“What Is Mercantilism: Everything You Need to Know”
Mercantilism is one of the most influential economic theories that shaped nations and international trade for centuries. But what is mercantilism? In this comprehensive guide, we will unravel the origins, principles, and impacts of mercantilism, exploring how this doctrine influenced the rise of modern economies and global trade. Whether you’re a student of history, economics, or simply curious about how past economic policies still echo in today’s world, this article offers everything you need to know about mercantilism.
Introduction
Imagine a time when nations competed fiercely for gold, silver, and other resources, believing that a country’s wealth was measured by its stockpile of precious metals. This was the world of mercantilism—a period when governments implemented policies to maximize exports and minimize imports, all in the pursuit of national prosperity and power. Did you know that mercantilist policies were instrumental in shaping the early economies of Europe, driving colonial expansion, and setting the stage for the modern global trade system?
In this article, we will cover:
- Definition and Fundamentals: A clear, straightforward explanation of mercantilism and its essential characteristics.
- Historical Evolution: The origins and development of mercantilist theory, along with key milestones and notable anecdotes.
- Core Principles: A detailed look at the key tenets of mercantilism, such as trade surpluses, protectionism, and the accumulation of wealth through precious metals.
- Real-World Examples and Case Studies: How mercantilist policies were implemented by nations like Spain, France, and England, and their lasting impact on international trade.
- Significance and Applications: The importance of mercantilism in shaping economic thought, national policies, and global interactions.
- Common Misconceptions and FAQs: Clarification of common myths surrounding mercantilism with easy-to-understand answers.
- Modern Relevance and Trends: An exploration of how the legacy of mercantilism influences contemporary economic policies and debates.
- Conclusion and Call to Action: A summary of key points, reinforced by a call-to-action for further exploration and discussion.
By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of what is mercantilism, why it matters, and how its influence can still be observed in today’s world. Let’s embark on this journey through economic history and discover the legacy of mercantilism.
What Is Mercantilism? A Straightforward Definition
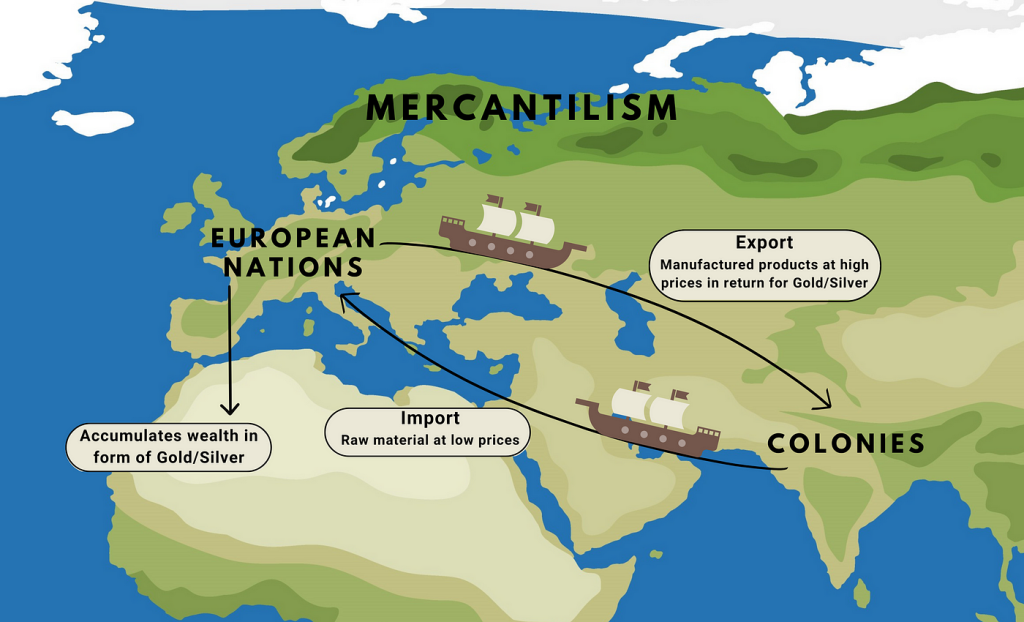
Mercantilism is an economic doctrine and system that dominated European trade from the 16th to the 18th centuries. It is based on the idea that a nation’s wealth and power are best served by increasing exports and accumulating precious metals, primarily gold and silver, while limiting imports. In essence, mercantilism views global trade as a zero-sum game where one nation’s gain is another’s loss.
Essential Characteristics of Mercantilism
When considering what is mercantilism, several key attributes define the doctrine:
- Export Maximization and Import Minimization: Mercantilist policies aim to create a trade surplus by exporting more than is imported, thereby increasing a nation’s stock of precious metals.
- Government Intervention: Unlike free-market economies, mercantilism involves significant state control over trade, including tariffs, subsidies, and strict regulation of colonial commerce.
- Colonial Expansion: Colonies are viewed as sources of raw materials and markets for manufactured goods, playing a vital role in enhancing the mother country’s wealth.
- Accumulation of Wealth: Wealth is measured by the quantity of precious metals a nation possesses. This accumulation is seen as both a source of national power and a safeguard against economic instability.
- Zero-Sum Perspective: Mercantilism operates on the belief that global wealth is fixed; therefore, nations must compete to secure the largest share of this wealth.
In summary, what is mercantilism? It is an economic system centered on the idea that national prosperity and power are achieved by exporting more than importing, accumulating precious metals, and maintaining strict state control over economic activities.
Historical and Contextual Background
The origins and evolution of mercantilism are deeply intertwined with the rise of nation-states, colonial expansion, and the quest for economic dominance in early modern Europe.
Early Origins and the Rise of Nation-States
Pre-Mercantilist Trade Practices
- Medieval Trade: Before the advent of mercantilism, medieval trade was characterized by localized markets and guild-controlled commerce. Trade was relatively limited, and wealth was measured more by land ownership than by the accumulation of precious metals.
- Renaissance Commerce: The Renaissance era saw the expansion of trade networks and the beginning of global exploration. Italian city-states such as Venice and Genoa became wealthy through commerce, setting the stage for new economic theories.
The Emergence of Mercantilism
- 16th Century Europe: With the discovery of the New World, European nations like Spain, Portugal, France, and England began to establish colonies. These colonies were seen as sources of raw materials and new markets, and their exploitation became central to mercantilist policy.
- Colonial Rivalries: The competition for colonies and trade routes spurred nations to adopt protectionist policies. Governments implemented tariffs, quotas, and subsidies to favor domestic industries and secure a trade surplus.
- Government Involvement: During this period, monarchs and governments took a direct role in economic affairs, using mercantilist policies to finance wars, support colonial ventures, and consolidate national power.
Milestones in the Evolution of Mercantilism
Key Figures and Writings
- Thomas Mun: Often considered the father of mercantilism, Thomas Mun was an English writer whose works advocated for a favorable balance of trade as a means to increase national wealth. His book, England’s Treasure by Forraign Trade, remains a seminal text in mercantilist thought.
- Jean-Baptiste Colbert: As the finance minister of France under King Louis XIV, Colbert implemented mercantilist policies that strengthened the French economy through state intervention, the promotion of industry, and the regulation of colonial trade.
- Mercantilist Treatises: Numerous economic treatises from the 16th to the 18th centuries detailed mercantilist policies, influencing the economic strategies of emerging European powers.
Decline and Transformation
- Critiques and Reforms: By the late 18th century, the limitations of mercantilism became increasingly apparent. Critics like Adam Smith argued that wealth was not finite and that free trade and competition could lead to greater prosperity for all nations.
- The Shift to Classical Economics: The ideas of the classical economists gradually replaced mercantilism, leading to the development of theories that emphasized market forces, competition, and the benefits of free trade.
- Legacy in Modern Policies: Although classical economics largely supplanted mercantilism, many elements of mercantilist thinking—such as protectionism and state intervention in trade—persist in modern economic policies, particularly in times of economic uncertainty.
Notable Historical Anecdotes
- The Spanish Treasure Fleets: Spain’s vast accumulation of gold and silver from its American colonies was a direct manifestation of mercantilist policy. However, this influx of wealth also contributed to economic imbalances and long-term inflation.
- The Navigation Acts: Implemented by England, these laws restricted the use of foreign ships for trade between England and its colonies. The Navigation Acts were a hallmark of mercantilist policy aimed at ensuring that the benefits of colonial trade flowed back to the mother country.
- Adam Smith’s Critique: In The Wealth of Nations, Adam Smith critiqued mercantilist policies, arguing that free trade and minimal government intervention were the keys to national prosperity—a perspective that laid the groundwork for modern economic thought.
In-Depth Exploration: Key Aspects and Categories of Mercantilism
To fully understand what is mercantilism, we need to explore its various dimensions, including its principles, practices, and real-world applications.
1. Core Principles of Mercantilism
a. Trade Surplus
- Definition: A trade surplus occurs when a country exports more than it imports, thereby accumulating wealth in the form of precious metals.
- Mercantilist Goal: Mercantilist policies were designed to ensure a constant flow of wealth into a nation by maintaining a favorable balance of trade.
b. Protectionism
- Definition: Protectionism involves using tariffs, quotas, and regulations to protect domestic industries from foreign competition.
- Rationale: By limiting imports, mercantilist policies aimed to reduce the outflow of precious metals and boost domestic production.
c. Colonial Expansion
- Definition: Colonial expansion refers to the acquisition and exploitation of territories outside a nation’s borders.
- Economic Impact: Colonies provided raw materials, new markets, and opportunities for profit, all of which were essential components of mercantilist strategy.
d. State Intervention
- Definition: State intervention in mercantilism involves direct government involvement in economic activities, including regulation, subsidies, and strategic planning.
- Objective: The government’s role was to support domestic industries, manage trade policies, and ensure national prosperity.
2. Practices and Policies Under Mercantilism
a. Tariffs and Trade Restrictions
- Purpose: To discourage imports and encourage domestic production.
- Example: High tariffs on imported goods ensured that local industries had a competitive advantage in their own markets.
b. Subsidies and Government Support
- Purpose: To promote the growth of domestic industries by providing financial support.
- Example: Subsidies for shipbuilding in England helped expand its navy and merchant fleet, supporting both military and commercial interests.
c. Accumulation of Precious Metals
- Purpose: To measure and secure national wealth.
- Mechanism: Nations aimed to maximize exports to earn gold and silver, which were considered the ultimate indicators of wealth.
- Example: Spain’s treasure fleets, which transported vast quantities of silver and gold from the Americas to Europe.
3. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Case Study 1: Mercantilism in Spain
- Overview: Spain’s colonial empire was built on mercantilist principles. The wealth extracted from its American colonies, especially in the form of precious metals, played a crucial role in financing Spain’s military and political ambitions.
- Application: The Spanish crown imposed strict controls over colonial trade, ensuring that the benefits of resource extraction flowed back to the mother country.
- Impact: While this policy initially enriched Spain, over-reliance on colonial wealth eventually led to economic stagnation and vulnerability to inflation.
Case Study 2: The Navigation Acts of England
- Overview: England’s Navigation Acts were designed to control colonial trade and ensure that England benefited from the commerce of its colonies.
- Application: These acts required that goods imported to England or its colonies be transported on English ships, effectively monopolizing trade routes.
- Impact: The Navigation Acts contributed to the growth of English maritime power and laid the groundwork for the British Empire, though they also fueled colonial discontent.
Case Study 3: Mercantilism’s Influence on Modern Economic Policies
- Overview: Although classical economics largely replaced mercantilism, elements of mercantilist thought persist in modern economic policies, particularly in protectionist measures and trade negotiations.
- Application: Contemporary debates over tariffs, trade deficits, and economic nationalism often echo mercantilist ideas.
- Impact: The legacy of mercantilism can be seen in policies aimed at protecting domestic industries and securing economic advantages in a globalized economy.
Importance, Applications, and Benefits of Understanding Mercantilism
Understanding what is mercantilism is crucial for multiple reasons, as it has left an indelible mark on economic thought, international trade, and state policy. Here are some key aspects of its significance:
1. Shaping Economic Theory and Policy
- Historical Impact: Mercantilism was the dominant economic doctrine in Europe from the 16th to the 18th century, influencing the policies of powerful nations and laying the foundation for modern economic systems.
- Evolution of Trade Policy: The mercantilist emphasis on export surpluses and state intervention paved the way for subsequent economic theories, including classical and neoclassical economics. Understanding its principles helps explain the evolution of trade policy and economic governance.
2. Lessons for Modern International Trade
- Protectionism vs. Free Trade: Mercantilist policies provide a historical context for modern debates on protectionism and free trade. Analyzing mercantilism helps policymakers understand the trade-offs between safeguarding domestic industries and participating in global markets.
- Global Economic Competition: The mercantilist focus on national wealth accumulation resonates with contemporary concerns about economic nationalism, trade deficits, and competitive strategies among nations.
3. Cultural and Political Implications
- Colonial Legacy: Mercantilism played a pivotal role in colonial expansion, influencing cultural exchanges, the spread of languages, and the shaping of national identities. Understanding mercantilism is key to grasping the historical roots of modern geopolitical dynamics.
- State Power and Intervention: The mercantilist model of state intervention in the economy has implications for modern governance, including debates over regulation, subsidies, and strategic trade policies.
4. Educational and Research Benefits
- Interdisciplinary Insights: The study of mercantilism intersects with history, economics, political science, and sociology, offering a rich, interdisciplinary perspective on how economies evolve.
- Critical Thinking: Analyzing mercantilist policies encourages critical thinking about the effectiveness and consequences of state intervention in the economy, providing valuable lessons for both academics and practitioners.
Addressing Common Misconceptions and FAQs
Despite its historical importance, several misconceptions about what is mercantilism still persist. Here, we address some common misunderstandings:
Misconception 1: Mercantilism Is an Outdated Concept
- Clarification: While mercantilism as a dominant economic doctrine has been replaced by classical and modern economic theories, its influence persists in modern trade policies, protectionism debates, and economic nationalism.
Misconception 2: Mercantilism Promotes Fair Trade
- Clarification: Mercantilist policies were primarily aimed at enriching the state at the expense of rival nations. They often involved restrictive trade practices and monopolistic behaviors that can lead to economic imbalances.
Misconception 3: All Nations Adopted Mercantilist Policies Equally
- Clarification: The application and success of mercantilist policies varied across nations and historical periods. While some countries thrived under mercantilist strategies, others experienced long-term economic challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is mercantilism in simple terms?
A1: Mercantilism is an economic doctrine that emphasizes the importance of a favorable balance of trade, state intervention, and the accumulation of precious metals to achieve national wealth and power.Q2: How did mercantilism influence colonial expansion?
A2: Mercantilism drove European nations to establish colonies to extract raw materials and secure markets for their manufactured goods, leading to extensive colonial empires.Q3: What are the main policies associated with mercantilism?
A3: Key policies include protectionism (tariffs and quotas), state intervention in the economy, and the pursuit of a trade surplus through export promotion and import restrictions.Q4: How does mercantilism differ from modern free trade theories?
A4: Mercantilism views international trade as a zero-sum game where one nation’s gain is another’s loss, whereas modern free trade theories argue that trade can be mutually beneficial and lead to overall economic growth.Q5: Can the principles of mercantilism be seen in today’s economy?
A5: Yes, elements of mercantilist thinking, such as protectionist policies and efforts to achieve a favorable trade balance, continue to influence modern economic policies and debates.
Modern Relevance and Current Trends
Though mercantilism as an economic system has largely faded, its legacy continues to shape modern economic thought and policy. Here are some trends and current developments related to what is mercantilism:
1. Protectionism and Trade Wars
- Resurgence of Nationalism: In recent years, many countries have adopted protectionist measures to shield domestic industries from foreign competition. These policies, reminiscent of mercantilist strategies, are often justified by a desire to secure national economic interests.
- Trade Disputes: Ongoing trade wars between major economies, such as those between the U.S. and China, reflect mercantilist concerns about trade deficits and the accumulation of wealth.
2. Economic Nationalism
- State-Led Economic Strategies: Some modern economies are returning to state-led economic policies that prioritize national industries, technology transfer, and self-sufficiency—a modern echo of mercantilist ideals.
- Subsidies and Tariffs: Government interventions in the form of subsidies, tariffs, and trade barriers are frequently debated as tools to achieve economic independence and competitiveness.
3. Globalization and Its Discontents
- Balancing Global and Local Interests: While globalization has increased interdependence among nations, it has also led to tensions over resource control, cultural identity, and economic sovereignty. Understanding mercantilism provides context for these debates.
- Sustainable Development: Modern discussions about sustainable development often involve balancing economic growth with environmental protection—a challenge that has parallels with the resource-driven policies of mercantilism.
4. Interdisciplinary Research and Policy Innovation
- Historical Analysis in Economics: Scholars continue to study mercantilism to understand its long-term impacts on economic development and international relations.
- Policy Lessons: Lessons from mercantilist practices inform contemporary policy debates, particularly in discussions about trade imbalances, economic sovereignty, and industrial policy.
Conclusion: Embracing the Lessons of Mercantilism
Our comprehensive exploration of what is mercantilism reveals that, although it is an economic doctrine from the past, its principles continue to resonate in modern economic and political debates. Mercantilism not only shaped the early modern world but also laid the groundwork for today’s discussions on trade, state intervention, and economic nationalism.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition: Mercantilism is an economic doctrine that emphasizes the accumulation of wealth—primarily through a favorable balance of trade and the accumulation of precious metals—through state intervention and protectionist policies.
- Historical Context: Emerging in 16th-century Europe, mercantilism influenced the rise of colonial empires and set the stage for modern economic theories.
- Core Principles: The pursuit of trade surpluses, protectionism, colonial expansion, and state intervention are central to mercantilist theory.
- Real-World Applications: Historical case studies, such as Spain’s colonial policies and England’s Navigation Acts, illustrate the practical application of mercantilist ideas.
- Modern Relevance: Elements of mercantilism continue to influence contemporary economic policies, particularly in debates over protectionism and economic nationalism.
- Practical Benefits: Understanding mercantilism provides valuable insights into the evolution of economic thought and helps inform policy decisions in a globalized world.
As you reflect on this guide, consider how the legacy of mercantilism continues to influence our modern economic landscape and international relations. Embracing what is mercantilism not only deepens our understanding of history but also equips us with the analytical tools to navigate today’s complex economic challenges.
Call to Action:
- Join the Conversation: Share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about mercantilism in the comments below. How do you see mercantilist ideas reflected in today’s global economy?
- Share This Post: If you found this guide insightful, please share it on social media or with friends, colleagues, and anyone interested in the history and evolution of economic thought.
- Keep Exploring: Continue your journey into the fascinating world of economic theory and international trade by exploring additional resources, enrolling in courses, and following the latest research on global economics.
Additional Resources
For further exploration of what is mercantilism and its impact on modern economics, consider these reputable sources:
- Encyclopedia Britannica – Mercantilism
- The History of Economic Thought – Mercantilism
- Investopedia – Mercantilism
- The Library of Economics and Liberty – Mercantilism
- TED Talks on Global Trade and Economic Policy
Final Thoughts
Mercantilism, with its emphasis on state power, trade surpluses, and resource accumulation, played a pivotal role in shaping early modern economies and colonial empires. Today, while the global economy has evolved, the echoes of mercantilist policies remain in contemporary debates over protectionism, economic nationalism, and trade imbalances. By understanding what is mercantilism, we gain not only insight into the past but also valuable perspectives that help inform the future of global economic policy.
Thank you for joining us on this comprehensive exploration of mercantilism. Stay curious, keep learning, and let the lessons of economic history empower you to navigate and shape the modern world.