Table of Contents
Toggle7.8 Continuing Evolution
The Constant Evolution of Life
Evolution is not a process that occurred only in the distant past; it is an ongoing process that shapes life around us every day. Genomic changes, natural selection, and population-level adaptations continue to provide evidence for evolutionary theory and give insights into how species, including bacteria and pathogens, evolve over time. Let’s explore some key mechanisms that drive continuing evolution! 🌍
Genomic Changes
One of the strongest arguments for evolution is that we see genomic changes occurring in almost every species, not just a few. Genomic changes include mutations, recombination, and natural selection that lead to adaptations and, in some cases, new species. These changes highlight the influence of a shared common ancestor among organisms.
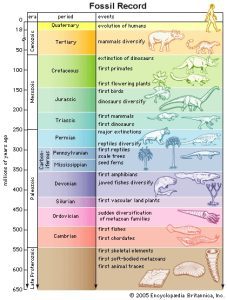
As scientists uncover fossils, they observe continuous changes in their characteristics and the fossil record overall, which helps us trace back the evolutionary lineage of various organisms. 📜 Fossils serve as direct evidence of change and allow scientists to connect historical organisms to modern species.
Natural Selection in Action
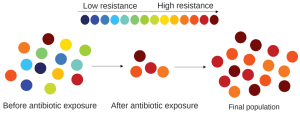
One of the most visible forms of evolution in our time is the constant adaptation of bacteria to resist antibiotics. This phenomenon is a form of natural selection, sometimes referred to as “malicious natural selection.” When a new antibiotic is introduced, most bacteria die; however, some bacteria may carry a mutation that makes them resistant. These resistant bacteria survive, reproduce, and pass along that mutation, resulting in an antibiotic-resistant population.

This cycle continues not only with antibiotics but also with pesticides, herbicides, and chemotherapy drugs. The continuous adaptation of pathogens also leads to the emergence of diseases that were previously eradicated or new strains of existing diseases. Evolution in action is never-ending! 🔄
Population Evolution: A Recap
The central idea of evolution involves populations, not individuals. Populations of organisms evolve over time through mechanisms like natural selection and genetic drift. Genetic variation within a population allows individuals with advantageous traits to survive and reproduce. Over generations, these adaptations accumulate, leading to significant changes in the genetic makeup and, eventually, the development of new species. 👑
Ways Populations Evolve
Genomic Changes Over Time: The genetic composition of populations changes due to mutations, genetic drift, and gene flow. These changes create new traits or eliminate existing ones, contributing to the diversity of life. 🧬

Continuous Change in the Fossil Record: Fossil evidence supports evolution by showing gradual changes in the physical characteristics of organisms. Extinct species provide valuable information about how ancient organisms evolved into the species we know today. 🦖
Evolution of Resistance: Organisms like bacteria, pests, and viruses evolve resistance to antibiotics, pesticides, and herbicides. This evolution occurs because individuals with natural resistance are able to survive and reproduce, leading to a population-level resistance. This phenomenon is a growing concern in medicine, agriculture, and public health. 💊
Pathogens and Emerging Diseases: Pathogens like viruses and bacteria continuously evolve, which can lead to new diseases or even reemergence of diseases we once had control over. An example of this is COVID-19, which evolved and led to the global pandemic starting in 2019. As the virus evolved, it led to more transmissible and dangerous variants. 🦠
Summary
Evolution is a continuous, dynamic process that impacts all living organisms. Genomic changes, the development of resistance, and the evolution of pathogens are all key indicators that evolution is ongoing. Through the processes of natural selection, genetic drift, and mutation, populations continue to adapt and evolve, shaping the incredible diversity of life that we see today. 🌱
For AP Biology students, understanding continuing evolution helps solidify the broader concepts of adaptation, survival, and the relentless flow of natural selection that drives change.
Want to test your understanding of evolution? Dive into our interactive quizzes and videos to help prepare for the AP exam! 🎓
Key Terms to Review (25)
Adaptations: Traits that increase an organism’s survival and reproductive success.
Antibiotic Resistance: The ability of bacteria to resist the effects of an antibiotic.
Pathogens: Microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses, that cause disease.
Genetic Drift: A mechanism of evolution involving random changes in the frequency of alleles in a population.
Mutation: A change in DNA that leads to genetic variation.
Natural Selection: The process in which individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Gene Flow: The movement of genes from one population to another, which can increase genetic diversity.
Recent Posts
- Laws of Indices – Number & Algebra – IB Mathematics AA HL
- Standard Form – Number & Algebra – IB Mathematics AA HL
- 9.2 Crafting an argument through stylistic choices like word choice and description
- 9.1 Strategically conceding, rebutting, or refuting information
- Unit 9 Overview: Developing a Complex Argument
- 8.4 Considering how style affects an argument
- 8.3 Considering how all choices made in an argument affect the audience
- 8.2 Considering how sentence development and word choice affect how the writer is perceived by an audience
- 8.1 Choosing comparisons based on an audience
- Unit 8 Overview: Stylistic Choices
- 7.4 Exploring how sentence development affects an argument
- Syllabus
- Study Guides for every class
- Short Notes
- 7.3 Examining how counterargument or alternative perspectives affect an argument
Choose Topic
- ACT (17)
- AP (20)
- AP Art and Design (5)
- AP Physics 1 (1)
- AQA (5)
- Artificial intelligence (AI) (2)
- Banking and Finance (6)
- Biology (13)
- Business Ideas (68)
- Calculator (72)
- ChatGPT (1)
- Chemistry (3)
- Colleges Rankings (48)
- Computer Science (4)
- Conversion Tools (136)
- Cosmetic Procedures (50)
- Cryptocurrency (49)
- Digital SAT (3)
- Edexcel (4)
- English (1)
- Environmental Science (2)
- Exam Updates (1)
- Finance (17)
- Fitness & Wellness (164)
- Free Learning Resources (209)
- GCSE (1)
- General Guides (40)
- Health (107)
- History and Social Sciences (152)
- IB (1)
- IGCSE (2)
- Image Converters (3)
- IMF (10)
- Math (39)
- Mental Health (58)
- News (8)
- OCR (3)
- Past Papers (463)
- Physics (5)
- SAT (39)
- Schools (3)
- Sciences (1)
- Short Notes (5)
- Study Guides (28)
- Syllabus (19)
- Tools (1)
- Tutoring (1)

