Female Mammary Gland
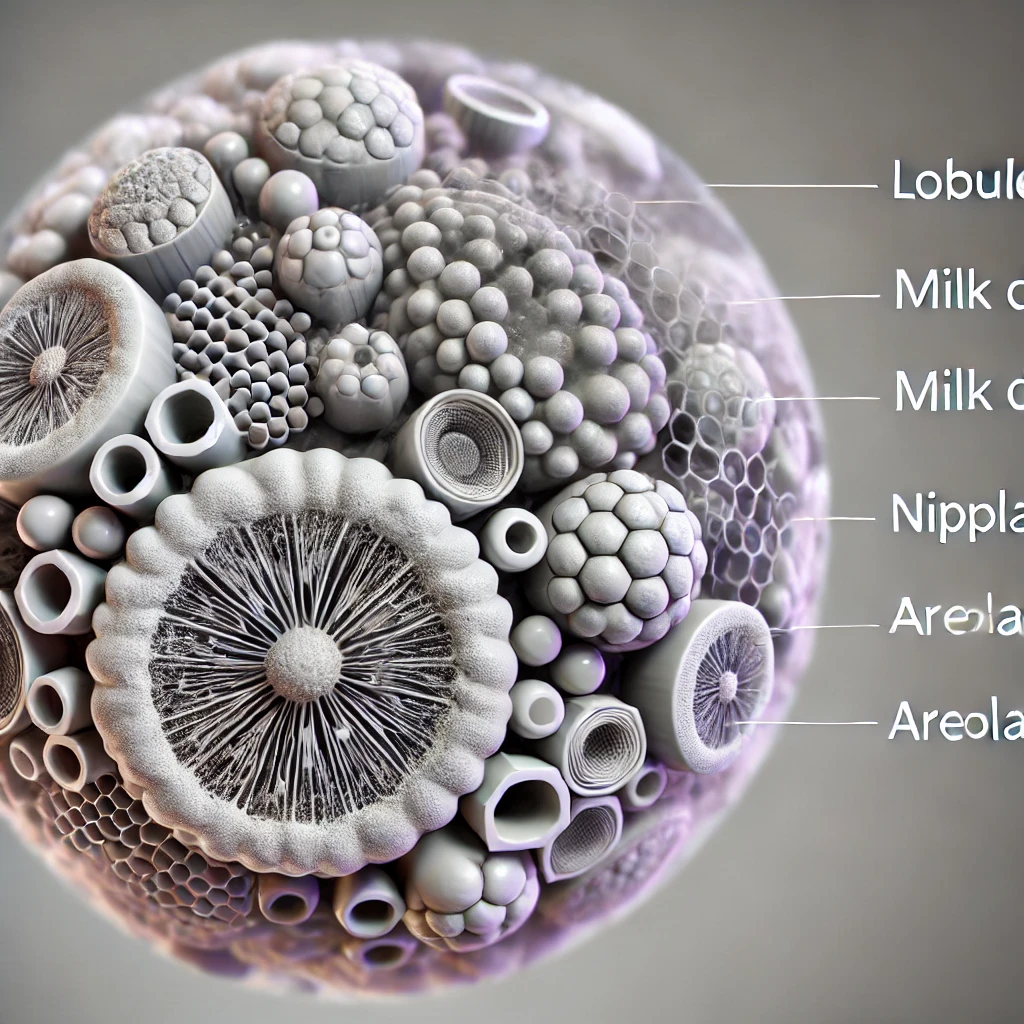
The female mammary glands are specialized organs located in the breasts that produce and secrete milk to nourish newborns. Below is a detailed explanation of the anatomy, physiology, and functions of the mammary glands.
Anatomy of the Mammary Glands
1. Location and Structure
- Location: The mammary glands are located in the breasts, which are situated on the chest wall over the pectoral muscles.
- Structure: Each mammary gland is composed of 15-20 lobes arranged in a radial pattern. These lobes are separated by adipose (fat) tissue and connective tissue.
2. Lobes and Lobules
- Lobes: Each lobe is a distinct section of the mammary gland.
- Lobules: Each lobe is further divided into smaller units called lobules. Lobules contain clusters of alveoli, the milk-producing glands.
3. Alveoli
- Structure: Alveoli are small, sac-like structures lined with milk-secreting epithelial cells and surrounded by myoepithelial cells.
- Function: The epithelial cells in the alveoli produce milk, while the myoepithelial cells contract to expel the milk into the ducts.
4. Duct System
- Lactiferous Ducts: Milk produced in the alveoli is transported through a network of ducts. The smaller ducts merge to form larger lactiferous ducts.
- Lactiferous Sinus: Near the nipple, each lactiferous duct expands to form a lactiferous sinus, which serves as a reservoir for milk.
- Nipple: The ducts open at the nipple, through which milk is released during breastfeeding.
5. Nipple and Areola
- Nipple: The nipple is a protruding structure on the breast through which milk is delivered to the baby.
- Areola: The areola is the pigmented area surrounding the nipple. It contains sebaceous glands (Montgomery glands) that lubricate the nipple during breastfeeding.
Physiology of the Mammary Glands
1. Hormonal Regulation
- Estrogen: Stimulates the growth and branching of the ductal system during puberty and the menstrual cycle.
- Progesterone: Promotes the development of the alveoli and lobules, especially during pregnancy.
- Prolactin: Secreted by the pituitary gland, prolactin is essential for milk production. Its levels rise significantly during pregnancy and after childbirth.
- Oxytocin: Also secreted by the pituitary gland, oxytocin causes the myoepithelial cells around the alveoli to contract, resulting in milk ejection (let-down reflex).
2. Lactation
- Milk Production: Initiated by prolactin, milk production begins in the alveoli. Prolactin levels are highest during and after childbirth to stimulate milk synthesis.
- Milk Ejection: Triggered by the baby’s suckling, which stimulates the release of oxytocin. Oxytocin causes the myoepithelial cells to contract and expel milk through the ducts and out of the nipple.
Functions of the Mammary Glands
1. Nourishment of Newborns
- Colostrum: The first milk produced after childbirth, colostrum, is rich in antibodies and nutrients to support the newborn’s immune system and development.
- Mature Milk: As lactation continues, mature milk is produced, providing balanced nutrition, including proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
2. Immunological Protection
- Antibodies: Breast milk contains immunoglobulins (IgA) that help protect the baby from infections.
- Lactoferrin: A protein that inhibits the growth of iron-dependent bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract of the newborn.
- Lysozyme: An enzyme that protects against bacterial infections.
3. Bonding and Psychological Benefits
- Mother-Infant Bonding: Breastfeeding promotes a strong emotional bond between mother and infant through close physical contact and interaction.
- Psychological Benefits: Both the mother and baby experience psychological benefits, including reduced stress and enhanced emotional well-being.
Developmental Changes
1. Puberty
- Hormonal Influence: Increased levels of estrogen and progesterone during puberty lead to the development of the ductal and alveolar systems, resulting in breast growth and maturation.
2. Pregnancy and Lactation
- Breast Changes: During pregnancy, the breasts undergo further development and enlargement in preparation for lactation, influenced by high levels of estrogen, progesterone, and prolactin.
- Lactation: After childbirth, the drop in estrogen and progesterone levels allows prolactin to stimulate milk production, while oxytocin facilitates milk ejection.
3. Post-Lactation
- Involution: After breastfeeding ends, the mammary glands undergo involution, where the alveolar structures regress and the breasts return to their pre-pregnancy state.
Clinical Aspects
1. Mastitis
- Definition: Inflammation of the breast tissue, often caused by bacterial infection.
- Symptoms: Redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes fever.
- Treatment: Antibiotics, continued breastfeeding or pumping, and pain relief measures.
2. Breast Cancer
- Risk Factors: Include genetics, hormonal factors, age, and lifestyle.
- Screening: Regular mammograms and self-examinations are important for early detection.
- Treatment: Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy.
3. Galactorrhea
- Definition: The production of breast milk in women who are not breastfeeding, often due to hormonal imbalances.
- Causes: Can include pituitary tumors, certain medications, and thyroid disorders.
- Treatment: Addressing the underlying cause, such as adjusting medication or treating hormonal imbalances.
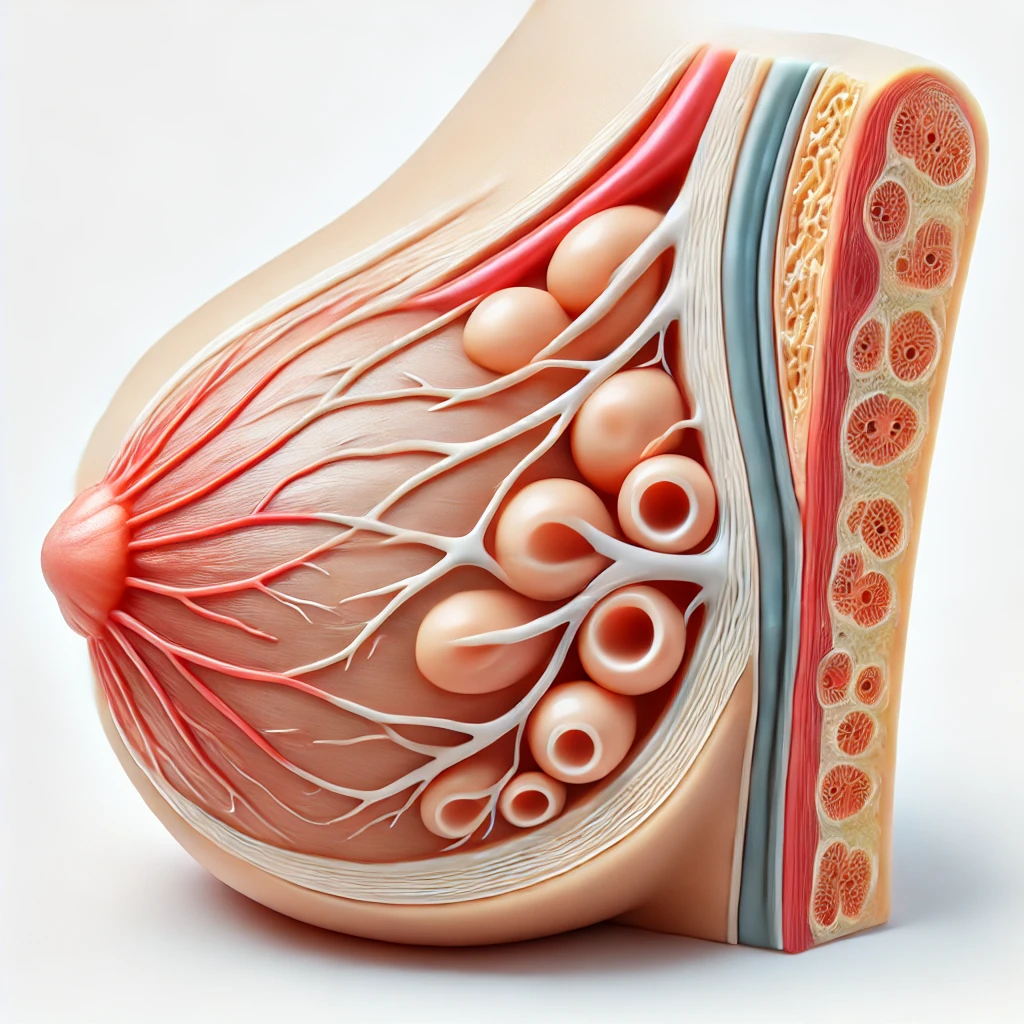
Anatomy of the Mammary Glands
Q: Where are the mammary glands located?
- A: In the breasts on the chest wall over the pectoral muscles.
Q: How many lobes are in each mammary gland?
- A: 15-20 lobes.
Q: What separates the lobes in the mammary glands?
- A: Adipose (fat) tissue and connective tissue.
Q: What are lobules in the mammary glands?
- A: Smaller units within each lobe that contain clusters of alveoli.
Q: What are alveoli in the context of the mammary glands?
- A: Small, sac-like structures that produce milk.
Q: What cells line the alveoli?
- A: Milk-secreting epithelial cells.
Q: What is the role of myoepithelial cells in the mammary glands?
- A: To contract and expel milk into the ducts.
Q: What is the function of lactiferous ducts?
- A: To transport milk from the alveoli to the nipple.
Q: What is the lactiferous sinus?
- A: An expanded portion of the lactiferous duct that serves as a reservoir for milk.
Q: Where do the lactiferous ducts open?
- A: At the nipple.
Q: What is the nipple?
- A: A protruding structure through which milk is delivered to the baby.
Q: What is the areola?
- A: The pigmented area surrounding the nipple.
Q: What are Montgomery glands?
- A: Sebaceous glands in the areola that lubricate the nipple.
Q: What type of tissue supports the structure of the mammary glands?
- A: Connective tissue.
Q: How do the mammary glands change during pregnancy?
- A: They enlarge and develop further to prepare for lactation.
Physiology of the Mammary Glands
Q: Which hormone stimulates milk production?
- A: Prolactin.
Q: Which hormone stimulates milk ejection?
- A: Oxytocin.
Q: What triggers the release of oxytocin?
- A: The baby’s suckling.
Q: What effect does estrogen have on the mammary glands?
- A: It stimulates the growth and branching of the ductal system.
Q: What role does progesterone play in the mammary glands?
- A: It promotes the development of the alveoli and lobules.
Q: What is the let-down reflex?
- A: The release of milk from the mammary glands in response to oxytocin.
Q: What is colostrum?
- A: The first milk produced after childbirth, rich in antibodies and nutrients.
Q: How does mature milk differ from colostrum?
- A: Mature milk contains a balanced mix of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
Q: What are the benefits of breastfeeding for the baby?
- A: Provides essential nutrients and antibodies, promotes growth and development, and protects against infections.
Q: What are the benefits of breastfeeding for the mother?
- A: Helps the uterus return to its pre-pregnancy size, reduces the risk of breast and ovarian cancers, and promotes bonding with the baby.
Developmental Changes
Q: What changes occur in the mammary glands during puberty?
- A: Increased levels of estrogen and progesterone lead to the development of the ductal and alveolar systems.
Q: What happens to the mammary glands during pregnancy?
- A: They undergo further development and enlargement in preparation for lactation.
Q: What is the process of involution in the mammary glands?
- A: The regression of the alveolar structures and return of the breasts to their pre-pregnancy state after breastfeeding ends.
Q: What hormonal changes occur during pregnancy to prepare the mammary glands for lactation?
- A: High levels of estrogen, progesterone, and prolactin stimulate the development of the mammary glands.
Q: How does prolactin influence milk production postpartum?
- A: Prolactin levels rise significantly after childbirth, stimulating milk synthesis.
Lactation
Q: What is the primary component of colostrum?
- A: Antibodies, particularly immunoglobulin A (IgA).
Q: How long is colostrum typically produced after childbirth?
- A: For the first few days postpartum.
Q: What changes occur in milk composition during lactation?
- A: Milk composition changes to meet the nutritional needs of the growing infant.
Q: What triggers the transition from colostrum to mature milk?
- A: Hormonal changes and continued breastfeeding.
Q: How does the frequency of breastfeeding affect milk production?
- A: Increased frequency of breastfeeding stimulates more milk production through a demand-supply mechanism.
Clinical Aspects
Q: What is mastitis?
- A: Inflammation of the breast tissue, often caused by bacterial infection.
Q: What are the symptoms of mastitis?
- A: Redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes fever.
Q: How is mastitis treated?
- A: With antibiotics, continued breastfeeding or pumping, and pain relief measures.
Q: What is galactorrhea?
- A: The production of breast milk in women who are not breastfeeding.
Q: What are common causes of galactorrhea?
- A: Hormonal imbalances, pituitary tumors, certain medications, and thyroid disorders.
Q: What is a mammogram?
- A: An X-ray imaging technique used to screen for breast cancer.
Q: What are common risk factors for breast cancer?
- A: Genetics, hormonal factors, age, lifestyle, and family history.
Q: What is the purpose of a breast self-examination?
- A: To detect any changes or lumps in the breast tissue that could indicate a problem.
Q: What is the treatment for breast cancer?
- A: Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy.
Q: What is the role of the BRCA genes in breast cancer?
- A: Mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes increase the risk of developing breast and ovarian cancers.
Hormonal Regulation
Q: What role does oxytocin play during breastfeeding?
- A: It causes the myoepithelial cells to contract and expel milk from the alveoli.
Q: How does prolactin affect the mammary glands?
- A: It stimulates the production of milk in the alveolar cells.
Q: What effect does progesterone have on the mammary glands during pregnancy?
- A: It promotes the development of the alveoli and prepares the breasts for milk production.
Q: What happens to prolactin levels after childbirth?
- A: They increase to stimulate milk production.
Q: What is the role of estrogen in the development of the mammary glands?
- A: It stimulates the growth and branching of the ductal system.
Development and Physiology
Q: How do the mammary glands develop during puberty?
- A: Increased levels of estrogen and progesterone lead to the growth of the ductal and alveolar systems.
Q: What is the role of adipose tissue in the breasts?
- A: It provides structural support and contributes to the size and shape of the breasts.
Q: How does pregnancy affect the mammary glands?
- A: Pregnancy hormones cause the glands to enlarge and develop further in preparation for lactation.
Q: What is the process of lactogenesis?
- A: The initiation of milk production in the mammary glands.
Q: How does suckling by the infant stimulate milk production?
- A: It triggers the release of prolactin and oxytocin, which stimulate milk production and ejection.
Milk Composition
Q: What are the main components of breast milk?
- A: Proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and antibodies.
Q: How does the composition of colostrum differ from mature milk?
- A: Colostrum is richer in antibodies and lower in fat compared to mature milk.
Q: What role do antibodies in breast milk play for the infant?
- A: They help protect the infant from infections and support the developing immune system.
Q: What is the main carbohydrate in breast milk?
- A: Lactose.
Q: How does breast milk support the infant’s growth and development?
- A: It provides all the essential nutrients needed for healthy growth and development.
Breastfeeding Benefits
Q: What are the benefits of breastfeeding for the mother?
- A: Reduces the risk of breast and ovarian cancers, promotes uterine contraction, and enhances mother-infant bonding.
Q: How does breastfeeding benefit the infant?
- A: Provides optimal nutrition, supports immune function, and promotes healthy growth and development.
Q: What is the recommended duration for exclusive breastfeeding?
- A: The first six months of life.
Q: How does breastfeeding affect postpartum weight loss?
- A: It helps the mother lose weight gained during pregnancy by burning extra calories.
Q: What are the psychological benefits of breastfeeding for the mother?
- A: It can reduce stress and promote emotional well-being.
Common Breastfeeding Challenges
Q: What is nipple soreness and how can it be managed?
- A: Nipple soreness can occur from improper latch or frequent feeding and can be managed with proper breastfeeding techniques and nipple creams.
Q: What is engorgement and how is it treated?
- A: Engorgement is the swelling of the breasts due to excess milk and can be treated by frequent breastfeeding or pumping.
Q: What is a blocked milk duct and how can it be resolved?
- A: A blocked milk duct is a blockage in the milk flow and can be resolved by massage, warm compresses, and frequent feeding.
Q: What is the treatment for mastitis?
- A: Antibiotics, pain relief measures, and continued breastfeeding or pumping.
Q: What is thrush and how can it affect breastfeeding?
- A: Thrush is a yeast infection that can affect the nipples and baby’s mouth, causing pain and discomfort during breastfeeding.
Breastfeeding Techniques
Q: What is the proper latch for breastfeeding?
- A: The baby’s mouth should cover both the nipple and part of the areola to ensure effective milk transfer and prevent nipple pain.
Q: How can a mother ensure a good latch?
- A: By positioning the baby’s mouth wide open before attaching to the breast.
Q: What is the football hold in breastfeeding?
- A: A breastfeeding position where the baby is tucked under the mother’s arm, like a football.
Q: What is the cradle hold in breastfeeding?
- A: A breastfeeding position where the baby’s head rests in the crook of the mother’s arm.
Q: How can a mother increase milk supply?
- A: By breastfeeding more frequently, ensuring proper latch, and staying hydrated.
Weaning
Q: What is weaning?
- A: The process of gradually introducing the baby to solid foods and reducing breastfeeding.
Q: When is the right time to start weaning?
- A: Around 6 months of age when the baby shows signs of readiness for solid foods.
Q: What are signs that a baby is ready for weaning?
- A: Ability to sit up, showing interest in solid foods, and losing the tongue-thrust reflex.
Q: How can weaning be made easier for the baby?
- A: By introducing new foods gradually and maintaining a comforting routine.
Q: What are common challenges during weaning?
- A: Resistance from the baby, changes in routine, and potential nutritional concerns.
Breast Health
Q: What is a breast self-examination?
- A: A method for women to check their own breasts for lumps or changes.
Q: When should women perform a breast self-examination?
- A: Monthly, preferably a few days after the menstrual period ends.
Q: What are common signs of breast cancer?
- A: Lumps, changes in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, and nipple discharge.
Q: What is a mammogram?
- A: An X-ray imaging test used to screen for breast cancer.
Q: What age should women start getting mammograms?
- A: Generally, women should start getting mammograms at age 40, but it may vary based on individual risk factors.
Common Breast Conditions
Q: What are fibrocystic breast changes?
- A: Noncancerous changes in the breast tissue that can cause lumpiness and discomfort.
Q: What is a fibroadenoma?
- A: A benign breast tumor that is usually smooth, firm, and movable.
Q: What is breast cyst?
- A: A fluid-filled sac within the breast, which is usually benign.
Q: What is gynecomastia?
- A: The enlargement of breast tissue in males.
Q: How are benign breast conditions typically treated?
- A: Depending on the condition, treatment may include monitoring, aspiration, or surgical removal.
Breast Cancer
Q: What are the risk factors for breast cancer?
- A: Age, family history, genetic mutations, hormonal factors, and lifestyle choices.
Q: What is the role of BRCA genes in breast cancer?
- A: Mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 increase the risk of developing breast and ovarian cancers.
Q: What are the treatment options for breast cancer?
- A: Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy.
Q: What is the purpose of hormone therapy in breast cancer treatment?
- A: To block the effects of estrogen, which can promote the growth of certain breast cancers.
Q: What is the importance of early detection in breast cancer?
- A: Early detection increases the chances of successful treatment and survival.
Breast Reconstruction
Q: What is breast reconstruction?
- A: A surgical procedure to restore the shape of the breast after mastectomy.
Q: What are the types of breast reconstruction?
- A: Implant-based reconstruction and autologous tissue reconstruction (using the patient’s own tissue).
Q: When can breast reconstruction be performed?
- A: It can be performed immediately after mastectomy or delayed until after other treatments.
Q: What factors influence the choice of breast reconstruction method?
- A: Patient preference, health status, cancer treatment plan, and available tissue.
Q: What are the benefits of breast reconstruction? – A: Improved body image, self-esteem, and quality of life after mastectomy.

Female Mammary Gland: An Overview
Anatomy
Lobules:
- Small, glandular structures that produce milk.
- Each breast contains 15-20 lobules.
Ducts:
- Network of channels that transport milk from the lobules to the nipple.
- Each lobule is connected to a duct, forming a lobuloalveolar unit.
Nipple:
- The protruding part of the breast through which milk exits.
- Contains numerous openings of the milk ducts.
Areola:
- The pigmented area surrounding the nipple.
- Contains Montgomery glands, which secrete lubricating and protective fluid.
Fat Tissue:
- Surrounds and protects the glandular tissue.
- Contributes to the shape and size of the breast.
Connective Tissue:
- Provides structural support and helps maintain the shape of the breast.
- Includes Cooper’s ligaments, which extend from the skin to the chest wall.
Physiology
Milk Production (Lactogenesis):
- Initiated by hormonal changes during pregnancy.
- Prolactin, produced by the pituitary gland, stimulates milk production.
- Oxytocin, also from the pituitary gland, triggers milk ejection (let-down reflex).
Hormonal Regulation:
- Estrogen and progesterone prepare the mammary glands for lactation during pregnancy.
- After childbirth, estrogen and progesterone levels drop, allowing prolactin and oxytocin to take over.
Milk Ejection Reflex:
- Suckling by the infant stimulates nerve endings in the nipple.
- Signals are sent to the brain, releasing oxytocin.
- Oxytocin causes the milk ducts to contract, pushing milk towards the nipple.
Development
Puberty:
- Estrogen stimulates the growth of ductal tissue.
- Progesterone supports the development of lobular and alveolar tissue.
Pregnancy:
- Increased levels of estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, and human placental lactogen promote extensive growth and maturation of the mammary glands.
Post-Menopause:
- Decrease in estrogen and progesterone leads to the involution of glandular tissue.
- Breasts may become less dense and more fatty.
Clinical Aspects
Breast Cancer:
- Originates in the ductal or lobular tissue.
- Risk factors include genetics, hormonal exposure, and lifestyle factors.
Mastitis:
- Infection of the breast tissue, often associated with breastfeeding.
- Symptoms include pain, redness, and swelling.
Fibrocystic Changes:
- Benign changes in the breast tissue, causing lumps or pain.
- Often related to hormonal fluctuations.
Gynecomastia:
- Enlargement of male breast tissue, caused by hormonal imbalances.
- Can occur during puberty, aging, or as a side effect of certain medications.
Imaging and Diagnosis
Mammography:
- X-ray imaging to detect breast cancer or other abnormalities.
- Recommended as a screening tool for women over 40 or with risk factors.
Ultrasound:
- Uses sound waves to create images of breast tissue.
- Useful for evaluating lumps or dense breast tissue.
MRI:
- Magnetic resonance imaging provides detailed images of the breast.
- Often used for high-risk patients or to assess the extent of breast cancer.
Biopsy:
- Removal of tissue samples for microscopic examination.
- Essential for diagnosing breast cancer and other conditions.
The female mammary gland is an integral part of the human anatomy, playing crucial roles in lactation and maternal bonding. Here are additional insights into its structure, function, development, and relevance:
Structure and Function
Composition:
- Glandular Tissue: Comprises the functional parts of the breast, including lobules and ducts that produce and transport milk.
- Adipose Tissue: Provides padding and protection, contributing to breast size and shape.
- Connective Tissue: Includes Cooper’s ligaments that support the breast by anchoring its tissue to the chest wall.
Nervous Supply:
- The breast is richly supplied by sensory nerves, particularly around the areola, enhancing the mother’s response to nursing.
Blood Supply:
- Supplied by branches of the internal mammary artery and lateral thoracic artery, ensuring adequate nutrition and hormonal delivery.
Developmental Changes
Embryological Development:
- Mammary glands begin to develop early in fetal life as milk lines or mammary ridges.
- By the end of gestation, a primitive ductal system has formed.
Changes During Menstrual Cycle:
- Hormonal fluctuations can lead to changes in the breast tissue, sometimes causing discomfort or lumpiness.
Pregnancy and Lactation:
- Significant hormonal changes lead to the maturation of milk-producing cells and expansion of ductal structures.
- After childbirth, lactation begins, regulated by hormonal and neuroendocrine pathways.
Pathophysiology
Common Conditions:
- Benign Breast Diseases: Fibroadenomas, cysts, and mastitis.
- Breast Cancer: Ranges from in situ forms to invasive types. Hormonal influences, genetic predispositions, and environmental factors play roles in its development.
Screening and Diagnosis:
- Regular mammographic screening is advised for early detection of breast cancer.
- Other diagnostic tools include ultrasound and biopsy for evaluating abnormalities.
Hormonal Influence
Estrogen and Progesterone:
- Play a significant role in the growth and differentiation of breast tissue.
- Influence changes during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause.
Prolactin and Oxytocin:
- Prolactin is vital for milk synthesis.
- Oxytocin triggers the milk ejection reflex during breastfeeding.
Cultural and Psychological Aspects
Breastfeeding Practices:
- Vary significantly across cultures but universally recognized for benefits to maternal and child health.
- World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life.
Body Image:
- Breasts are often subject to cultural and individual perceptions affecting self-esteem and body image.
- Changes in breast appearance due to age, pregnancy, or medical treatments can impact psychological well-being.






