Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages – Everything you need to know
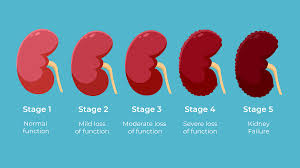
Table of Contents
ToggleChronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages
Below is a comprehensive, structured report on Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages. This report covers definitions, history, symptoms, causes, risk factors, complications, diagnostic methods, treatment options, prevention strategies, global statistics, recent research, and interesting insights. All information is grounded in current evidence and clinical guidelines.
1. Overview
What is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages?
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) stages are a classification system that describes the progression and severity of kidney damage and dysfunction. These stages are primarily determined by the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and, in many guidelines, by the degree of albuminuria.
Definition & Affected Body Parts/Organs:
- Definition:
CKD is defined as an irreversible, progressive decline in kidney function lasting at least three months. The stages range from mild kidney damage with normal eGFR (Stage 1) to kidney failure (Stage 5). - Affected Areas:
- Kidneys: The primary organs affected, exhibiting reduced filtering capability and structural changes.
- Cardiovascular System: Secondary effects include hypertension and increased cardiovascular risk due to fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
- Bone and Mineral Metabolism: Altered mineral balance (phosphorus, calcium) may affect bone health.
Prevalence and Significance:
- Prevalence:
- CKD affects approximately 10% of the global adult population, with higher rates in individuals with diabetes and hypertension.
- Significance:
- CKD is associated with a high risk of cardiovascular events, morbidity, and mortality.
- Early identification through staging is critical for intervention strategies to slow progression and reduce complications.
2. History & Discoveries
When and How Was CKD Staging First Identified?
- Early Recognition:
- The concept of chronic kidney dysfunction has been recognized for decades. However, it was not until the latter half of the 20th century that clinical research began to formalize the staging of CKD based on measurable parameters.
- Modern Classification:
- In the early 2000s, the Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI) introduced a staging system based on eGFR, later refined by the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guidelines.
Who Contributed to Its Discovery?
- The development of CKD staging was a collaborative effort among nephrologists and researchers worldwide, with key contributions from the National Kidney Foundation and KDIGO.
Major Discoveries & Breakthroughs:
- eGFR Measurement:
- The development of formulas to estimate glomerular filtration rate revolutionized the ability to quantify kidney function.
- Albuminuria as a Marker:
- Recognizing albuminuria as an important marker for kidney damage helped refine risk stratification.
- Guidelines:
- The establishment of KDOQI and later KDIGO guidelines provided a standardized framework for diagnosis, management, and research.
Evolution of Medical Understanding Over Time:
- Early approaches to kidney disease were based on symptomatic and laboratory findings.
- Today, CKD staging integrates biochemical markers with clinical outcomes to guide timely interventions, reflecting decades of research in nephrology and epidemiology.
3. Symptoms
Early Symptoms vs. Advanced-Stage Symptoms:
- Early Symptoms:
- Often asymptomatic; mild CKD (Stages 1 and 2) may show subtle signs such as fatigue or changes in urine output.
- Advanced-Stage Symptoms:
- As kidney function declines (Stages 3–5), symptoms may include edema, anemia, nausea, loss of appetite, hypertension, and cognitive difficulties.
- In Stage 5 (end-stage renal disease), patients may experience uremia (accumulation of waste products), leading to severe systemic effects.
Common vs. Rare Symptoms:
- Common:
- Fatigue, weakness, and fluid retention.
- Rare:
- Severe uremic symptoms like pericarditis or encephalopathy are less common and typically occur in advanced CKD.
How Symptoms Progress Over Time:
- CKD is often a silent disease in its early stages, with symptoms becoming more pronounced as kidney function deteriorates. Without intervention, patients may progress from Stage 1 (normal or high eGFR with evidence of kidney damage) to Stage 5, where dialysis or transplantation becomes necessary.
4. Causes
Biological and Environmental Causes:
- Biological Causes:
- The most common causes of CKD include diabetes mellitus, hypertension, glomerulonephritis, and polycystic kidney disease.
- Environmental Causes:
- Exposure to nephrotoxic substances (certain medications, heavy metals) and chronic infections may also contribute.
Genetic and Hereditary Factors:
- Genetic Disorders:
- Conditions such as autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) are inherited and lead to CKD.
- Hereditary Predispositions:
- Genetic factors can influence susceptibility to conditions like diabetes and hypertension, which are major contributors to CKD.
Known Triggers or Exposure Risks:
- Triggers:
- Poor control of diabetes and high blood pressure, exposure to nephrotoxins, and recurrent urinary tract infections.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Obesity, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle are significant contributors to the development and progression of CKD.
5. Risk Factors
Who is Most at Risk?
- Age:
- The risk of CKD increases with age.
- Gender:
- CKD is prevalent in both men and women, though certain causes may be more common in one gender.
- Lifestyle:
- Individuals with obesity, poor dietary habits, and sedentary lifestyles are at higher risk.
- Medical History:
- Those with diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, or a family history of kidney disease are particularly vulnerable.
Environmental, Occupational, and Genetic Factors:
- Environmental:
- Exposure to pollution and occupational nephrotoxins can elevate risk.
- Genetic:
- A family history of kidney disease significantly increases risk.
- Occupational:
- Workers in environments with high exposure to chemicals may be at increased risk.
Impact of Pre-Existing Conditions:
- Chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension not only cause CKD but also accelerate its progression, making early management critical.
6. Complications
What Complications Can Arise from CKD?
- Cardiovascular Disease:
- CKD is a major risk factor for heart disease, including coronary artery disease and heart failure.
- Bone and Mineral Disorders:
- Altered calcium and phosphate metabolism can lead to renal osteodystrophy.
- Anemia:
- Reduced production of erythropoietin results in anemia, contributing to fatigue and reduced quality of life.
- Electrolyte Imbalances:
- Imbalances in potassium, sodium, and acid-base homeostasis can cause cardiac arrhythmias and other systemic issues.
Long-Term Impact on Organs and Overall Health:
- Progressive kidney damage can lead to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), necessitating dialysis or transplantation.
- Systemic complications such as cardiovascular events are a leading cause of death in CKD patients.
Potential Disability or Fatality Rates:
- CKD significantly increases morbidity and mortality; advanced stages are associated with high rates of cardiovascular events and a substantial reduction in life expectancy.
7. Diagnosis & Testing
Common Diagnostic Procedures:
- Clinical Evaluation:
- Detailed medical history and physical examination, focusing on risk factors like diabetes and hypertension.
- Blood Tests:
- Serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and calculation of eGFR.
- Urine Tests:
- Analysis for proteinuria (especially albuminuria) is critical for staging and prognosis.
Medical Tests:
- Imaging:
- Renal ultrasound is used to assess kidney size and structure.
- Biopsy:
- In selected cases, a kidney biopsy may be performed to determine the underlying cause.
Early Detection Methods and Their Effectiveness:
- Routine screening in at-risk populations (e.g., diabetics, hypertensives) using blood and urine tests is highly effective for early detection and timely intervention.
8. Treatment Options
Standard Treatment Protocols:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary changes (low sodium, controlled protein intake, balanced nutrients), regular exercise, and smoking cessation.
- Pharmacologic Therapy:
- Blood Pressure Control:
- ACE inhibitors or ARBs are recommended to slow CKD progression.
- Glycemic Control:
- Strict diabetes management to reduce kidney damage.
- Medications:
- Diuretics, statins, phosphate binders, and erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) may be used based on individual needs.
- Blood Pressure Control:
- Renal Replacement Therapy:
- In advanced CKD (Stage 5), dialysis or kidney transplantation is required.
Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials:
- SGLT2 Inhibitors:
- Recently shown to reduce progression of CKD in diabetic and non-diabetic patients.
- Novel Agents:
- Research is ongoing into anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic drugs that may further slow disease progression.
- Personalized Medicine:
- Genomic and biomarker studies are being integrated into treatment planning to tailor therapy more precisely.
9. Prevention & Precautionary Measures
How Can CKD Be Prevented?
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight control.
- Management of Risk Factors:
- Tight control of blood pressure and blood sugar, along with cessation of smoking.
- Regular Screening:
- Routine monitoring of kidney function in high-risk populations helps in early detection and intervention.
Vaccines and Preventive Screenings:
- No vaccines exist for CKD, but preventive strategies include regular screening (blood and urine tests) to detect early kidney damage.
10. Global & Regional Statistics
Incidence and Prevalence Rates Globally:
- CKD affects an estimated 10–15% of the adult population worldwide.
- Incidence and prevalence vary by region, with higher rates reported in areas with increasing rates of diabetes and hypertension.
Mortality and Survival Rates:
- CKD is a leading contributor to cardiovascular mortality.
- End-stage renal disease has high mortality despite advances in dialysis and transplantation.
Country-Wise Comparison and Trends:
- Developed countries tend to have better outcomes due to early detection and management programs.
- In developing regions, limited access to healthcare contributes to higher prevalence and poorer outcomes.
11. Recent Research & Future Prospects
Latest Advancements in Treatment and Research:
- Pharmacological Advances:
- The use of SGLT2 inhibitors and other novel agents shows promise in reducing CKD progression.
- Biomarker Research:
- New biomarkers for early detection and risk stratification are under investigation.
- Regenerative Medicine:
- Research into stem cell therapies and other regenerative approaches aims to repair kidney tissue.
- Digital Health:
- Telemedicine and remote monitoring are enhancing patient management and adherence to therapy.
Ongoing Studies & Future Medical Possibilities:
- Multiple clinical trials are evaluating combination therapies and personalized medicine approaches.
- Future prospects include improved diagnostic tools and therapies that can delay or even reverse kidney damage.
Potential Cures or Innovative Therapies Under Development:
- While no cure exists, ongoing research into gene therapies and novel pharmacologic agents offers hope for substantially improved outcomes.
12. Interesting Facts & Lesser-Known Insights
Uncommon Knowledge about CKD Stages:
- CKD staging is primarily based on eGFR and albuminuria, with even mild reductions in kidney function being significant risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
- Many individuals with early-stage CKD remain asymptomatic, emphasizing the importance of routine screening.
Myths vs. Medical Facts:
- Myth: Kidney disease only affects the elderly.
Fact: CKD can affect individuals of all ages, particularly those with risk factors like diabetes and hypertension. - Myth: A normal creatinine level means your kidneys are fine.
Fact: Creatinine can be misleading; estimated GFR and albuminuria are more sensitive markers of kidney health. - Myth: CKD is not preventable.
Fact: Many cases of CKD can be prevented or slowed by controlling risk factors such as blood pressure and blood sugar.
Impact on Specific Populations or Professions:
- High-Risk Groups:
- Individuals with diabetes, hypertension, obesity, or a family history of kidney disease.
- Healthcare Providers:
- Primary care physicians and nephrologists play a critical role in early detection and management.
- Public Health:
- Effective screening and preventive strategies can reduce the overall burden of CKD and its associated complications.
References
The information in this report is synthesized from peer-reviewed medical literature, clinical guidelines from organizations such as the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO), and epidemiological studies available via reputable databases (e.g., PubMed).
Conclusion:
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a widespread and progressive condition that poses significant health challenges globally. Staging based on kidney function and albuminuria guides clinical management, enabling early intervention and targeted therapy. Advances in pharmacologic treatments, emerging biomarkers, and personalized medicine hold promise for better outcomes and quality of life for CKD patients. Continued efforts in prevention, early detection, and research are essential to curb the growing burden of kidney disease worldwide.
Recent Posts
- Common Cold – Everything you need to know
- Asbestosis – Everything you need to know
- Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) – Everything you need to know
- Food Poisoning Symptoms – Everything you need to know
- Bronchiectasis – Everything you need to know
- Whooping Cough Symptoms – Everything you need to know
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) – Everything you need to know
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) – Everything you need to know
- Type 2 Diabetes Diet – Everything you need to know
- Heart and Stroke – Everything you need to know
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages – Everything you need to know
- Syphilis – Everything you need to know
- Malaria – Everything you need to know
- Hypophosphatasia – Everything you need to know
- Symptoms of Allergies – Everything you need to know
Choose Topic
- ACT (17)
- AP (20)
- AP Art and Design (5)
- AP Physics 1 (1)
- AQA (5)
- Artificial intelligence (AI) (2)
- Banking and Finance (6)
- Biology (13)
- Business Ideas (68)
- Calculator (72)
- ChatGPT (1)
- Chemistry (3)
- Colleges Rankings (48)
- Computer Science (4)
- Conversion Tools (136)
- Cosmetic Procedures (50)
- Cryptocurrency (49)
- Digital SAT (3)
- Disease (143)
- Edexcel (4)
- English (1)
- Environmental Science (2)
- Etiology (7)
- Exam Updates (1)
- Finance (129)
- Fitness & Wellness (164)
- Free Learning Resources (210)
- GCSE (1)
- General Guides (40)
- Health (107)
- History and Social Sciences (152)
- IB (1)
- IGCSE (2)
- Image Converters (3)
- IMF (10)
- Math (43)
- Mental Health (58)
- News (9)
- OCR (3)
- Past Papers (463)
- Physics (5)
- Research Study (5)
- SAT (39)
- Schools (3)
- Sciences (1)
- Short Notes (5)
- Study Guides (28)
- Syllabus (19)
- Tools (1)
- Tutoring (1)
- What is? (312)
Recent Comments

Common Cold - Everything you need to know
Asbestosis - Everything you need to know
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) - Everything you need to know

Food Poisoning Symptoms - Everything you need to know

Common Cold - Everything you need to know

Asbestosis - Everything you need to know

Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) - Everything you need to know

