Type 2 Diabetes
Below is a comprehensive, structured report on Type 2 Diabetes. This detailed overview covers essential aspects—from definition and history to symptoms, causes, risk factors, complications, diagnosis, treatment, prevention strategies, global statistics, recent research, and interesting insights. The report is designed to be accessible to both the general public and healthcare professionals.
1. Overview
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion, leading to elevated blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia). It is the most common form of diabetes, predominantly affecting adults, though it is increasingly being diagnosed in younger populations.
Concise yet Detailed Definition
Type 2 diabetes is defined by the body’s inability to effectively use insulin—a hormone produced by the pancreas—to regulate blood sugar levels. This results in persistent hyperglycemia, which over time can cause damage to blood vessels and various organs. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes is typically associated with lifestyle factors and a gradual decline in pancreatic function.
Affected Body Parts/Organs
- Pancreas: Responsible for insulin production; dysfunction leads to inadequate insulin secretion.
- Liver: Plays a key role in glucose regulation and is affected by insulin resistance.
- Muscle and Adipose Tissue: Insulin resistance in these tissues reduces glucose uptake.
- Blood Vessels and Heart: Chronic high blood sugar increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Kidneys, Eyes, and Nerves: Organs commonly affected by long-term complications.
Prevalence and Significance of the Disease
- Prevalence: Type 2 diabetes accounts for approximately 90–95% of all diabetes cases worldwide. In many countries, its prevalence is increasing rapidly due to rising obesity rates and sedentary lifestyles.
- Significance: Type 2 diabetes is a major public health concern given its association with serious complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, blindness, and lower-limb amputations. It also imposes significant economic burdens on healthcare systems and affects quality of life.
2. History & Discoveries
When and How was Type 2 Diabetes First Identified?
- Historical Recognition: Descriptions of diabetes date back to ancient civilizations; however, distinctions between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes were not made until the early 20th century.
- Modern Classification: The concept of insulin resistance and non–insulin-dependent diabetes emerged during the 1950s and 1960s, as clinicians began to observe that many adult patients had a slower disease progression and responded differently to treatment compared to Type 1 diabetes.
Who Discovered It?
- Pioneering Contributions: Although no single individual is credited with “discovering” Type 2 diabetes, the work of researchers like Dr. Elliott P. Joslin and later scientists helped delineate the clinical and pathophysiological differences between the types of diabetes.
Major Discoveries and Breakthroughs
- Insulin Resistance: The identification of insulin resistance as a key mechanism in Type 2 diabetes shifted the focus from solely insulin deficiency.
- Lifestyle and Genetic Factors: Research in the late 20th century established the strong link between obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition with the development of Type 2 diabetes.
- Therapeutic Advances: The development of oral hypoglycemic agents (e.g., metformin, sulfonylureas) and later, newer classes such as DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists, revolutionized management.
Evolution of Medical Understanding Over Time
- Early treatments were rudimentary, but with advances in biochemistry and endocrinology, a more nuanced understanding emerged. Today, personalized approaches considering genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle factors guide the management of Type 2 diabetes.
3. Symptoms
Early Symptoms vs. Advanced-Stage Symptoms
- Early Symptoms:
- Mild fatigue and increased thirst
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Blurred vision and slow healing of wounds
- Increased hunger (polyphagia)
- Advanced-Stage Symptoms:
- Persistent hyperglycemia leading to weight loss despite increased appetite
- Recurrent infections and skin issues
- Numbness or tingling in extremities (neuropathy)
- Signs of cardiovascular complications
Common vs. Rare Symptoms
- Common Symptoms:
- Increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision
- Rare Symptoms:
- Severe recurrent infections, diabetic ketoacidosis (more common in Type 1 but can occur in Type 2 under stress)
- Advanced neuropathy or foot ulcers
How Symptoms Progress Over Time
- Symptoms may develop gradually over several years. Initially, mild hyperglycemia may cause subtle symptoms that patients often overlook. As insulin resistance increases and pancreatic beta-cell function declines, symptoms become more pronounced, and chronic complications begin to develop.
4. Causes
Biological and Environmental Causes
- Insulin Resistance: A primary mechanism where body tissues become less responsive to insulin.
- Beta-Cell Dysfunction: Progressive decline in the ability of pancreatic cells to produce insulin.
- Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation is implicated in the development of insulin resistance.
- Environmental Factors: Diet high in processed foods and sugars, physical inactivity, and obesity are major contributors.
Genetic and Hereditary Factors
- Family History: Individuals with a first-degree relative with Type 2 diabetes have a significantly higher risk.
- Genetic Variants: Multiple genes (e.g., TCF7L2) have been associated with increased susceptibility to the disease.
Known Triggers or Exposure Risks
- Obesity: Excess body fat, particularly visceral fat, increases insulin resistance.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction.
- Diet: High caloric intake, processed carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats are linked with increased risk.
- Aging: The risk increases with age, as metabolic processes slow down.
5. Risk Factors
Who is Most at Risk?
- Age: Typically develops in individuals over 40, though increasing in younger populations.
- Gender: Both men and women are affected; some studies suggest slightly higher prevalence in men.
- Ethnicity: Higher rates observed in certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and some Asian populations.
- Lifestyle: Sedentary behavior, poor diet, and obesity significantly increase risk.
Environmental, Occupational, and Genetic Factors
- Environmental: Urban lifestyles, exposure to endocrine disruptors, and access to unhealthy food.
- Occupational: Jobs with minimal physical activity may contribute to a sedentary lifestyle.
- Genetic: A strong familial component exists, with multiple genetic markers identified.
Impact of Pre-existing Conditions
- Metabolic Syndrome: Conditions like hypertension, dyslipidemia, and central obesity greatly elevate risk.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): In women, PCOS is associated with insulin resistance.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Pre-existing heart conditions can be both a risk factor and a complication of Type 2 diabetes.
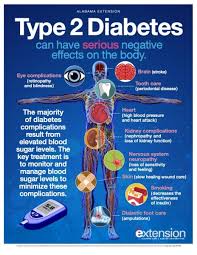
6. Complications
What Complications Can Arise from Type 2 Diabetes?
- Microvascular Complications:
- Retinopathy leading to vision loss
- Nephropathy progressing to kidney failure
- Neuropathy resulting in pain and loss of sensation
- Macrovascular Complications:
- Coronary artery disease and heart attacks
- Stroke
- Peripheral arterial disease, potentially leading to amputations
Long-Term Impact on Organs and Overall Health
- Persistent hyperglycemia damages blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of cardiovascular events, kidney disease, and infections. Chronic complications can significantly reduce quality of life and increase healthcare utilization.
Potential Disability or Fatality Rates
- Type 2 diabetes is a leading cause of disability worldwide. Cardiovascular complications are a major contributor to mortality in diabetic patients. Early and aggressive management is critical to reducing these risks.
7. Diagnosis & Testing
Common Diagnostic Procedures
- Clinical Evaluation: Detailed medical history and physical examination focusing on symptoms and risk factors.
- Blood Glucose Testing: Fasting plasma glucose, oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), and HbA1c measurements are key to diagnosis.
Medical Tests
- Fasting Plasma Glucose: A value ≥126 mg/dL on two occasions indicates diabetes.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Blood glucose levels measured after a 75-gram glucose load.
- HbA1c: Reflects average blood glucose levels over the past 2–3 months; values ≥6.5% indicate diabetes.
- Additional Tests: Lipid profiles, kidney function tests, and blood pressure measurements help assess overall risk and complications.
Early Detection Methods and Their Effectiveness
- Routine screening in high-risk populations (e.g., those with obesity, family history) is effective in early diagnosis. Early detection enables timely lifestyle intervention and treatment to prevent or delay complications.
8. Treatment Options
Standard Treatment Protocols
- Lifestyle Modifications: Diet, exercise, and weight management are the cornerstones of therapy.
- Medications:
- Oral Hypoglycemic Agents: Metformin is typically the first-line therapy. Others include sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, and thiazolidinediones.
- Insulin Therapy: May be required as the disease progresses or during periods of acute decompensation.
- Self-Monitoring: Regular blood glucose monitoring is critical for effective management.
Medications, Surgeries, and Therapies
- Medications: Combination therapies are common, tailored to the patient’s glycemic control and comorbid conditions.
- Bariatric Surgery: For obese patients, weight-loss surgery has been shown to improve glycemic control and, in some cases, induce remission.
- Adjunct Therapies: Blood pressure and lipid-lowering medications are used to manage associated cardiovascular risks.
Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
- New Drug Classes: Research into novel agents that target inflammation and insulin resistance is ongoing.
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in genomics are paving the way for tailored treatments based on individual patient profiles.
- Regenerative Therapies: Experimental approaches, including islet cell transplantation, are under investigation.
9. Prevention & Precautionary Measures
How Can Type 2 Diabetes be Prevented?
- Primary Prevention: Focuses on lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, regular physical activity, and a balanced diet.
- Secondary Prevention: Involves early detection and management of prediabetes to prevent progression.
Lifestyle Changes and Environmental Precautions
- Diet: Emphasize whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins; limit processed foods and sugary beverages.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week) helps improve insulin sensitivity.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is critical.
- Regular Screening: For high-risk populations, periodic blood glucose testing is recommended.
Vaccines (if Applicable) or Preventive Screenings
- Vaccinations: While no vaccine exists for Type 2 diabetes, immunizations (e.g., influenza, pneumococcal) are recommended due to the increased risk of infections.
- Screenings: Regular monitoring of blood glucose and HbA1c levels in at-risk individuals aids in early intervention.
10. Global & Regional Statistics
Incidence and Prevalence Rates Globally
- Global Prevalence: Over 400 million people are estimated to have diabetes worldwide, with Type 2 diabetes accounting for the vast majority of cases.
- Regional Variations: Higher prevalence is observed in developed countries and regions undergoing rapid urbanization. Rates are increasing in Asia, Africa, and Latin America due to lifestyle changes.
Mortality and Survival Rates
- Mortality: Type 2 diabetes is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, largely due to its cardiovascular complications.
- Survival: Advances in treatment have improved life expectancy, though complications continue to contribute significantly to mortality rates.
Country-Wise Comparison and Trends
- Developed Countries: Better screening and management have helped control complications, though prevalence remains high.
- Developing Regions: Increasing incidence is noted due to lifestyle changes, with disparities in healthcare access affecting outcomes.
11. Recent Research & Future Prospects
Latest Advancements in Treatment and Research
- Innovative Medications: Newer agents such as SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists not only improve glycemic control but also offer cardiovascular and renal benefits.
- Technology Integration: Continuous glucose monitoring systems and digital health platforms are enhancing personalized diabetes management.
- Genomic Insights: Research into the genetic basis of Type 2 diabetes is identifying biomarkers that could lead to more individualized therapies.
Ongoing Studies and Future Medical Possibilities
- Clinical Trials: Numerous studies are exploring combination therapies, novel drug targets, and lifestyle intervention strategies.
- Regenerative Medicine: Research into beta-cell regeneration and islet transplantation holds promise for restoring endogenous insulin production.
- Precision Medicine: Tailoring treatment based on genetic and metabolic profiles is a key area of future research.
Potential Cures or Innovative Therapies
- While a complete cure for Type 2 diabetes remains elusive, advances in pharmacotherapy, lifestyle interventions, and regenerative approaches are converging to dramatically improve management and quality of life.
12. Interesting Facts & Lesser-Known Insights
Uncommon Knowledge about Type 2 Diabetes
- Reversibility: In some cases, significant lifestyle changes have been shown to put Type 2 diabetes into remission.
- Economic Impact: Diabetes management represents a substantial portion of healthcare spending in many countries.
- Interdisciplinary Research: Studies on the gut microbiome and its impact on insulin resistance are opening new therapeutic avenues.
Myths and Misconceptions vs. Medical Facts
- Myth: Type 2 diabetes is solely a lifestyle disease.
- Fact: Although lifestyle factors play a major role, genetic predisposition and other metabolic factors are also important.
- Myth: Only overweight individuals develop Type 2 diabetes.
- Fact: While obesity is a significant risk factor, individuals with normal weight can also develop the disease.
- Myth: Once diagnosed, there is no way to reverse diabetes.
- Fact: With early intervention and intensive lifestyle modification, some patients can achieve remission.
Impact on Specific Populations or Professions
- Workforce Impact: Diabetes can significantly affect productivity and increase healthcare costs, making workplace wellness programs critical.
- Vulnerable Populations: Certain ethnic groups and older adults are disproportionately affected.
- Pediatric Considerations: Although less common in children, the rise of childhood obesity has led to increased Type 2 diabetes in adolescents.
References
– Provides comprehensive clinical guidelines and treatment options for Type 2 diabetes.
– Offers epidemiological data and global trends related to diabetes.
– Summarizes recent research and advancements in the understanding and treatment of Type 2 diabetes.