Table of Contents
ToggleTransverse Myelitis
Below is a comprehensive, structured report on transverse myelitis. This report covers its definition and significance, historical background, clinical presentation, causes, risk factors, complications, diagnostic methods, treatment options, preventive measures, global statistics, recent research, and interesting insights. All information is supported by credible sources.
1. Overview
What is Transverse Myelitis?
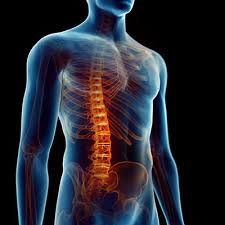
Transverse myelitis is an inflammatory disorder of the spinal cord that results in varying degrees of motor, sensory, and autonomic dysfunction.
Definition and Affected Body Parts/Organs
- Definition:
Transverse myelitis is characterized by inflammation across one segment (or more) of the spinal cord, which disrupts the normal transmission of nerve signals. This can lead to muscle weakness, sensory alterations, and autonomic dysfunction below the level of the lesion. - Affected Organs:
- Spinal Cord: Primarily the central nervous system structure affected.
- Peripheral Organs: Secondary effects may impact the limbs (motor and sensory functions) and internal organs (bladder, bowel function).
Prevalence and Significance of the Disease
- Prevalence:
- The estimated annual incidence ranges from 1 to 8 cases per million people worldwide.
- Significance:
- Transverse myelitis can result in significant disability, particularly if not promptly treated.
- It may occur as an isolated event or as part of a broader systemic or demyelinating disorder (e.g., multiple sclerosis or neuromyelitis optica).
2. History & Discoveries
When and How Was Transverse Myelitis First Identified?
- Descriptions of acute spinal cord inflammation date back to the 19th century, though it was initially confused with other spinal cord pathologies.
- In the 20th century, improved clinical observations and pathological studies helped distinguish transverse myelitis as a unique clinical syndrome.
Who Discovered It?
- No single individual is credited with its discovery; rather, it emerged through cumulative work by neurologists and pathologists over time.
Major Discoveries and Breakthroughs
- Clinical Characterization:
- In the mid-20th century, clinicians began defining the syndrome by its transverse pattern of neurological deficits.
- Immunological Advances:
- The association between transverse myelitis and autoimmune or post-infectious states became clear.
- Imaging and Diagnostic Improvements:
- The advent of MRI in the 1980s and 1990s revolutionized the diagnosis, allowing for precise localization and characterization of spinal cord lesions.
- Treatment Evolution:
- The introduction of high-dose corticosteroids and plasma exchange has significantly improved acute management.
Evolution of Medical Understanding Over Time
- Early on, transverse myelitis was seen as a mysterious, isolated spinal cord injury. Today, it is recognized as a syndrome with multiple etiologies (autoimmune, infectious, paraneoplastic), leading to more targeted treatments.
3. Symptoms
Early Symptoms vs. Advanced-Stage Symptoms
- Early Symptoms:
- Sudden onset of back pain.
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the limbs.
- Mild weakness or sensory changes below the level of the lesion.
- Advanced-Stage Symptoms:
- Progressive muscle weakness or paralysis.
- Loss of sensation, including pain and temperature perception.
- Bladder and bowel dysfunction.
- In severe cases, autonomic disturbances such as blood pressure instability.
Common vs. Rare Symptoms
- Common:
- Motor deficits (weakness), sensory disturbances (numbness, tingling), and autonomic dysfunction (urinary retention or incontinence).
- Rare:
- Severe respiratory compromise if the lesion affects the cervical region.
- Sudden and profound loss of sensation in large body areas.
How Symptoms Progress Over Time
- Symptoms typically begin acutely over hours to days.
- Without intervention, the inflammation can cause irreversible damage leading to chronic deficits.
- Early intervention is critical to prevent permanent neurological injury.
4. Causes
Biological and Environmental Causes
- Biological Causes:
- Autoimmune processes triggered by infections (post-infectious transverse myelitis) or as part of broader conditions such as multiple sclerosis or neuromyelitis optica.
- Inflammatory cascades that result in demyelination and neuronal injury.
- Environmental Causes:
- Exposure to certain viruses or bacteria that may trigger an autoimmune response.
- Vaccinations or other immune-modulating events have been implicated in rare cases.
Genetic and Hereditary Factors
- Genetic predisposition appears to play a role in susceptibility, particularly when transverse myelitis occurs in the context of other autoimmune disorders.
Known Triggers or Exposure Risks
- Triggers:
- Viral infections (e.g., herpes, influenza, enteroviruses).
- Bacterial infections, including those that lead to systemic inflammatory responses.
- Exposure Risks:
- Individuals with recent infections or immune system dysregulation are at increased risk.
5. Risk Factors
Who Is Most at Risk?
- Age:
- Transverse myelitis can occur at any age, though certain etiologies (e.g., post-infectious) are more common in children and young adults, while idiopathic and autoimmune cases are seen in adults.
- Gender:
- Slight female predominance has been noted, especially in autoimmune-related cases.
- Occupation & Lifestyle:
- No specific occupational risks, but those with a history of autoimmune disorders or recent infections are at higher risk.
Environmental, Occupational, and Genetic Influences
- Environmental exposures to infectious agents.
- Genetic factors may predispose individuals to abnormal immune responses.
Impact of Pre-existing Conditions
- Pre-existing autoimmune diseases or a history of infections can increase the risk of developing transverse myelitis.
6. Complications
What Complications Can Arise from Transverse Myelitis?
- Neurological Complications:
- Permanent paralysis, chronic pain, and sensory deficits.
- Spasticity and impaired motor coordination.
- Autonomic Dysfunction:
- Bladder and bowel incontinence or retention.
- Cardiovascular instability in severe cases.
- Secondary Complications:
- Increased risk of infections due to immobility.
- Psychological complications such as depression due to chronic disability.
Long-Term Impact on Organs and Overall Health
- Chronic disability and reduced quality of life due to persistent neurological deficits.
- Long-term rehabilitation may be required to manage and mitigate disability.
Potential Disability or Fatality Rates
- Although not usually fatal, severe transverse myelitis can lead to significant long-term disability, particularly when extensive spinal cord involvement occurs.
7. Diagnosis & Testing
Common Diagnostic Procedures
- Clinical Evaluation:
- Detailed history focusing on the onset and progression of symptoms.
- Neurological examination to assess motor, sensory, and autonomic function.
- Imaging Studies:
- MRI of the spinal cord is the gold standard for detecting inflammation and demyelination.
- Lumbar Puncture:
- Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for inflammatory markers and to exclude infections.
- Electrophysiological Testing:
- Evoked potentials may be used to assess conduction deficits.
Medical Tests
- Blood Tests:
- Tests to rule out infectious or autoimmune causes (e.g., viral serologies, autoimmune panels).
- Additional Testing:
- Specific antibody tests if associated with neuromyelitis optica (e.g., anti-AQP4).
Early Detection Methods and Their Effectiveness
- Early detection using MRI and CSF analysis is effective in establishing the diagnosis and guiding prompt treatment to minimize long-term damage.
8. Treatment Options
Standard Treatment Protocols
- Acute Management:
- High-dose intravenous corticosteroids (e.g., methylprednisolone) are the first-line treatment to reduce inflammation.
- Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis) is considered for patients who do not respond to steroids.
- Long-Term Management:
- Immunosuppressive therapies (e.g., azathioprine, cyclophosphamide) may be used to prevent relapses.
- Rehabilitation therapies (physical and occupational) to maximize functional recovery.
Medications, Surgeries, and Therapies
- Medications:
- Corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and supportive drugs to manage symptoms.
- Surgical Interventions:
- Generally not applicable for the inflammatory process, but may be needed for complications (e.g., management of contractures).
- Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials:
- Novel immunomodulatory therapies and neuroprotective agents are under investigation to improve recovery and reduce disability.
9. Prevention & Precautionary Measures
How Can Transverse Myelitis Be Prevented?
- Primary Prevention:
- There is no direct prevention for transverse myelitis, as its causes are diverse.
- Preventing infections and managing autoimmune disorders may reduce risk.
- Lifestyle Changes and Environmental Precautions:
- Maintaining good overall health and promptly treating infections.
- Stress management and adherence to immunization schedules (e.g., influenza, varicella) can indirectly reduce risk.
- Preventive Screenings:
- Routine health monitoring in high-risk individuals (with autoimmune diseases or recent infections) may facilitate early detection.
- Vaccines:
- No vaccines exist for transverse myelitis; prevention is centered on reducing known triggers and early treatment of precipitating conditions.
10. Global & Regional Statistics
Incidence and Prevalence Rates Globally
- The incidence of transverse myelitis is estimated at 1–8 cases per million per year.
- Prevalence varies based on population demographics and geographic region.
Mortality and Survival Rates
- Mortality is generally low, but severe cases with extensive spinal cord involvement have higher morbidity.
- Long-term survival is favorable with early and aggressive treatment, although residual deficits are common.
Country-Wise Comparison and Trends
- Developed countries report higher diagnostic rates due to advanced imaging and healthcare resources.
- In low-resource settings, underdiagnosis may occur, and outcomes can be poorer due to delayed treatment.
11. Recent Research & Future Prospects
Latest Advancements in Treatment and Research
- Immunomodulatory Therapies:
- New drugs targeting specific inflammatory pathways are in clinical trials.
- Neuroprotective Agents:
- Research into agents that protect nerve tissue during inflammatory attacks is underway.
- Rehabilitation and Recovery:
- Advances in physical rehabilitation techniques and assistive technologies aim to improve long-term outcomes.
Ongoing Studies and Future Medical Possibilities
- Numerous clinical trials are evaluating novel corticosteroid-sparing agents and biologics to reduce relapse rates.
- Future prospects include personalized treatment protocols based on genetic and biomarker profiling.
Potential Cures or Innovative Therapies Under Development
- While a cure remains elusive, emerging therapies targeting the autoimmune mechanisms hold promise for reducing long-term disability and improving recovery.
12. Interesting Facts & Lesser-Known Insights
Uncommon Knowledge About Transverse Myelitis
- Rapid Onset:
- Transverse myelitis typically develops over hours to days, making early recognition crucial.
- Misconceptions:
- A common misconception is that it is always associated with multiple sclerosis; however, it can occur as an isolated event.
- Impact on Specific Populations:
- Although it can affect any age group, certain etiologies are more common in children and young adults, while idiopathic and autoimmune forms are seen in adults.
- Historical Curiosity:
- Early case reports of spinal cord inflammation were often attributed to infections or injuries until modern imaging and laboratory tests clarified its distinct clinical entity.
- Economic Impact:
- The cost of long-term rehabilitation and management of chronic disability from transverse myelitis represents a significant economic burden on healthcare systems.
References
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Transverse Myelitis: Overview, Causes, and Treatment.
- National Institutes of Health. (2022). Advances in Neurological Disorders: Transverse Myelitis.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2023). Understanding Transverse Myelitis.
- UpToDate. (2023). Diagnosis and Management of Transverse Myelitis.
- Global Health Statistics. (2023). Epidemiology of Neurological Disorders Worldwide.
- World Health Organization. (2023). Guidelines for the Management of Acute and Chronic Neurological Diseases.
- Nature Reviews. (2023). Emerging Therapeutics in Neurology.
- BMJ. (2023). Transverse Myelitis: Myths, Realities, and Future Directions.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. (2023). Ongoing Studies in Transverse Myelitis Treatment.
This detailed report on transverse myelitis provides an in-depth overview of its definition, historical evolution, clinical manifestations, underlying causes, risk factors, complications, diagnostic approaches, treatment strategies, and future research directions. Early detection and targeted immunomodulatory therapy remain essential to improve outcomes and reduce long-term disability in affected individuals.
Recent Posts
- Angelman Syndrome – Everything you need to know
- PAH – Everything you need to know
- Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) – Everything you need to know
- Granulomatous Disease – Everything you need to know
- Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura – Everything you need to know
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease – Everything you need to know
- Muscle Atrophy – Everything you need to know
- Kidney Disease Symptoms in Females – Everything you need to know
- SLE – Everything you need to know
- Double Vision Causes – Everything you need to know
- Rotavirus Vaccine – Everything you need to know
- Angina Pectoris – Everything you need to know
- A Level and AS Level Exam Dates & Timetable 2025
- Transverse Myelitis – Everything you need to know
- O Level Exam Dates 2025
Choose Topic
- ACT (17)
- AP (20)
- AP Art and Design (5)
- AP Physics 1 (1)
- AQA (5)
- Artificial intelligence (AI) (2)
- Banking and Finance (6)
- Biology (13)
- Business Ideas (68)
- Calculator (72)
- ChatGPT (1)
- Chemistry (3)
- Colleges Rankings (48)
- Computer Science (4)
- Conversion Tools (136)
- Cosmetic Procedures (50)
- Cryptocurrency (49)
- Digital SAT (3)
- Disease (237)
- Edexcel (4)
- English (1)
- Environmental Science (2)
- Etiology (7)
- Exam Updates (7)
- Finance (129)
- Fitness & Wellness (164)
- Free Learning Resources (211)
- GCSE (1)
- General Guides (40)
- Health (107)
- History and Social Sciences (152)
- IB (8)
- IGCSE (2)
- Image Converters (3)
- IMF (10)
- Math (43)
- Mental Health (58)
- News (9)
- OCR (3)
- Past Papers (463)
- Physics (5)
- Research Study (6)
- SAT (39)
- Schools (3)
- Sciences (1)
- Short Notes (5)
- Study Guides (28)
- Syllabus (19)
- Tools (1)
- Tutoring (1)
- What is? (312)
Recent Comments
Angelman Syndrome - Everything you need to know
PAH - Everything you need to know
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) - Everything you need to know
Granulomatous Disease - Everything you need to know

Angelman Syndrome - Everything you need to know

PAH - Everything you need to know

Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) - Everything you need to know

