement Targeting
- Research Placements Thoroughly: Analyze the content and audience of targeted placements to ensure alignment with your brand.
- Monitor Placement Performance: Regularly review metrics to identify and prioritize high-performing placements.
- Exclude Low-Performing Placements: Remove placements that do not contribute to your campaign goals.
- Use Managed Placements: Combine placement targeting with managed placements for better control and optimization.
Demographic Targeting
Demographic targeting allows advertisers to reach users based on specific demographic attributes such as age, gender, income, parental status, and more. This method enhances the relevance of your ads by aligning them with the characteristics of your ideal customers.
Age & Gender
Age and Gender targeting enables advertisers to display ads to users within specific age ranges and gender categories. This is particularly useful for products or services tailored to particular demographic groups.
Examples of Age & Gender Targeting
- Youth-Oriented Products: Targeting younger age groups (e.g., 18-24) for fashion or tech gadgets.
- Senior Services: Reaching older age groups (e.g., 65+) for retirement planning or healthcare services.
- Gender-Specific Products: Displaying ads for men’s grooming products or women’s fitness apparel.
Benefits of Age & Gender Targeting
- Enhanced Relevance: Ensure ads resonate with the specific needs and preferences of different demographic groups.
- Improved Conversion Rates: Tailored messaging can lead to higher engagement and conversions.
- Budget Efficiency: Allocate budgets towards demographics that are more likely to convert.
Best Practices for Age & Gender Targeting
- Analyze Demographic Performance: Use platform analytics to identify which age and gender groups perform best.
- Customize Ad Creative: Develop different ad creatives for different demographic segments to increase relevance.
- Combine with Other Targeting Options: Layer age and gender targeting with interests or behaviors for more precise reach.
- Test and Iterate: Continuously test different demographic segments to optimize performance.
Household Income
Household Income targeting allows advertisers to reach users based on their estimated household income levels. This feature is particularly useful for premium products or services that cater to specific income brackets.
Examples of Household Income Targeting
- Luxury Goods: Targeting higher-income brackets for high-end fashion, automobiles, or electronics.
- Affordable Products: Reaching lower-income brackets for budget-friendly products or services.
- Financial Services: Offering financial planning or investment services to higher-income households.
Benefits of Household Income Targeting
- Precision: Aligns your advertising efforts with users who have the financial capacity to purchase your offerings.
- Enhanced ROI: Improves the efficiency of your ad spend by focusing on income segments that are more likely to convert.
- Market Segmentation: Helps in understanding and targeting different segments of the market based on income levels.
Best Practices for Household Income Targeting
- Use Income Targeting Judiciously: Ensure that the income segments align with your product pricing and value proposition.
- Combine with Location Targeting: Refine income targeting by combining it with geographic locations to account for regional income variations.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review the performance of different income segments and adjust targeting accordingly.
- Respect Privacy: Be mindful of privacy concerns and avoid making assumptions based solely on income targeting.
Parental Status
Parental Status targeting allows advertisers to reach users based on whether they have children, and in some cases, the age of their children. This is especially useful for products and services tailored to parents or families.
Examples of Parental Status Targeting
- Baby Products: Targeting parents with infants or toddlers for products like diapers, baby food, or strollers.
- Educational Services: Reaching parents of school-aged children for tutoring services or educational materials.
- Family Activities: Advertising family-friendly events, vacations, or entertainment options.
Benefits of Parental Status Targeting
- High Relevance: Directly reaches users who are likely to be interested in family-oriented products or services.
- Personalized Messaging: Tailor ad content to address the specific needs and concerns of parents.
- Improved Engagement: Ads that resonate with parental experiences can drive higher engagement and conversions.
Best Practices for Parental Status Targeting
- Segment Based on Children’s Age: Customize ads based on whether users have infants, toddlers, or older children.
- Create Relevant Ad Content: Develop messaging that speaks directly to parents’ challenges and needs.
- Combine with Other Targeting Options: Enhance parental targeting by layering it with interests related to parenting, education, or family activities.
- Monitor and Optimize: Track the performance of parental segments and adjust targeting strategies to maximize effectiveness.
Advanced Targeting Options
For advertisers seeking more granular control over their PPC campaigns, advanced targeting options offer powerful tools to refine audience reach and enhance campaign performance.
Ad Scheduling (Dayparting)
Ad Scheduling, also known as Dayparting, allows advertisers to control the times and days their ads are displayed. This ensures that ads are shown when users are most likely to engage and convert.
Benefits of Ad Scheduling
- Increased Relevance: Display ads during peak times when your target audience is most active.
- Budget Efficiency: Allocate budgets to times with higher conversion rates, reducing wasted spend.
- Enhanced Performance: Improve overall campaign performance by targeting high-performing time slots.
Best Practices for Ad Scheduling
- Analyze Performance Data: Use historical campaign data to identify peak performance times.
- Adjust Bids by Time: Increase bids during high-conversion periods and decrease them during low-performing times.
- Consider Time Zones: Account for different time zones if targeting a global or multi-regional audience.
- Test Different Schedules: Experiment with various scheduling options to determine the most effective times for your ads.
Language Targeting
Language Targeting enables advertisers to display ads to users based on their preferred language settings. This is crucial for reaching multilingual audiences and ensuring ads are communicated effectively.
Benefits of Language Targeting
- Enhanced Communication: Deliver ads in the user’s preferred language, improving understanding and engagement.
- Cultural Relevance: Tailor ad content to align with cultural nuances and preferences.
- Expanded Reach: Access diverse markets by targeting multiple language segments.
Best Practices for Language Targeting
- Translate Ad Copy Accurately: Ensure high-quality translations to maintain message clarity and professionalism.
- Localize Content: Adapt not just the language but also the cultural references and imagery in your ads.
- Segment by Language: Create separate campaigns or ad groups for different languages to better manage targeting and performance.
- Monitor Performance: Track metrics by language segment to identify which languages yield the best results and adjust strategies accordingly.
Device-Specific Targeting
Device-Specific Targeting allows advertisers to customize their ad strategies based on the type of device users are using, such as desktops, tablets, or smartphones.
Benefits of Device-Specific Targeting
- Optimized User Experience: Ensure that ads and landing pages are tailored to the device’s screen size and capabilities.
- Improved Engagement: Users are more likely to engage with ads that are designed for their specific device.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Customized ads can lead to smoother user journeys and increased conversions.
Best Practices for Device-Specific Targeting
- Optimize Ad Formats: Use responsive ad formats that adapt to different screen sizes and devices.
- Tailor Messaging: Adjust ad copy and calls-to-action based on device usage patterns (e.g., mobile-friendly CTAs).
- Analyze Device Performance: Regularly review performance metrics by device to identify trends and optimize accordingly.
- Ensure Fast Load Times: Optimize landing pages for speed on all devices, particularly mobile, to prevent user drop-off.
Optimizing Your PPC Targeting Strategy
To achieve the best results from your PPC campaigns, it’s essential to continuously optimize your targeting strategy. Here are key areas to focus on:
A/B Testing
A/B Testing involves creating multiple versions of your ads or targeting settings to determine which performs better. This method helps identify the most effective strategies and optimizes campaign performance.
How to Conduct A/B Testing
- Define Your Variables: Decide what you want to test, such as ad copy, targeting options, or bid strategies.
- Create Variations: Develop different versions based on the variables you’re testing.
- Run the Tests Simultaneously: Ensure that the different versions run under similar conditions to obtain accurate results.
- Analyze Results: Compare the performance metrics to determine which variation is more effective.
- Implement Changes: Apply the winning variation to your campaign and continue testing other variables.
Best Practices for A/B Testing
- Test One Variable at a Time: Isolate each variable to accurately assess its impact.
- Use Sufficient Sample Sizes: Ensure your tests run long enough and gather enough data to produce statistically significant results.
- Track Relevant Metrics: Focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) like CTR, conversion rate, and ROI.
- Iterate Continuously: Use insights from A/B tests to make incremental improvements to your campaigns.
Utilizing Analytics
Analytics provide critical insights into the performance of your PPC campaigns, helping you make data-driven decisions to optimize targeting and improve results.
Key Analytics Tools
Google Analytics:
- Features: Tracks website traffic, user behavior, conversion paths, and more.
- Use Case: Analyze how PPC traffic interacts with your site and identify areas for improvement.
Google Ads Dashboard:
- Features: Offers detailed metrics on ad performance, including impressions, clicks, conversions, and cost.
- Use Case: Monitor and adjust campaign settings based on real-time performance data.
Third-Party Tools:
- Examples: SEMrush, Ahrefs, HubSpot.
- Use Case: Gain additional insights into keyword performance, competitor strategies, and overall market trends.
Best Practices for Utilizing Analytics
- Set Clear Goals: Define what success looks like for your campaigns, such as specific conversion rates or ROI targets.
- Monitor Key Metrics: Focus on essential KPIs that align with your campaign goals.
- Segment Data: Analyze performance by different segments (e.g., demographics, devices) to identify trends and opportunities.
- Use Attribution Models: Understand the customer journey and assign credit to different touchpoints to optimize your strategy.
Budget Allocation
Budget allocation is the process of distributing your advertising budget across different targeting options to maximize ROI. Effective budget management ensures that funds are spent on the most impactful areas.
Strategies for Budget Allocation
Performance-Based Allocation:
- Allocate more budget to high-performing targeting segments.
- Reduce or eliminate spending on underperforming segments.
Priority-Based Allocation:
- Focus on key audience segments that align closely with your business objectives.
- Reserve budget for strategic campaigns like brand awareness or product launches.
Seasonal Allocation:
- Adjust budgets based on seasonal trends and peak periods relevant to your business.
- Increase spending during high-demand times and scale back during off-peak periods.
Best Practices for Budget Allocation
- Regularly Review Performance: Continuously assess the performance of different targeting options and adjust budgets accordingly.
- Diversify Spending: Avoid putting all your budget into one targeting method; diversify to mitigate risks and capture multiple audience segments.
- Set Clear Budget Limits: Define maximum spending limits for each campaign to maintain financial control.
- Use Automated Bidding Strategies: Leverage platform features like Target CPA or ROAS to optimize budget allocation automatically based on performance goals.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even with the best strategies, certain pitfalls can hinder the success of your PPC campaigns. Here are some common mistakes and how to avoid them:
1. Neglecting Negative Keywords
Mistake: Failing to use negative keywords can lead to ads being displayed for irrelevant searches, wasting budget.
Solution:
- Regularly Update Negative Keyword Lists: Continuously add irrelevant keywords to prevent ads from showing in undesired contexts.
- Analyze Search Terms: Review search term reports to identify and exclude irrelevant queries.
2. Overlooking Ad Copy Relevance
Mistake: Using generic ad copy that doesn’t resonate with the target audience can result in low engagement and CTR.
Solution:
- Tailor Ad Copy: Customize ad messaging to align with the interests and needs of your target audience segments.
- Highlight Unique Selling Points (USPs): Clearly communicate what sets your product or service apart from competitors.
- Include Strong Calls-to-Action (CTAs): Encourage users to take specific actions, such as “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” or “Sign Up Today.”
3. Ignoring Mobile Optimization
Mistake: Neglecting mobile users can result in poor user experience and lost conversions, especially given the increasing use of mobile devices.
Solution:
- Optimize Landing Pages for Mobile: Ensure your landing pages are responsive, fast-loading, and user-friendly on all devices.
- Use Mobile-Specific Ad Formats: Leverage ad formats designed for mobile, such as responsive search ads and mobile-friendly display ads.
- Monitor Mobile Performance: Track and optimize metrics specifically for mobile traffic to identify and address any issues.
4. Setting Unrealistic Budgets
Mistake: Allocating insufficient budgets can limit your campaign’s reach and effectiveness, while overspending can deplete resources without guaranteed returns.
Solution:
- Start with a Realistic Budget: Base your budget on historical data, industry benchmarks, and campaign goals.
- Allocate Based on Performance: Adjust budgets dynamically based on the performance of different targeting segments.
- Implement Budget Caps: Set daily or monthly budget limits to maintain control over spending.
5. Failing to Test and Iterate
Mistake: Sticking with the same targeting options and ad creatives without testing can prevent you from discovering more effective strategies.
Solution:
- Conduct Regular A/B Tests: Continuously test different ad copies, targeting options, and bidding strategies to identify what works best.
- Iterate Based on Data: Use insights from tests and analytics to refine and optimize your campaigns.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of new features and best practices to ensure your campaigns remain competitive and effective.
Tools and Resources
Leveraging the right tools can significantly enhance your PPC targeting strategy by providing insights, automating tasks, and optimizing performance.
1. Google Ads
Features:
- Comprehensive PPC management platform with extensive targeting options.
- Integration with Google Analytics for detailed performance tracking.
- Automated bidding strategies to optimize budget allocation.
Use Case: Managing and optimizing search, display, and video campaigns across Google’s vast network.
2. Microsoft Advertising (Bing Ads)
Features:
- Access to Bing’s search network, including Yahoo and AOL.
- Similar targeting options to Google Ads with some unique features.
- Potential for lower competition and CPC compared to Google Ads.
Use Case: Reaching a different segment of search users, particularly in regions where Bing has a significant market share.
3. SEMrush
Features:
- Comprehensive keyword research and competitive analysis tools.
- PPC audit tools to identify and fix campaign issues.
- Ad builder and tracking features for managing ad copy.
Use Case: Conducting in-depth keyword research, competitor analysis, and optimizing PPC campaigns based on comprehensive data.
4. Ahrefs
Features:
- Robust keyword research and backlink analysis tools.
- Competitor analysis to identify successful PPC strategies.
- Site audit features to improve website performance for PPC campaigns.
Use Case: Enhancing keyword strategies and understanding competitor PPC tactics to inform your own campaigns.
5. Google Analytics
Features:
- Detailed insights into website traffic, user behavior, and conversion paths.
- Integration with Google Ads for seamless performance tracking.
- Custom reporting and dashboard capabilities.
Use Case: Analyzing the performance of PPC campaigns, understanding user interactions, and making data-driven optimization decisions.
6. Optmyzr
Features:
- PPC management and automation tools to streamline campaign optimization.
- One-click optimizations and automated reporting.
- Advanced bid management and keyword research tools.
Use Case: Automating routine PPC tasks, optimizing bids, and generating insightful reports to improve campaign performance.
7. SpyFu
Features:
- Competitor keyword research and analysis tools.
- Historical data on competitor PPC strategies.
- Domain comparison features to identify strengths and weaknesses.
Use Case: Gaining insights into competitor PPC strategies, identifying profitable keywords, and discovering new targeting opportunities.
Conclusion
Mastering PPC ad targeting is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a deep understanding of various targeting options and how they interplay to reach your ideal audience effectively. From leveraging search targeting with precise keywords and dynamic search ads to harnessing the power of audience targeting and display network strategies, each method offers unique advantages that can drive your campaign’s success.
Key Takeaways:
- Diverse Targeting Options: Utilize a combination of search, audience, display, and demographic targeting to maximize reach and relevance.
- Continuous Optimization: Regularly analyze performance data, conduct A/B tests, and refine your strategies to stay ahead.
- Leverage Advanced Tools: Use PPC management tools and analytics platforms to gain deeper insights and streamline campaign management.
- Avoid Common Pitfalls: Be mindful of negative keywords, mobile optimization, budget management, and the importance of testing and iteration.
By implementing these comprehensive targeting strategies and continuously optimizing your approach, you can ensure that your PPC campaigns not only reach the right audience but also drive meaningful engagement and conversions. Embrace the complexity of PPC targeting, and watch as your campaigns achieve new heights of effectiveness and ROI.