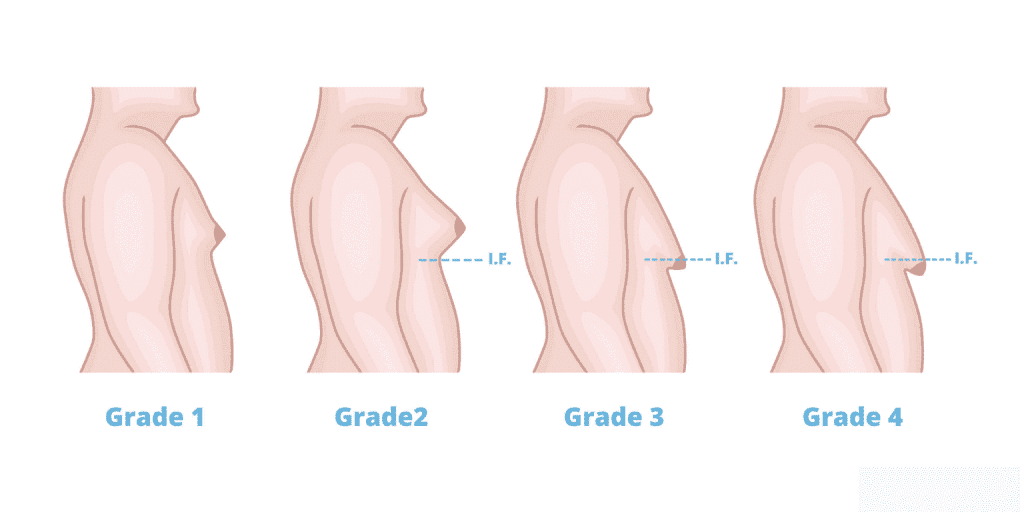
Understanding Gynecomastia: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Gynecomastia is a condition in boys and men where the breast gland tissue increases due to an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone hormones. This can affect one or both breasts. In this post, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for gynecomastia.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
Common symptoms associated with gynecomastia include:
- Breast Tenderness
- Swollen Breast Tissue
- Pain
- Nipple Discharge (from one or both breasts)
If you experience these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia occurs when there is a decrease in testosterone levels relative to estrogen. Several factors can contribute to this hormonal imbalance:
1. Natural Hormone Changes
The hormones estrogen and testosterone control sex characteristics in men and women. While estrogen is often thought of as a “female hormone,” men produce it in smaller amounts. When estrogen levels rise or testosterone levels drop, gynecomastia can develop.
2. Medications
Certain medications may lead to gynecomastia, including:
- Anti-androgens for prostate conditions
- Anabolic Steroids and Androgens
- AIDS Medications
- Anti-Anxiety Medications
- Antibiotics
- Tricyclic Antidepressants
- Ulcer Medications
- Cancer Treatment Drugs
- Heart Medications
- Stomach-Emptying Medications
3. Alcohol and Street Drugs
Substances that can cause gynecomastia include:
- Alcohol
- Marijuana
- Heroin
- Amphetamines (used for ADHD treatment)
- Methadone
4. Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions can lead to hormonal imbalances that trigger gynecomastia:
- Hypogonadism: Conditions like pituitary insufficiency and Klinefelter syndrome can interfere with testosterone production.
- Tumors: Tumors involving the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, and testes may alter hormone levels.
- Hyperthyroidism: An overproduction of thyroxine by the thyroid gland.
- Liver Failure and Cirrhosis: Hormonal changes related to liver conditions can be linked to gynecomastia.
Diagnosing Gynecomastia
To diagnose gynecomastia, your doctor will ask about your family health history, medical history, and medications. A physical examination will be conducted, including an evaluation of your breast tissue, genitals, and abdomen.
Common diagnostic tests may include:
- Mammograms
- Blood Tests
Depending on initial results, additional tests may be necessary:
- MRI Scans
- CT Scans
- Tissue Biopsies
- Testicular Ultrasounds
Doctors aim to rule out other potential causes of breast swelling, such as:
- Fatty Breast Tissue: Resembling gynecomastia but without gland enlargement.
- Breast Cancer: Though rare in men, it can present similarly.
- Breast Abscess: An infection of breast tissue.
Treatment for Gynecomastia
In many cases, gynecomastia resolves without treatment. However, if the condition is due to underlying issues such as malnutrition, hypogonadism, or cirrhosis, these conditions may need to be treated first.
1. Medication Adjustments
If gynecomastia is caused by medication, your doctor may recommend stopping or substituting the medication.
2. Periodic Reevaluation
For adolescents with no clear cause beyond normal hormonal changes, doctors may suggest periodic evaluations every 3 to 6 months to monitor the condition. Gynecomastia often resolves within two years without treatment.
3. Medications
Certain medications used for breast cancer and other conditions may help reduce breast tissue in gynecomastia.
4. Surgery
If other treatments are ineffective and the enlarged breasts are causing discomfort or distress, surgery may be considered:
- Liposuction: Removes excess breast fat but not gland tissue.
- Mastectomy: Removes gland tissue, often performed through small incisions, leading to shorter recovery time.
Before considering surgery, it’s important to discuss all options and potential outcomes with your doctor.
Conclusion
Gynecomastia is a common condition that can cause physical and emotional discomfort. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is the first step toward managing this condition. If you suspect you have gynecomastia or have any concerns, consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Understanding Gynecomastia: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Gynecomastia is a condition in boys and men where the breast gland tissue increases due to an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone hormones. This can affect one or both breasts. In this post, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for gynecomastia.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
Common symptoms associated with gynecomastia include:
- Breast Tenderness
- Swollen Breast Tissue
- Pain
- Nipple Discharge (from one or both breasts)
If you experience these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia occurs when there is a decrease in testosterone levels relative to estrogen. Several factors can contribute to this hormonal imbalance:
1. Natural Hormone Changes
The hormones estrogen and testosterone control sex characteristics in men and women. While estrogen is often thought of as a “female hormone,” men produce it in smaller amounts. When estrogen levels rise or testosterone levels drop, gynecomastia can develop.
2. Medications
Certain medications may lead to gynecomastia, including:
- Anti-androgens for prostate conditions
- Anabolic Steroids and Androgens
- AIDS Medications
- Anti-Anxiety Medications
- Antibiotics
- Tricyclic Antidepressants
- Ulcer Medications
- Cancer Treatment Drugs
- Heart Medications
- Stomach-Emptying Medications
3. Alcohol and Street Drugs
Substances that can cause gynecomastia include:
- Alcohol
- Marijuana
- Heroin
- Amphetamines (used for ADHD treatment)
- Methadone
4. Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions can lead to hormonal imbalances that trigger gynecomastia:
- Hypogonadism: Conditions like pituitary insufficiency and Klinefelter syndrome can interfere with testosterone production.
- Tumors: Tumors involving the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, and testes may alter hormone levels.
- Hyperthyroidism: An overproduction of thyroxine by the thyroid gland.
- Liver Failure and Cirrhosis: Hormonal changes related to liver conditions can be linked to gynecomastia.
Diagnosing Gynecomastia
To diagnose gynecomastia, your doctor will ask about your family health history, medical history, and medications. A physical examination will be conducted, including an evaluation of your breast tissue, genitals, and abdomen.
Common diagnostic tests may include:
- Mammograms
- Blood Tests
Depending on initial results, additional tests may be necessary:
- MRI Scans
- CT Scans
- Tissue Biopsies
- Testicular Ultrasounds
Doctors aim to rule out other potential causes of breast swelling, such as:
- Fatty Breast Tissue: Resembling gynecomastia but without gland enlargement.
- Breast Cancer: Though rare in men, it can present similarly.
- Breast Abscess: An infection of breast tissue.
Treatment for Gynecomastia
In many cases, gynecomastia resolves without treatment. However, if the condition is due to underlying issues such as malnutrition, hypogonadism, or cirrhosis, these conditions may need to be treated first.
1. Medication Adjustments
If gynecomastia is caused by medication, your doctor may recommend stopping or substituting the medication.
2. Periodic Reevaluation
For adolescents with no clear cause beyond normal hormonal changes, doctors may suggest periodic evaluations every 3 to 6 months to monitor the condition. Gynecomastia often resolves within two years without treatment.
3. Medications
Certain medications used for breast cancer and other conditions may help reduce breast tissue in gynecomastia.
4. Surgery
If other treatments are ineffective and the enlarged breasts are causing discomfort or distress, surgery may be considered:
- Liposuction: Removes excess breast fat but not gland tissue.
- Mastectomy: Removes gland tissue, often performed through small incisions, leading to shorter recovery time.
Before considering surgery, it’s important to discuss all options and potential outcomes with your doctor.
Conclusion
Gynecomastia is a common condition that can cause physical and emotional discomfort. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is the first step toward managing this condition. If you suspect you have gynecomastia or have any concerns, consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.