

Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Kinetics in Chemistry?
Welcome to the first part of Unit 5 in AP Chemistry! This unit dives deep into Kinetics, the study of the rate of chemical reactions. Have you ever wondered why some reactions, like the explosion of a methane-filled balloon when lit, happen instantaneously, while others, such as the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide, occur much more slowly? Kinetics helps us understand why certain reactions are faster than others and how quickly they occur.
Understanding the Rate of a Reaction
The rate of a reaction refers to how fast reactants turn into products. Measuring this rate involves observing concentration changes over time.
- As a reaction progresses, the concentration of reactants decreases as they form products, while the concentration of products increases. The rate is expressed mathematically as: Rate=−tΔ[Reactant]orRate=tΔ[Product] The units for rate are typically mol/Ls (Ms⁻¹), but may vary (e.g., hours, minutes). Always ensure that your units are consistent when performing calculations!
Graphically Representing Reaction Rates
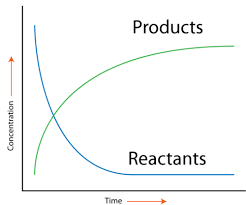

Image Courtesy of CK-12
The rate of a reaction can be visualized graphically. As a reaction proceeds, the concentration of products increases while the concentration of reactants decreases until equilibrium is reached. Equilibrium occurs when the forward and reverse reaction rates are equal, keeping the concentrations constant. (More on this in Unit 7!)
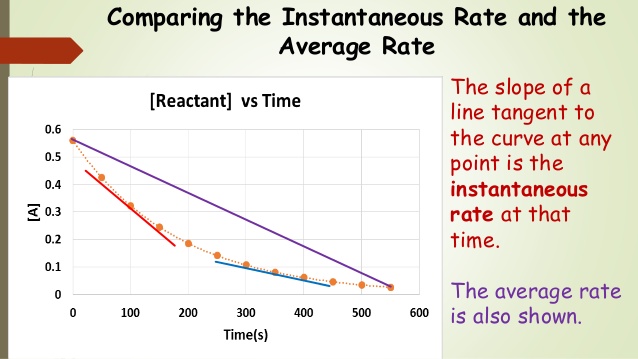
- Average rate of a reaction: This is the change in concentration over a specific time interval and is calculated by dividing the concentration change by the time interval.
- Instantaneous rate of a reaction: This represents the rate at a specific moment, found by taking the slope of a tangent line on a concentration vs. time graph.

Applying Stoichiometry to Reaction Rates
Consider the reaction: 2A + 3B → C. Suppose in 2 seconds, the concentration of A decreases by 0.2M. The rate, in terms of A, would be:
Rate=−2s0.2M=−0.1mol A/Ls
To find the rate at which B is consumed, use stoichiometry:
Rate of B consumption=(−0.1mol A/Ls)×2mol A3mol B=−0.15mol B/Ls
Stoichiometry helps determine the rates of change for all reactants and products!
👉 Need a stoichiometry refresher? Check out our Unit 4 guide for practice.
Factors Affecting Reaction Rate
Several physical factors influence how fast reactions occur:
- Concentration: Higher concentrations increase the rate due to more frequent collisions between reactant molecules.
- Temperature: Increasing temperature raises the kinetic energy of molecules, resulting in more frequent and effective collisions.
- Surface Area: Greater surface area (e.g., grinding solids into powder) allows more reactant molecules to collide, increasing reaction rates.
- Catalysts: Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction without being consumed.
- Pressure (for gases): Higher pressure increases reaction rates by increasing the number of gas molecules in a given volume.
Examples and Applications
Example 1: The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is slow, but adding a catalyst like manganese dioxide (MnO₂) speeds it up dramatically.
Example 2: When you light a methane-filled balloon, the reaction with oxygen happens instantaneously, causing an explosion due to rapid energy release.
Conclusion
Kinetics provides a deeper understanding of the “why” and “how fast” behind chemical reactions. By mastering concepts like reaction rates, stoichiometry, and the effects of temperature, concentration, and catalysts, you’ll gain invaluable insights into the dynamic nature of chemistry. Stay tuned as we dive further into this unit and explore rate laws, reaction mechanisms, and more!


5.10 Multistep Reaction Energy Profile


5.8 Reaction Mechanism and Rate Law

3.8 Applications of Circular Motion and Gravitation

3.7 Free-Body Diagrams for Objects in Uniform Circular Motion


3.6 Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force

