“What Is Absolute Zero? Everything You Need to Know”
Have you ever wondered about the lowest possible temperature in the universe—an unimaginable chill where all molecular motion nearly stops? Imagine a world where nothing moves at all, where even the tiniest vibration of atoms ceases. If you’ve ever asked yourself, what is absolute zero, then you’re in the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the concept of absolute zero. We’ll define what absolute zero is, explore its historical evolution, break down its essential characteristics, and discuss its significance in science, technology, and everyday life. Whether you’re a student of physics, a curious learner, or a professional in the scientific community, this article will provide you with everything you need to know about what is absolute zero and why it matters.
Introduction: The Ultimate Chill in Our Universe
Imagine a temperature so low that all molecular motion nearly stops—a state where matter reaches its absolute calm. This is the realm of absolute zero, a concept that challenges our everyday understanding of heat and energy. But what is absolute zero? More than just a number on a temperature scale, absolute zero represents the theoretical limit of how cold something can get. It is the point at which a substance would have minimal thermal energy, and its atoms would be at their lowest possible energy state.
An Intriguing Fact
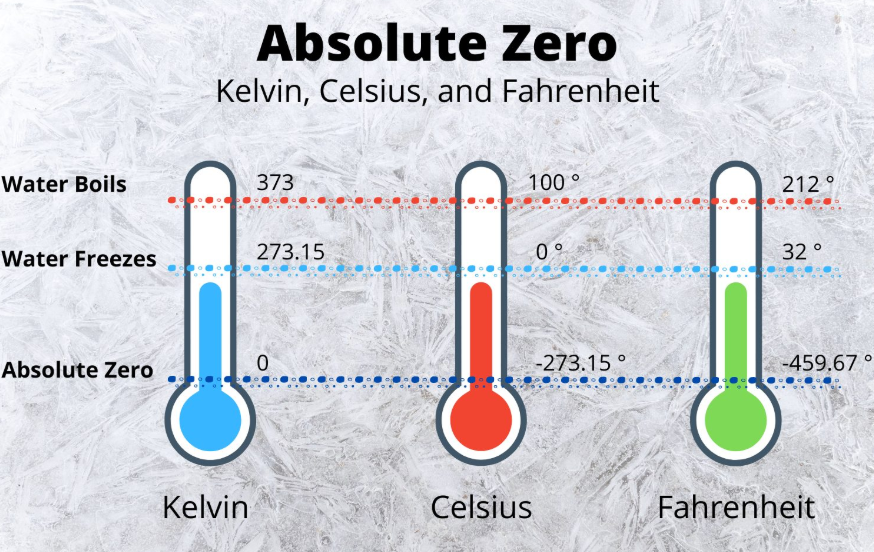
Did you know that absolute zero is defined as 0 Kelvin (K), which is equivalent to -273.15°C or -459.67°F? This figure isn’t arbitrary; it is based on fundamental physical laws. At absolute zero, classical motion of particles would theoretically stop, and only quantum mechanical motion (zero-point energy) would remain. Despite being an unattainable ideal in practice, absolute zero is a crucial reference point in thermodynamics and low-temperature physics.
What This Post Will Cover and Why It Matters
In today’s post, we will explore:
- Definition and Core Characteristics:
What exactly is absolute zero? We will provide a clear, concise definition and explain its fundamental properties. - Historical and Contextual Background:
Discover the origins of the concept, from early thermodynamic theories to modern quantum mechanics. Learn about key milestones and notable historical anecdotes that have shaped our understanding. - In-Depth Exploration:
We’ll break down the science behind absolute zero, including discussions of temperature scales, molecular motion, and quantum effects. Real-world examples and case studies will illustrate how scientists study and apply the concept. - Importance, Applications, and Benefits:
Understand why absolute zero is essential in fields such as cryogenics, superconductivity, astrophysics, and advanced materials science. We’ll discuss how this concept drives technological innovations and deepens our understanding of the universe. - Addressing Common Misconceptions and FAQs:
We’ll clear up common myths and answer frequently asked questions about absolute zero in a short Q&A section. - Modern Relevance and Current Trends:
Explore recent developments in ultra-low temperature physics, including breakthroughs in Bose-Einstein condensates and quantum computing. See how ongoing research continues to push the boundaries of what is possible. - Conclusion and Call-to-Action:
A succinct summary of the key points and an invitation to reflect, share your insights, and further explore the exciting world of thermodynamics and quantum physics.
Understanding what is absolute zero is crucial because it is the bedrock of thermodynamics, a fundamental concept in physics that underpins everything from energy production to the behavior of materials at extreme temperatures. Whether you’re fascinated by the science of the very cold or interested in its practical applications, this guide will enrich your knowledge and inspire your curiosity.
What Is Absolute Zero? A Straightforward Definition
Defining Absolute Zero
At its core, what is absolute zero? Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which a thermodynamic system reaches its lowest possible energy state. It is defined as 0 Kelvin (K), equivalent to -273.15 degrees Celsius (°C) or -459.67 degrees Fahrenheit (°F). At this point, the particles within a substance would possess minimal thermal energy, and classical molecular motion would cease—although due to quantum mechanics, a residual “zero-point” energy remains.
Essential Characteristics of Absolute Zero
To fully understand what is absolute zero, consider these defining properties:
- Theoretical Limit:
Absolute zero represents the lowest limit on the thermodynamic temperature scale. It is a benchmark rather than an achievable state in practice. - Minimal Thermal Energy:
At absolute zero, particles have minimal vibrational motion. In classical terms, they would be completely still; in quantum terms, however, they retain zero-point energy. - Universal Standard:
Absolute zero serves as a reference point in the Kelvin scale and is integral to the laws of thermodynamics and statistical mechanics. - Implications for Material Behavior:
As temperatures approach absolute zero, substances exhibit unique properties—such as superconductivity in certain materials—that are fundamentally different from their behavior at higher temperatures. - Scientific Significance:
Although absolute zero is never reached in practice, experiments in ultra-low temperature physics strive to get as close as possible. These experiments help scientists understand quantum phenomena and the fundamental limits of physical systems.
These core characteristics highlight that what is absolute zero is not just a number—it is a crucial concept that informs our understanding of energy, matter, and the fundamental laws of nature.
Historical and Contextual Background
The Evolution of the Concept of Absolute Zero
The journey to understand what is absolute zero spans centuries of scientific inquiry, from early thermodynamic experiments to modern quantum mechanics.
Early Thermodynamic Theories
- Pre-Modern Ideas:
Long before the modern scientific method, ancient and medieval scholars pondered the nature of heat and cold. Early thinkers like the Greek philosopher Empedocles speculated about the elements and their transformations, laying the groundwork for later studies in thermodynamics. - The Birth of Thermodynamics:
In the 17th and 18th centuries, scientists such as Robert Boyle and Joseph Black began to study heat, energy, and temperature more systematically. Their experiments led to the development of early temperature scales and the understanding that there is a lower limit to temperature.
The Kelvin Scale and Scientific Milestones
- William Thomson (Lord Kelvin):
The modern concept of absolute zero was formalized in the mid-19th century by William Thomson, later known as Lord Kelvin. He developed the Kelvin scale, which defines absolute zero as 0 K—the point at which molecular motion is minimized. - Advances in Low-Temperature Physics:
The 20th century witnessed tremendous progress in reaching temperatures close to absolute zero. Techniques such as laser cooling and evaporative cooling have allowed scientists to create ultracold environments where quantum phenomena, such as Bose-Einstein condensates, can be observed. - Quantum Mechanics:
The development of quantum mechanics in the early 20th century further refined our understanding of absolute zero, introducing the concept of zero-point energy—the minimal energy that particles retain even at absolute zero.
Notable Historical Anecdotes
- The Quest for Absolute Zero:
Early experiments in cryogenics aimed to reach ever-lower temperatures, culminating in breakthroughs that allowed scientists to approach absolute zero within fractions of a degree. These experiments have not only advanced our understanding of physics but have also led to technological innovations such as superconductors and ultra-sensitive detectors. - Scientific Debates:
The idea of absolute zero has sparked debates among scientists and philosophers about the nature of energy and the limits of cooling, debates that continue in modern research as physicists explore the quantum realm.
This historical context underscores that what is absolute zero is a concept rooted in centuries of scientific progress and remains a central topic in modern physics.
In-Depth Exploration: Types, Attributes, and Categories of Systems Related to Absolute Zero
To truly appreciate what is absolute zero, we must explore its implications, applications, and the science behind it. In this section, we break down the key components, experimental approaches, and phenomena associated with absolute zero.
1. Temperature Scales and the Concept of Zero
Understanding Temperature
- Definition of Temperature:
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. The higher the temperature, the faster the particles move. - The Kelvin Scale:
The Kelvin scale is the standard unit of thermodynamic temperature used in science. It is an absolute scale, meaning it starts at absolute zero (0 K). Unlike Celsius and Fahrenheit, Kelvin does not use the degree symbol (e.g., 0 K).
Historical Development of the Kelvin Scale
- Lord Kelvin’s Contribution:
Lord Kelvin proposed the absolute temperature scale in the 19th century, establishing 0 K as the point where particles have minimal thermal motion. This scale revolutionized the study of thermodynamics by providing a true zero point. - Comparisons with Other Scales:
While the Celsius scale sets the freezing point of water at 0 °C and boiling point at 100 °C, the Kelvin scale aligns with these values but shifts the zero point to absolute zero. For example, 0 °C is equivalent to 273.15 K.
2. The Physical Meaning of Absolute Zero
Molecular Motion at Absolute Zero
- Classical Perspective:
In classical physics, as temperature decreases, the kinetic energy of particles decreases. At absolute zero, theoretically, particles would be at a complete standstill. - Quantum Perspective and Zero-Point Energy:
However, quantum mechanics introduces the concept of zero-point energy, meaning that even at 0 K, particles retain a minimal amount of energy due to the uncertainty principle. This energy prevents particles from being completely motionless.
Experimental Approaches to Reaching Absolute Zero
- Cryogenics:
The study of extremely low temperatures, known as cryogenics, has developed techniques to approach absolute zero. Methods include:- Laser Cooling: Using lasers to reduce the kinetic energy of atoms.
- Evaporative Cooling: Allowing the most energetic particles to escape, thereby lowering the temperature of the remaining particles.
- Modern Achievements:
Scientists have achieved temperatures within billionths of a Kelvin above absolute zero. These ultracold conditions have enabled the observation of quantum phenomena that are otherwise hidden at higher temperatures.
3. Phenomena and Applications at Ultracold Temperatures
Superconductivity
- Definition:
Superconductivity is a phenomenon where a material conducts electricity with zero resistance when cooled below a certain critical temperature, which is often very close to absolute zero. - Practical Applications:
Superconductors are used in medical imaging (MRI machines), particle accelerators, and potentially in future energy transmission systems, reducing energy loss.
Bose-Einstein Condensates (BEC)
- Definition:
A Bose-Einstein condensate is a state of matter formed when particles known as bosons are cooled to temperatures very near absolute zero, causing them to occupy the same quantum state. - Significance:
BECs allow scientists to observe quantum phenomena on a macroscopic scale, providing insights into the behavior of matter at ultracold temperatures. - Real-World Example:
In 1995, researchers achieved the first Bose-Einstein condensate with rubidium atoms, a breakthrough that has since spurred extensive research in quantum physics.
Other Applications in Low-Temperature Physics
- Quantum Computing:
Ultralow temperatures are critical for the operation of quantum computers, where superconducting circuits and quantum bits (qubits) require near-absolute zero conditions to function properly. - Sensitive Detectors:
Cryogenic detectors, which operate at very low temperatures, are used in astrophysics and particle physics to detect faint signals that would otherwise be lost in thermal noise.
Importance, Applications, and Benefits of Understanding What Is Absolute Zero
Understanding what is absolute zero is crucial for multiple reasons that extend far beyond academic curiosity. Here are some of the key benefits and applications:
1. Advancing Scientific Research and Innovation
- Fundamental Physics:
Absolute zero is a cornerstone concept in thermodynamics and quantum mechanics. Understanding it enables scientists to probe the limits of matter and energy, leading to groundbreaking discoveries in fields such as condensed matter physics and quantum computing. - Technological Breakthroughs:
Research at ultralow temperatures has led to the development of superconductors, quantum sensors, and other advanced materials that have practical applications in medicine, energy, and technology. - New States of Matter:
Investigations into conditions near absolute zero have revealed unique states of matter, such as Bose-Einstein condensates, which help us understand the behavior of particles in extreme environments.
2. Practical Applications in Industry and Medicine
- Cryogenics and Medical Imaging:
Technologies such as MRI machines rely on superconducting magnets, which require ultracold temperatures to operate efficiently. Advances in cryogenics also contribute to the preservation of biological samples and organs. - Energy Efficiency:
Superconductors, which function near absolute zero, promise revolutionary improvements in energy transmission by eliminating resistance and reducing power loss. - Quantum Technologies:
The field of quantum computing, which could transform industries from cybersecurity to pharmaceuticals, depends on maintaining systems at temperatures near absolute zero to preserve quantum coherence.
3. Enhancing Education and Public Understanding
- Science Literacy:
Grasping the concept of absolute zero enhances our overall understanding of temperature, energy, and the laws of physics. It fosters curiosity and critical thinking, essential skills in science education. - Interdisciplinary Learning:
The study of absolute zero intersects with various fields, including physics, chemistry, and engineering. This multidisciplinary approach enriches educational curricula and prepares students for the challenges of modern research. - Inspiring Future Generations:
The pursuit of absolute zero and the fascinating phenomena it reveals—like superconductivity and Bose-Einstein condensates—can inspire students to pursue careers in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics).
4. Societal and Economic Impact
- Innovation and Competitiveness:
Countries and companies that invest in low-temperature research and technology gain a competitive edge in the global market. Advances in this field drive innovation in industries ranging from healthcare to energy. - Sustainability:
Improved energy transmission through superconductors and other technologies emerging from low-temperature physics can contribute to more sustainable and efficient energy systems, reducing environmental impact and supporting economic growth. - Policy and Research Funding:
A deep understanding of fundamental scientific concepts like absolute zero helps shape public policy and drive research funding. This, in turn, fosters a scientific community that pushes the boundaries of what is possible.
Addressing Common Misconceptions and FAQs
Despite its importance, several misconceptions persist about what is absolute zero. Let’s clear up these myths and answer some frequently asked questions.
Misconception 1: Absolute Zero Means All Motion Stops Completely
Myth:
Some people believe that at absolute zero, all particle motion ceases entirely.
Reality:
- Quantum Zero-Point Energy:
Even at absolute zero, particles retain a minimal level of energy known as zero-point energy due to the uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics. This means that while classical motion would theoretically stop, quantum fluctuations persist. - Theoretical vs. Practical:
Absolute zero is a theoretical limit that cannot be reached in practice. Scientists can come very close, but some residual energy always remains.
Misconception 2: Absolute Zero Can Be Achieved in Everyday Conditions
Myth:
There is a belief that absolute zero can be reached with simple cooling techniques.
Reality:
- Unattainable Ideal:
Absolute zero represents the lowest possible temperature on the Kelvin scale, and while scientists can achieve temperatures extremely close to it, reaching absolute zero itself is impossible due to fundamental physical laws. - Specialized Laboratories:
Experiments approaching absolute zero require highly specialized equipment and controlled environments, far beyond everyday conditions.
Misconception 3: Absolute Zero Has No Practical Applications
Myth:
Some assume that absolute zero is only of theoretical interest with no real-world benefits.
Reality:
- Technological Applications:
Research near absolute zero has led to the development of superconductors, advanced cryogenics, and quantum computing technologies. - Scientific Breakthroughs:
Understanding absolute zero has been key to discovering new states of matter, such as Bose-Einstein condensates, and has informed numerous practical applications in various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is absolute zero?
A: Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which a system reaches its minimum internal energy, defined as 0 Kelvin (0 K), equivalent to -273.15°C or -459.67°F. At this temperature, the thermal motion of particles is minimized, though quantum fluctuations (zero-point energy) still persist.Q: Why can’t we reach absolute zero?
A: According to the third law of thermodynamics, it is impossible to reach absolute zero through any finite number of processes. As a system gets closer to absolute zero, removing additional energy becomes increasingly difficult, and quantum effects prevent complete stillness.Q: What happens to materials at temperatures near absolute zero?
A: Materials exhibit unique properties near absolute zero. For example, some materials become superconductors, meaning they conduct electricity without resistance, while others form Bose-Einstein condensates, a state of matter where particles occupy the same quantum state.Q: How is absolute zero measured?
A: Absolute zero is measured using the Kelvin scale, which is an absolute temperature scale starting at 0 K. Instruments such as cryogenic thermometers and advanced spectroscopic methods are used to measure temperatures in the ultracold range.Q: What are some applications of research conducted near absolute zero?
A: Research near absolute zero has led to significant technological advancements, including the development of superconducting materials, improvements in quantum computing, and enhanced medical imaging techniques. It also provides insights into the fundamental laws of physics and the behavior of matter under extreme conditions.
Modern Relevance and Current Trends
Absolute Zero in Today’s Technological and Scientific Landscape
In today’s high-tech world, the quest to approach absolute zero continues to drive innovation and discovery. Here’s how what is absolute zero remains a critical concept in modern research and applications:
Advances in Cryogenics and Low-Temperature Physics
- Cutting-Edge Research:
Scientists are constantly pushing the boundaries of how close they can get to absolute zero. Advances in cryogenic techniques, such as laser cooling and evaporative cooling, have enabled researchers to reach temperatures mere billionths of a degree above absolute zero. - Quantum Phenomena:
At these ultralow temperatures, quantum effects become pronounced. The study of Bose-Einstein condensates and superfluidity has opened up new avenues in understanding quantum mechanics and developing new materials with extraordinary properties.
Impact on Technology and Innovation
- Superconductivity:
The discovery of superconductivity—a state where materials conduct electricity with zero resistance at very low temperatures—has profound implications for energy transmission, magnetic levitation, and medical imaging. Modern superconducting technologies are integral to applications such as MRI machines and particle accelerators. - Quantum Computing:
Many quantum computing systems rely on ultracold environments to maintain quantum coherence in qubits. Achieving temperatures near absolute zero is essential for the operation of these next-generation computing systems, which promise to revolutionize information processing. - Precision Measurements:
Low-temperature physics enables highly sensitive measurement devices used in various scientific fields, including astronomy, particle physics, and materials science. These instruments can detect minute changes in energy and matter, leading to groundbreaking discoveries.
Global and Societal Implications
- Environmental Sustainability:
Advances in cryogenics and superconductivity have the potential to improve energy efficiency and reduce energy losses in power grids, contributing to more sustainable energy practices. - Economic and Industrial Impact:
The technologies developed from low-temperature research drive innovation across multiple industries, from healthcare and transportation to electronics and renewable energy. Investing in low-temperature research can yield significant economic benefits by fostering new technologies and industries.
Educational and Cultural Influence
- STEM Education:
The study of absolute zero is a key component of physics and chemistry curricula around the world. It inspires students to explore the frontiers of science and understand the underlying principles of energy and matter. - Public Outreach:
Documentaries, science museums, and online educational platforms frequently feature ultracold physics and the quest for absolute zero, sparking public interest and curiosity about the natural world.
Conclusion: The Ultimate Frontier of Cold
In exploring what is absolute zero, we have journeyed into one of the most fascinating and fundamental concepts in science. Absolute zero is not just a number on a thermometer—it is the theoretical limit of temperature, a benchmark for understanding the behavior of matter, and a gateway to uncovering the mysteries of the quantum world. From the earliest thermodynamic theories to modern breakthroughs in quantum computing and superconductivity, the pursuit of absolute zero has driven scientific progress and technological innovation.
Key Takeaways
- Definition and Core Concepts:
Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature at which a system has minimal internal energy, defined as 0 Kelvin (0 K), or -273.15°C (-459.67°F). It represents the theoretical point where molecular motion nearly ceases, though quantum fluctuations persist. - Historical Evolution:
The concept of absolute zero has evolved from early studies of heat and energy in ancient civilizations to a cornerstone of modern thermodynamics and quantum mechanics, significantly influenced by pioneers such as Lord Kelvin and Albert Einstein. - Diverse Applications:
Research near absolute zero has led to transformative advancements in superconductivity, Bose-Einstein condensates, quantum computing, and precision measurement, impacting various fields including medicine, energy, and technology. - Modern Relevance:
In today’s digital and globalized world, the exploration of ultralow temperatures continues to drive innovation, foster sustainable practices, and push the boundaries of scientific knowledge. - Practical and Societal Impact:
Understanding absolute zero is essential for addressing real-world challenges, from improving energy efficiency to developing new medical technologies, while also deepening our grasp of the fundamental laws that govern the universe.
Call-to-Action
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of what is absolute zero, here’s how you can put this knowledge to work:
- Explore Further:
Delve deeper into the fascinating world of low-temperature physics by reading additional resources. Check out reputable sites such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) or MIT Technology Review for the latest research on ultracold technologies. - Join the Conversation:
Share your thoughts, questions, or insights in the comments below. How has learning about absolute zero changed your perspective on energy, matter, or the limits of physical science? - Spread the Knowledge:
If you found this post informative, please share it with friends, colleagues, or anyone interested in the cutting-edge world of physics. Use social media hashtags like #WhatIsAbsoluteZero and #LowTemperatureScience to join the broader discussion. - Apply in Your Field:
Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional, use your understanding of absolute zero to inform your work—be it in developing new technologies, conducting scientific research, or engaging in public education about science.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what is absolute zero is a gateway to exploring the ultimate limits of temperature and energy. It challenges our perceptions of matter and motion, revealing a world where classical physics gives way to quantum phenomena. From the foundational theories that describe the behavior of particles to the modern applications that power technological breakthroughs, absolute zero remains one of the most intriguing and essential concepts in science.
As you continue your exploration of the physical world, remember that every scientific breakthrough begins with a fundamental understanding of nature’s limits. Embrace the knowledge of absolute zero, let it inspire your curiosity, and use it as a stepping stone to unlock new ideas and innovations.
Thank you for joining us on this in-depth exploration of what is absolute zero. We hope this guide has enriched your understanding, sparked your interest, and provided valuable insights into one of the cornerstones of modern physics. Happy exploring, and may your journey into the world of ultracold science lead you to endless discoveries and inspiration!