What is Hydrolysis: Everything You Need to Know
Have you ever wondered how complex molecules break down into simpler ones with the help of water? Or how essential processes like digestion and cellular metabolism depend on a chemical reaction that might seem simple at first glance? In this comprehensive guide, we explore what is hydrolysis, a fascinating chemical reaction that plays a crucial role in both biological systems and industrial processes. Whether you’re a student, a science enthusiast, or a professional in the field, this article will walk you through the definition, history, mechanisms, applications, and modern trends surrounding hydrolysis.
Introduction: Unlocking the Secrets of Hydrolysis
Imagine being able to break down the complex polymers in your food into nutrients that your body can absorb. Or envision a process where water acts as a catalyst, splitting molecules and powering everything from digestion to biofuel production. This is the magic of hydrolysis. But what is hydrolysis exactly, and why is it so important?
In this article, we will cover:
- A clear and straightforward definition of hydrolysis, including its essential characteristics.
- Historical and contextual background that highlights key milestones in our understanding of hydrolysis.
- In-depth exploration of the mechanisms behind hydrolysis, including various types, examples, and real-world applications.
- The significance and benefits of hydrolysis in everyday life, from biological processes to industrial applications.
- Common misconceptions and FAQs to clear up any confusion.
- Modern relevance and current trends in hydrolysis research and application.
By the end of this post, you will have a robust understanding of what is hydrolysis and appreciate its indispensable role in science, technology, and life itself.
What is Hydrolysis? A Straightforward Definition
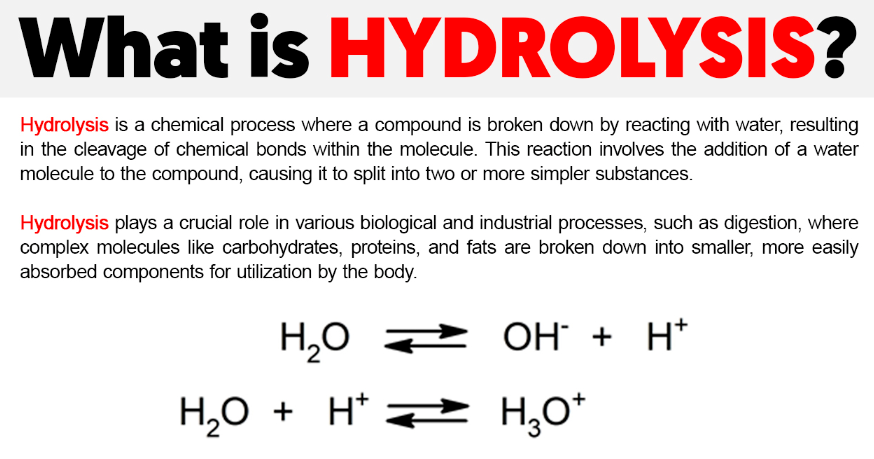
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which a molecule is cleaved into two parts by the addition of a water molecule. The term “hydrolysis” comes from the Greek words hydro, meaning water, and lysis, meaning to break apart. In this reaction, water serves as a reactant, providing the necessary elements to break chemical bonds in a compound.
Essential Characteristics of Hydrolysis
- Involves Water: At its core, hydrolysis requires water (H₂O) to split the target molecule.
- Bond Cleavage: The reaction breaks chemical bonds, typically resulting in the formation of two or more new compounds.
- Widely Occurring: Hydrolysis is a fundamental reaction in both biological systems (e.g., digestion, metabolism) and industrial processes (e.g., production of biofuels, synthesis of chemicals).
- Catalyzed Reactions: In many cases, hydrolysis is catalyzed by acids, bases, or enzymes, which speed up the reaction under milder conditions.
Understanding what is hydrolysis is crucial because it explains how water drives essential chemical transformations that impact everything from our daily nutrition to advanced manufacturing processes.
Historical and Contextual Background of Hydrolysis
The concept of hydrolysis has evolved over centuries, with early chemists and biologists laying the groundwork for our modern understanding.
Early Discoveries and Theoretical Foundations
- Ancient Observations: Although ancient scholars did not have the modern terminology, early observations of water’s ability to alter substances laid the groundwork for the concept of hydrolysis. For instance, early alchemists noticed that water could change the properties of various materials.
- Development of Chemical Science: With the advent of modern chemistry in the 18th and 19th centuries, scientists began to understand reactions at the molecular level. Researchers like Antoine Lavoisier and Jöns Jakob Berzelius made significant contributions to the study of chemical reactions, including those involving water.
- Enzyme Discovery: The discovery of enzymes in the 19th century further propelled our understanding of hydrolysis. Scientists realized that enzymes could accelerate hydrolytic reactions in biological systems, a breakthrough that laid the foundation for biochemistry.
Milestones in Hydrolysis Research
- Saponification: One of the earliest well-documented hydrolytic processes is saponification, the reaction by which fats are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids in the presence of a base. This process, known for producing soap, has been used for centuries.
- Digestive Enzymes: In the early 20th century, research into digestion revealed that enzymes like amylase and protease facilitate hydrolysis, breaking down carbohydrates and proteins into simpler molecules that the body can absorb.
- Industrial Applications: By the mid-20th century, hydrolysis began to play a critical role in industrial processes. The development of methods for hydrolyzing cellulose into sugars for biofuel production is one such example.
This historical journey demonstrates that what is hydrolysis is not only a central concept in chemistry but also one that has evolved alongside our technological and scientific advancements.
In-Depth Exploration of Hydrolysis: Mechanisms, Types, and Applications
To fully understand what is hydrolysis, we need to delve into the various mechanisms by which it occurs, the different types of hydrolytic reactions, and real-world examples that illustrate its significance.
1. The Mechanism of Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis involves a water molecule interacting with a target compound, leading to the cleavage of chemical bonds. The reaction generally follows these steps:
Step-by-Step Process
- Attack by Water: A water molecule approaches the compound and uses its lone pairs to attack a specific bond, often a covalent bond between atoms.
- Formation of Transition State: The attack results in the formation of a transition state, a temporary structure where bonds are partially broken and formed.
- Bond Cleavage: The chemical bond is cleaved, and the water molecule is split into a hydrogen ion (H⁺) and a hydroxide ion (OH⁻), which attach to the respective fragments of the original molecule.
- Formation of Products: The reaction concludes with the formation of two or more new compounds, each incorporating part of the original molecule and part of the water molecule.
Catalysis in Hydrolysis
- Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis: In an acid-catalyzed reaction, the presence of extra hydrogen ions (H⁺) from an acid increases the electrophilic character of certain atoms in the compound, making them more susceptible to attack by water.
- Base-Catalyzed Hydrolysis: In a base-catalyzed reaction, hydroxide ions (OH⁻) play the role of nucleophiles, attacking the target molecule and facilitating bond cleavage.
- Enzymatic Hydrolysis: Enzymes act as biological catalysts, dramatically increasing the rate of hydrolysis under the mild conditions found in living organisms. These enzymes are highly specific, often catalyzing hydrolysis for particular substrates.
2. Types of Hydrolysis Reactions
Hydrolysis can occur in various contexts, and it can be classified into several types based on the nature of the bonds broken and the environment in which the reaction occurs.
a. Ester Hydrolysis
- Definition: Ester hydrolysis involves the breakdown of an ester into an acid and an alcohol.
- Mechanism: In acid- or base-catalyzed conditions, water attacks the ester linkage, resulting in the formation of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
- Example: In the production of soaps, fats (which are esters) are hydrolyzed through saponification to produce glycerol and fatty acid salts (soap).
b. Amide Hydrolysis
- Definition: Amide hydrolysis is the cleavage of an amide bond, resulting in a carboxylic acid and an amine.
- Mechanism: This reaction is typically slower than ester hydrolysis due to the resonance stabilization in amides, often requiring higher temperatures or catalysts.
- Example: Protein digestion involves the hydrolysis of peptide bonds (a type of amide bond) to yield amino acids, a process essential for nutrition.
c. Glycosidic Bond Hydrolysis
- Definition: This reaction involves the cleavage of glycosidic bonds found in carbohydrates.
- Mechanism: Enzymes such as amylase hydrolyze glycosidic bonds in starch, breaking it down into simpler sugars like maltose and glucose.
- Example: The digestion of dietary starch in humans relies on glycosidic bond hydrolysis, making complex carbohydrates accessible for energy production.
d. ATP Hydrolysis
- Definition: ATP (adenosine triphosphate) hydrolysis is the process by which ATP loses one of its phosphate groups, releasing energy.
- Mechanism: Water reacts with ATP, breaking the bond between the phosphate groups and yielding ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and an inorganic phosphate.
- Example: ATP hydrolysis is the primary energy source for many cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and active transport across membranes.
3. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
a. Digestion and Metabolism
- Overview: In biological systems, hydrolysis is fundamental to the digestion and metabolism of food.
- Case Study: When you eat a meal, enzymes in your saliva, stomach, and intestines catalyze the hydrolysis of complex molecules like proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. This process breaks them down into simpler molecules (amino acids, sugars, and fatty acids) that can be absorbed and utilized by the body.
- Importance: Without hydrolysis, essential nutrients would remain locked in complex structures, and life as we know it would not be possible.
b. Industrial Applications
- Overview: Hydrolysis is widely used in various industries, from chemical manufacturing to environmental management.
- Case Study: In the production of biofuels, lignocellulosic biomass (such as agricultural waste) is hydrolyzed to release sugars. These sugars are then fermented into ethanol, a renewable fuel source.
- Importance: Hydrolysis enables the conversion of non-food biomass into valuable energy resources, promoting sustainability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
c. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- Overview: The synthesis and breakdown of compounds via hydrolysis are central to pharmaceutical development.
- Case Study: Many drug delivery systems rely on hydrolysis for controlled release. For example, biodegradable polymers used in drug encapsulation slowly hydrolyze in the body, ensuring a steady release of the therapeutic agent.
- Importance: Understanding what is hydrolysis and how to control it is essential for creating effective and safe pharmaceutical products.
Importance, Applications, and Benefits of Hydrolysis
The study of what is hydrolysis is not just academic—it has practical implications that affect our daily lives, industries, and even environmental policies.
Biological Significance
- Digestion and Nutrition: Hydrolysis is vital for breaking down food into absorbable nutrients, which in turn supports growth, energy production, and overall health.
- Cellular Energy: The hydrolysis of ATP is a cornerstone of cellular energy transfer, enabling a vast array of biological functions.
- Enzymatic Reactions: Many metabolic pathways depend on enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis, which ensures that complex molecules are converted into simpler forms that cells can use.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
- Manufacturing Processes: Hydrolysis reactions are employed in the synthesis of chemicals, production of biofuels, and manufacturing of everyday products like soaps and detergents.
- Environmental Management: Hydrolysis plays a role in waste treatment and pollution control. For example, the breakdown of pollutants in water treatment facilities often involves hydrolytic reactions.
- Pharmaceuticals: Controlled hydrolysis is used in drug design and delivery, enhancing the effectiveness and safety of medications.
Technological Innovations
- Green Chemistry: Hydrolysis is a key reaction in the development of environmentally friendly chemical processes. By using water as a reactant, industries can reduce the use of hazardous chemicals and promote sustainability.
- Material Science: The hydrolysis of polymers is crucial in designing biodegradable materials that can reduce plastic waste and environmental pollution.
Societal and Economic Benefits
- Health and Well-Being: Improved understanding of hydrolysis has led to advances in nutrition, medicine, and health care, directly impacting quality of life.
- Sustainable Energy: Hydrolysis-based technologies in biofuel production contribute to energy security and environmental sustainability.
- Innovation and Job Creation: Industries that rely on hydrolytic processes drive innovation and create employment opportunities in research, manufacturing, and environmental management.
Addressing Common Misconceptions and FAQs about Hydrolysis
Despite its wide applications, several misconceptions about what is hydrolysis persist. Here, we clarify common myths and provide straightforward answers to frequently asked questions.
Misconception 1: Hydrolysis is Only Relevant in Biology
- Clarification: While hydrolysis is crucial in biological systems, it is also a fundamental chemical reaction in industrial processes, environmental management, and material science. Its applications span from the microscopic level in cells to large-scale manufacturing operations.
Misconception 2: All Hydrolysis Reactions Occur at the Same Rate
- Clarification: The rate of hydrolysis varies greatly depending on the chemical structure of the substrate, the conditions (such as temperature and pH), and the presence of catalysts (acid, base, or enzymes). For example, ATP hydrolysis is rapid and highly regulated, while amide hydrolysis may require harsher conditions.
Misconception 3: Hydrolysis is a Simple Process
- Clarification: Although the basic concept of hydrolysis is straightforward—using water to break bonds—the underlying mechanisms can be complex, involving various catalysts, intermediate steps, and specific conditions that determine the reaction’s outcome.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the role of catalysts in hydrolysis reactions?
A: Catalysts, including acids, bases, and enzymes, increase the rate of hydrolysis by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction. They ensure that the reaction proceeds efficiently under milder conditions than would otherwise be possible.
Q2: Can hydrolysis be reversed?
A: In some cases, hydrolysis is reversible. The reverse reaction, known as condensation or dehydration synthesis, involves the removal of a water molecule to form a new bond. The equilibrium between these reactions depends on the conditions such as water concentration and temperature.
Q3: How does temperature affect hydrolysis?
A: Temperature can significantly impact the rate of hydrolysis. Higher temperatures generally increase the reaction rate by providing more kinetic energy, although excessively high temperatures may also lead to unwanted side reactions or degradation of sensitive compounds.
Q4: Why is hydrolysis important in environmental processes?
A: Hydrolysis is essential in environmental processes such as the degradation of pollutants and waste management. It helps break down harmful compounds into less toxic substances, facilitating natural recycling and remediation efforts.
Modern Relevance and Current Trends in Hydrolysis
The concept of what is hydrolysis continues to evolve as new technologies and research methods shed light on its diverse applications and potential.
1. Advances in Enzymatic Hydrolysis
- Biotechnology: Recent advances in biotechnology have led to the development of highly specific enzymes that catalyze hydrolysis with exceptional efficiency. These enzymes are being harnessed in biofuel production, waste management, and the synthesis of high-value chemicals.
- Case Example: Researchers are engineering novel enzymes capable of breaking down cellulose more effectively, paving the way for more efficient conversion of plant biomass into renewable energy.
2. Hydrolysis in Green Chemistry
- Sustainable Processes: Modern chemical research emphasizes green chemistry, where hydrolysis plays a central role. By utilizing water as a benign reagent, industries are reducing the reliance on hazardous solvents and chemicals.
- Impact: Green hydrolysis methods contribute to safer industrial processes and a lower environmental footprint, aligning with global sustainability goals.
3. Nanotechnology and Material Science
- Innovative Materials: In the field of material science, controlled hydrolysis is used to synthesize novel nanomaterials and biodegradable polymers. These materials have applications in medicine, packaging, and environmental remediation.
- Emerging Trends: Nanotechnology research is exploring how hydrolysis can be optimized to create materials with specific properties, such as enhanced strength or controlled degradation rates.
4. Computational Modeling and Simulation
- Predictive Tools: Advances in computational chemistry have enabled the simulation of hydrolysis reactions at the molecular level. These models help predict reaction kinetics, optimize conditions, and design more efficient catalysts.
- Application: Computational models are now integral in academic and industrial research, reducing the time and cost associated with experimental trials.
5. Integration with Renewable Energy Technologies
- Biofuel Production: As the world seeks renewable energy sources, hydrolysis is becoming increasingly important in converting biomass into biofuels. The development of cost-effective hydrolytic processes is key to making biofuels a viable alternative to fossil fuels.
- Future Directions: Ongoing research aims to improve the efficiency of hydrolysis in converting lignocellulosic biomass, thereby enhancing the sustainability of biofuel production.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Hydrolysis
In our exploration of what is hydrolysis, we have uncovered the intricate processes by which water breaks chemical bonds and transforms molecules. From its fundamental role in digestion and cellular energy to its wide-ranging applications in industry, pharmaceuticals, and environmental management, hydrolysis is a cornerstone of both natural and engineered systems.
Key Takeaways
- Definition and Mechanism: Hydrolysis is a reaction where water is used to break chemical bonds, producing new compounds. It is characterized by its reliance on water, the involvement of catalysts, and its varied rates and conditions.
- Historical Evolution: The concept of hydrolysis has evolved over centuries—from early observations to modern enzyme research—highlighting its critical role in both biological and industrial processes.
- Diverse Applications: Hydrolysis is essential for digestion, ATP production, soap making, biofuel production, and many other processes that impact daily life and the global economy.
- Modern Relevance: Advances in biotechnology, green chemistry, nanotechnology, and computational modeling are driving innovative applications of hydrolysis, making it more efficient and sustainable.
- Common Misconceptions: By understanding the nuances of hydrolysis, we can dispel myths and appreciate its complexity and versatility.
Call-to-Action
Now that you have a deeper understanding of what is hydrolysis, we encourage you to:
- Explore Further: Delve into additional resources such as scientific journals, educational websites like PubChem, or textbooks on chemical kinetics to expand your knowledge.
- Engage with Science: Whether you’re a student or a professional, consider how the principles of hydrolysis apply to your field of study or work. Participate in discussions, online forums, or local science events to share insights.
- Share Your Thoughts: If you found this article insightful, share it with friends, colleagues, or on social media. We invite you to leave comments or questions below—your engagement helps spread knowledge and fosters a deeper appreciation for the chemical processes that shape our world.
- Keep Learning: The world of chemistry is ever-evolving. Stay updated on new research and breakthroughs in hydrolysis and related fields by subscribing to reputable science news outlets and academic journals.
By embracing the science of hydrolysis, we not only gain insight into the molecular mechanisms of life but also unlock innovative solutions for some of today’s most pressing challenges in energy, health, and the environment.
Additional Resources and Further Reading
For those eager to explore more about what is hydrolysis and its many applications, here are some recommended resources:
Books:
- “Organic Chemistry” by Paula Yurkanis Bruice – A comprehensive text covering reaction mechanisms, including hydrolysis.
- “Biochemistry” by Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, and Lubert Stryer – Explores enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis and metabolic pathways.
- “Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice” by Paul T. Anastas and John C. Warner – Delves into environmentally friendly chemical processes, including hydrolytic reactions.
Websites:
- Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) – Provides educational materials and research updates on various chemical reactions.
- Khan Academy – Offers free tutorials and videos on chemical reactions, including hydrolysis.
- American Chemical Society (ACS) – Features articles and research highlights on contemporary chemical processes.
Online Courses:
- Coursera and edX offer courses in organic chemistry and biochemistry that cover hydrolysis mechanisms and applications.
- MIT OpenCourseWare provides free access to lecture notes and videos on chemical engineering and reaction kinetics.
Academic Journals:
- Journal of the American Chemical Society – Publishes cutting-edge research in chemistry, including studies on hydrolysis.
- Green Chemistry – Focuses on sustainable chemical processes, often featuring innovative hydrolysis techniques.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what is hydrolysis means delving into a chemical reaction that is as fundamental as it is transformative. Whether it’s breaking down food in your digestive system, powering cellular processes through ATP hydrolysis, or enabling the production of sustainable fuels, hydrolysis is a process that touches every aspect of life and industry. By grasping the principles of hydrolysis, we equip ourselves with knowledge that can drive innovation, enhance sustainability, and foster a deeper appreciation for the intricate dance of molecules that underpins our existence.
Thank you for joining us on this in-depth exploration of hydrolysis. We hope this guide has clarified your understanding of this essential chemical reaction and inspired you to further investigate its many applications. Please feel free to share your thoughts, ask questions, or contribute additional insights in the comments below. Your participation is invaluable in spreading the knowledge of science and its profound impact on our world.