Electrical Outlets or Receptacles
14 Different Types of Electrical Outlets for Homes and Offices
Electrical outlets, also known as receptacles, are essential for powering our devices and appliances. They come in different shapes, sizes, and functionalities to meet specific needs. This guide simplifies the types of outlets you might encounter at home or in the office and explains what each is best used for.
Why Do We Need Electrical Outlets?
Electrical outlets provide access to the power distributed throughout your home from the utility company. They allow you to plug in devices, flip a switch, and get electricity where you need it.

How Do Electrical Outlets Work?
An electrical outlet has two key components:
- Hot Slot: Supplies the electric current.
- Neutral Slot: Completes the circuit and sends current back.
- Grounding Slot (for three-pronged outlets): Provides safety by directing excess current away.
14 Types of Electrical Outlets
1. 15A, 120V Outlet

- Description: The most common outlet in homes for small to medium devices.
- Usage: Chargers, laptops, and desktops.
- Wiring: Uses 14-gauge wires and is protected by a 15A breaker.
2. 20A, 120V Outlet

- Description: Designed for slightly more powerful appliances like microwaves.
- Usage: Kitchen appliances and heaters.
- Wiring: Uses thicker 12- or 10-gauge wires with a 20A breaker.
3. 20A, 250V Outlet
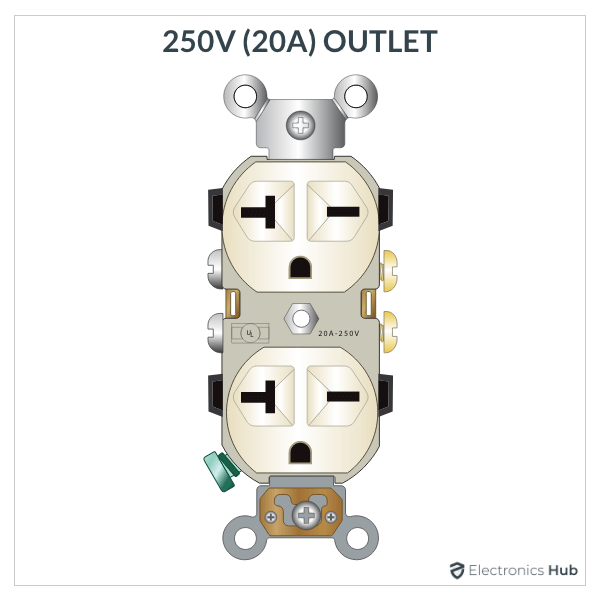
- Description: Provides higher voltage and is used for large appliances.
- Usage: Electric stoves and large ovens.
4. 30A, 250V Outlet

- Description: Suitable for heavy-duty equipment.
- Usage: Air conditioners and compressors.
5. 30A, 125/250V Outlet
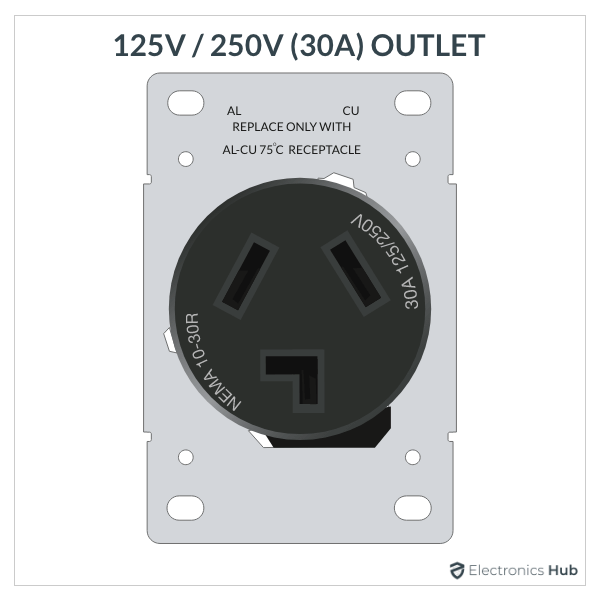
- Description: A heavy-duty outlet for high-power appliances.
- Usage: Clothes dryers and industrial machines.
6. 50A, 125/250V Outlet
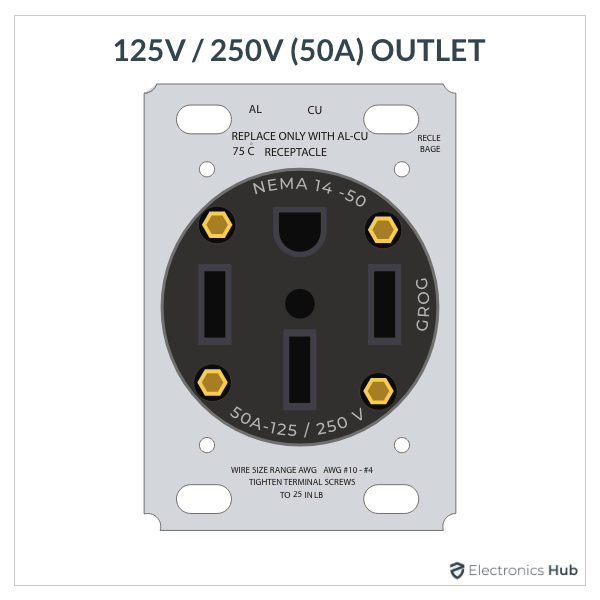

- Description: Industrial-grade outlet, often found in RVs and workshops.
- Usage: Welding machines and RV hookups.
7. GFCI Outlet (Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter)
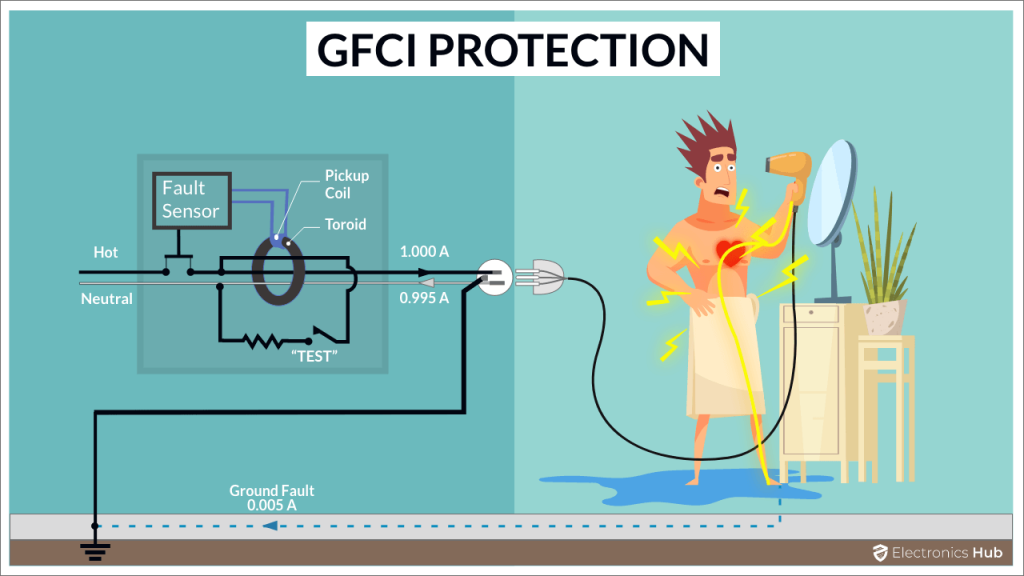
- Description: Detects electrical leaks and cuts off power to prevent shocks.
- Usage: Bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor areas.
- Feature: Has “TEST” and “RESET” buttons for easy control.
8. AFCI Outlet (Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupter)

- Description: Prevents fires caused by sparks or loose wires.
- Usage: Bedrooms, living rooms, and laundry areas.
9. Tamper-Resistant Outlet

- Description: Safe outlet with a built-in barrier to prevent objects other than plugs from entering.
- Usage: Homes with children.
10. Weather-Resistant Outlet

- Description: Designed to withstand rain, snow, and extreme temperatures.
- Usage: Outdoor spaces and garages.
11. Rotating Outlet

- Description: Rotates 360 degrees to accommodate bulky plugs without blocking other outlets.
- Usage: Areas with multiple devices.
12. Ungrounded Outlet

- Description: Two-slot outlet without a grounding pin. Not recommended for modern homes.
- Usage: Older homes (should be upgraded for safety).
13. USB Outlets

- Description: Includes USB ports for charging devices without an adapter.
- Usage: Phones, tablets, and power banks.
14. Smart Outlets

- Description: Can be controlled via apps or voice assistants like Alexa. Helps monitor power usage.
- Usage: Smart homes for automation and energy efficiency.
Final Thoughts
Each type of outlet serves a specific purpose. Whether you need safety features, higher power, or smart functionality, there’s an outlet that fits your needs. Always consult an electrician for proper installation and upgrades.








