What Is Osmosis? Everything You Need to Know
Introduction
Have you ever wondered how plants draw water from the soil, or how modern water purification systems turn salt water into drinking water? These everyday miracles of nature and technology hinge on a fascinating scientific process called osmosis. But you might be asking yourself, “what is osmosis?” This simple question opens the door to understanding one of the most fundamental processes in biology, chemistry, and engineering.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore:
- A clear, straightforward definition of osmosis and its essential characteristics.
- The historical and scientific background that has shaped our understanding of osmosis.
- A deep dive into the science behind osmosis, including key principles such as semi-permeable membranes and osmotic pressure.
- Real-world examples and case studies—from plant physiology and medical applications to industrial water treatment.
- The importance and benefits of understanding osmosis in everyday life, science, business, and technology.
- Common misconceptions and frequently asked questions about osmosis.
- Modern trends and current research shaping our understanding and applications of osmosis today.
By the end of this article, you’ll not only have a solid answer to “what is osmosis?” but also an appreciation for how this process influences everything from cellular function to global water scarcity solutions. Whether you’re a student, educator, or a curious mind eager to explore the marvels of science, this guide is designed to illuminate the process of osmosis in a clear and engaging way.
A Straightforward Definition: What Is Osmosis?
Core Explanation
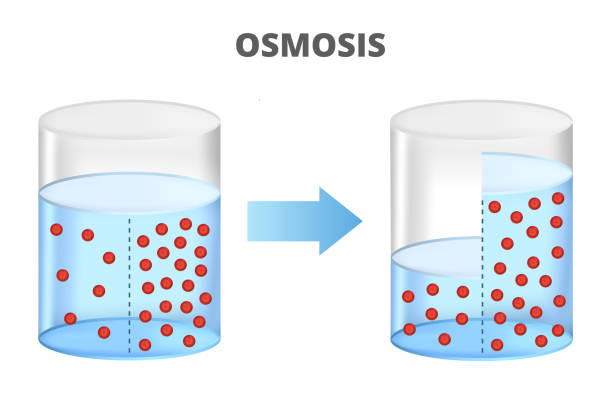
In its most basic form, osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. This movement continues until equilibrium is reached, meaning the concentration of solutes becomes equal on both sides of the membrane.
Mathematically, if we denote the solute concentration on one side as
and on the other side as
(with
), water will flow from the
side to the
side. Osmosis is driven by the chemical potential difference between the two sides.
Key Characteristics
- Semi-Permeable Membrane:
- Osmosis occurs only across membranes that allow the passage of water molecules while blocking most solute molecules.
- Concentration Gradient:
- The driving force behind osmosis is the difference in solute concentration (or water potential) on either side of the membrane.
- Equilibrium:
- The process continues until the water potential on both sides of the membrane is equal, establishing an equilibrium state.
- Passive Transport:
- Osmosis is a passive process; it does not require energy (ATP) to occur. Instead, it relies on the inherent kinetic energy of water molecules.
- Osmotic Pressure:
- The pressure required to stop the net flow of water across the membrane is known as osmotic pressure. It is a critical parameter in biological and industrial applications.
When you ask “what is osmosis?”, you are essentially inquiring about how and why water moves to balance concentrations—a concept that underlies much of life’s processes and modern technological applications.
Historical and Contextual Background
Ancient Observations and Early Theories
The phenomenon of osmosis has intrigued scientists for centuries—even if early observers did not call it by that name. Early civilizations, while not fully understanding the molecular basis, noticed that liquids tended to “balance out” when separated by barriers. For example, ancient Egyptian farmers observed that water naturally seeped through porous materials, an early hint at the principles of osmosis.
The 18th and 19th Centuries: Formal Discovery
- Jean-Antoine Nollet (1751):
- A French clergyman and physicist, Nollet is credited with early experiments that demonstrated the movement of water across membranes. His work laid the groundwork for the formal study of osmosis.
- Thomas Graham (1830s):
- Often called the “Father of Dialysis,” Graham conducted experiments on the diffusion of gases and liquids, significantly advancing the understanding of semi-permeable membranes and the osmotic process.
- 19th-Century Advances:
- As scientists began to understand the nature of solutions and the behavior of molecules, osmosis became recognized as a fundamental process governing not just water flow, but also nutrient absorption in plants and waste removal in animals.
The 20th Century and Beyond: Modern Perspectives
- Biological Applications:
- With the advent of cell biology, osmosis was recognized as vital for maintaining cell turgor in plants and regulating fluid balance in animal tissues. The development of the cell theory further emphasized the importance of osmosis in sustaining life.
- Technological Innovations:
- The discovery of reverse osmosis—a process where pressure is applied to force water from a higher solute concentration to a lower one—has revolutionized water purification and desalination technologies.
- Contemporary Research:
- Modern research explores osmosis at the nanoscale, using advanced imaging techniques and computational models to understand how water molecules interact with membranes. This work informs cutting-edge fields like nanotechnology, biomedical engineering, and environmental science.
The evolution of our understanding of osmosis—from early empirical observations to sophisticated modern models—illustrates its enduring importance in both natural and engineered systems.
In-Depth Exploration / Main Body
To fully answer “what is osmosis?”, let’s delve into its mechanisms, variations, and applications in more detail.
1. The Science Behind Osmosis
The Process
At its heart, osmosis is a type of diffusion—a passive movement of molecules driven by kinetic energy. However, unlike simple diffusion where all molecules move freely, osmosis is restricted to water (or another solvent) moving through a membrane that selectively permits its passage.
- Semi-Permeable Membranes:
- These membranes act as gatekeepers. They allow small molecules like water to pass through while preventing larger solute molecules (e.g., salt, sugars) from crossing.
- Examples include cell membranes, dialysis tubing, and certain synthetic membranes used in industrial processes.
- Concentration Gradient:
- Water moves from areas where it is in higher concentration (and solute concentration is lower) to areas where it is in lower concentration (and solute concentration is higher).
- This movement continues until the water potential on both sides of the membrane is equalized.
- Osmotic Pressure:
- Osmotic pressure is the pressure needed to stop water from diffusing through the membrane. It’s directly proportional to the difference in solute concentration across the membrane.
Diagram of Osmosis
Imagine a U-tube with a semi-permeable membrane in the middle. One side contains pure water, and the other side contains a salt solution. Over time, water will flow from the pure side into the saltier side until the water levels balance, or until an external pressure is applied to halt the process. This simple setup is the basis for many laboratory demonstrations of osmosis.
2. Key Characteristics and Properties
Passive Transport
- No Energy Required:
- Osmosis does not require energy input from cells or machines because it relies solely on the natural kinetic energy of water molecules.
- Equilibrium-Based:
- The process continues until there is no net movement of water—a state of dynamic equilibrium is reached.
Importance of Membrane Permeability
- Selective Barrier:
- The specific characteristics of the membrane—its pore size, chemical composition, and structure—determine which molecules can pass.
- Biological Relevance:
- In living cells, membranes are critical for maintaining homeostasis. The balance of water inside and outside the cell is regulated precisely by osmosis.
Osmotic Pressure and Its Measurement
- Definition and Significance:
- Osmotic pressure is a quantitative measure of the force driving osmosis. It’s a vital parameter in various applications, from understanding blood pressure regulation in the human body to designing reverse osmosis systems for water purification.
- Practical Measurement:
- Osmometers are instruments used to measure osmotic pressure, providing data that can be used in medical diagnostics and chemical engineering.
3. Variations on the Theme: Reverse Osmosis and Other Processes
Reverse Osmosis
- Definition:
- Reverse osmosis is a process in which external pressure is applied to overcome osmotic pressure, forcing water from a region of higher solute concentration to a region of lower concentration.
- Applications:
- It’s widely used in water purification, desalination, and in some industrial processes where pure water is required.
- Mechanism:
- By applying a pressure greater than the osmotic pressure of the solution, water molecules are pushed through the membrane in the reverse direction, leaving the solutes behind.
Other Related Processes
- Dialysis:
- A medical process that relies on osmosis (and diffusion) to remove waste products from the blood in patients with kidney failure. A dialysis machine uses a semi-permeable membrane to filter the blood.
- Diffusion vs. Osmosis:
- While both involve the movement of molecules, diffusion is a general process applicable to all types of molecules, whereas osmosis is specific to the movement of a solvent (typically water) across a membrane.
- Active Transport:
- In contrast to osmosis, active transport requires energy (ATP) to move substances against their concentration gradient. Many biological processes rely on both osmosis and active transport to maintain cellular balance.
4. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Biological Examples
- Plant Water Uptake:
- Plants absorb water from the soil through their roots via osmosis. The semi-permeable membranes in root cells allow water to flow into the cells where the solute concentration is higher.
- Human Physiology:
- In human cells, osmosis is crucial for maintaining cell volume and pressure. For example, red blood cells rely on osmosis to keep their shape and function.
- Homeostasis in Animals:
- The kidneys regulate water balance through osmosis, reabsorbing water from urine to maintain proper hydration levels.
Industrial and Technological Applications
- Water Purification and Desalination:
- Reverse osmosis is a cornerstone of modern water treatment technology. It’s used to remove salt and other impurities from seawater, producing fresh water for consumption.
- Food Preservation:
- Osmosis is exploited in food processing—for example, in curing meats or making jams—where high concentrations of salt or sugar draw out moisture, inhibiting bacterial growth.
- Pharmaceuticals and Medicine:
- Controlled drug delivery systems sometimes use osmotic pumps to regulate the release of medication in the body.
Everyday Life Applications
- Cooking and Food Preparation:
- When you soak dried fruits or vegetables in water, osmosis helps rehydrate them by drawing water into the dried cells.
- Household Practices:
- Osmosis is at work when you observe how water moves through a paper towel or a sponge, a principle that underlies many cleaning and absorption processes.
Importance, Applications, or Benefits of Understanding Osmosis
Understanding what is osmosis? is vital because it is a fundamental concept that bridges multiple disciplines and everyday experiences.
1. Enhancing Biological Literacy
- Cell Function and Health:
- Knowledge of osmosis helps explain critical physiological processes, such as how cells maintain their structure and function. This understanding is key in biology, medicine, and healthcare.
- Agricultural Practices:
- Farmers and agricultural scientists rely on osmosis to understand water uptake in plants, which is crucial for optimizing irrigation and ensuring crop health.
2. Advancing Technological Innovations
- Water Treatment Technologies:
- Reverse osmosis systems are at the forefront of addressing global water scarcity. As water demand increases, efficient purification and desalination techniques become increasingly vital.
- Industrial Processes:
- Industries ranging from food processing to pharmaceuticals use osmosis to control fluid movements and concentrate solutions, making the process integral to production efficiency and quality control.
3. Promoting Environmental Sustainability
- Efficient Water Use:
- By harnessing natural osmotic processes, engineers can design systems that minimize water waste and optimize resource use, contributing to more sustainable practices.
- Ecosystem Balance:
- Understanding osmosis helps ecologists appreciate how water and nutrients circulate in natural systems, aiding in conservation and restoration efforts.
4. Empowering Personal and Academic Growth
- Critical Thinking in Science:
- Grasping the concept of osmosis fosters analytical thinking and problem-solving skills, as you learn to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios.
- Educational Success:
- Students who understand osmosis are better prepared for advanced studies in biology, chemistry, environmental science, and related fields.
Addressing Common Misconceptions or FAQs
Even a well-established concept like osmosis can generate misunderstandings. Let’s clear up some frequent questions and misconceptions.
Misconception 1: Osmosis Only Involves Water
- Reality:
- While osmosis is most commonly associated with the movement of water, it is a specific type of diffusion that applies to any solvent moving through a semi-permeable membrane. However, water is the most familiar solvent in biological systems.
Misconception 2: Osmosis Is the Same as Diffusion
- Reality:
- Osmosis is a subset of diffusion. All osmotic processes are diffusion, but not all diffusion is osmosis. Diffusion refers to the movement of molecules from high to low concentration, regardless of whether a membrane is involved, whereas osmosis specifically refers to the movement of a solvent through a semi-permeable membrane.
Misconception 3: Osmosis Requires Energy
- Reality:
- Osmosis is a passive process that relies solely on the kinetic energy of molecules and the natural tendency toward equilibrium. It does not require external energy input in the form of ATP or other fuels.
FAQ 1: What is osmosis? in a Nutshell
Answer:
Osmosis is the passive movement of a solvent (usually water) through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration until equilibrium is reached.
FAQ 2: How Does Reverse Osmosis Work?
Answer:
Reverse osmosis applies external pressure to force water to move from a region of high solute concentration to a region of low solute concentration. This process is used for water purification and desalination.
FAQ 3: What Is a Semi-Permeable Membrane?
Answer:
A semi-permeable membrane is a barrier that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion while blocking others. In osmosis, it typically allows water molecules to pass but restricts larger solute molecules.
FAQ 4: Why Is Osmotic Pressure Important?
Answer:
Osmotic pressure is the pressure required to stop the net flow of water across a semi-permeable membrane. It is crucial in biological systems for maintaining cell integrity and is a key factor in industrial applications such as reverse osmosis water purification.
Modern Relevance and Current Trends
In today’s data-driven and environmentally conscious world, what is osmosis? remains a topic of both scientific inquiry and practical innovation. Here are some contemporary trends and developments:
1. Technological Advances in Water Purification
- Reverse Osmosis Innovations:
- Advances in membrane technology, energy efficiency, and scaling solutions are continuously improving reverse osmosis systems. These innovations are crucial in addressing global water scarcity by making desalination and water purification more accessible and cost-effective.
- Nanotechnology and Membranes:
- Researchers are exploring nanomaterials to create more effective, durable, and selective semi-permeable membranes. These developments could revolutionize water treatment and environmental remediation.
2. Environmental and Agricultural Applications
- Sustainable Irrigation:
- Understanding osmosis is essential for designing irrigation systems that optimize water use and reduce waste, especially in arid regions.
- Soil and Plant Health:
- Osmosis plays a key role in nutrient uptake in plants. Enhanced knowledge about osmotic processes is helping agronomists develop better fertilization techniques and drought-resistant crops.
3. Biomedical and Health-Related Fields
- Dialysis and Medical Devices:
- Osmosis is critical in designing dialysis machines that remove waste products from the blood. Ongoing research seeks to improve these devices to make them more effective and less taxing on patients.
- Drug Delivery Systems:
- Osmotic pumps in drug delivery systems are engineered to release medication at controlled rates, ensuring optimal therapeutic effects while minimizing side effects.
4. Advances in Computational Modeling
- Molecular Dynamics Simulations:
- With the help of high-powered computers, researchers can simulate osmotic processes at the molecular level, providing deeper insights into how water and solutes interact with membranes.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Material Science:
- AI-driven models are being developed to design new membranes with optimal properties for various applications, from industrial water treatment to bioengineering.
Practical Applications and Benefits
Understanding what is osmosis? has a wide range of applications that affect everyday life, scientific research, and industrial processes:
1. Everyday Life
- Food Preparation:
- Osmosis is at work when you soak dried fruits to rehydrate them, or when you marinate meat. It explains how flavors penetrate and how textures change.
- Household Uses:
- The principle of osmosis helps in cleaning processes. For example, placing a sponge in water demonstrates osmosis as the sponge absorbs water through its porous structure.
2. Science and Medicine
- Cellular Function:
- In biology, osmosis is fundamental for cell survival. It explains how cells maintain their shape, how nutrients are absorbed, and how waste products are expelled.
- Medical Treatments:
- Osmosis is critical for processes such as dialysis in kidney failure patients, where waste products are removed from the blood via osmotic gradients.
3. Industry and Engineering
- Water Purification:
- Reverse osmosis is a cornerstone technology in water treatment plants, turning seawater into potable water and removing impurities from industrial wastewater.
- Agricultural Efficiency:
- Engineers and agronomists use osmotic principles to design more efficient irrigation systems and improve crop water retention, contributing to sustainable farming practices.
4. Technological Innovation
- Membrane Technology:
- Advances in osmosis have spurred innovations in membrane design, crucial for applications ranging from fuel cells to environmental monitoring devices.
- Data-Driven Modeling:
- In research and development, modeling osmotic processes helps scientists optimize systems for energy efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced performance.
Conclusion
Summarizing Key Points
- Definition: At its core, what is osmosis? It is the passive movement of a solvent—typically water—through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration until equilibrium is reached.
- Mechanism: Osmosis relies on concentration gradients, semi-permeable membranes, and the natural kinetic energy of molecules. It is a passive process governed by osmotic pressure.
- Historical Evolution: From early observations in ancient civilizations to the formal studies by scientists like Nollet and Graham, the concept of osmosis has evolved into a fundamental principle of modern science.
- Applications: Osmosis is not only central to biological processes but also underpins critical technologies in water purification, agriculture, medicine, and industrial engineering.
- Modern Relevance: In our data-driven era, osmosis continues to inspire innovations in water treatment, environmental sustainability, and biomedical engineering.
Reinforcing the Importance
Understanding what is osmosis? is essential for anyone engaged in science, technology, or daily life. Whether you’re studying cellular processes, developing advanced water filtration systems, or simply curious about how nature balances itself, osmosis is a gateway to comprehending the complex interplay between matter and energy.
Call to Action
- Explore Further: Dive deeper into topics like reverse osmosis, membrane technology, and cellular physiology to expand your understanding of how osmosis shapes our world.
- Share Your Insights: If you found this article enlightening, please share it with friends, colleagues, or fellow students. Start a discussion on social media or in your local study group about the fascinating process of osmosis.
- Engage with Resources: Check out reputable educational resources such as Khan Academy, MIT OpenCourseWare, and scholarly articles on platforms like PubMed for further exploration.
- Apply Your Knowledge: Next time you observe water moving through a sponge, watch a plant absorb water, or even use a reverse osmosis filter at home, reflect on the amazing science behind osmosis. Consider how this knowledge might influence your everyday decisions or inspire a new project.
Understanding what is osmosis? equips you with a fundamental insight into the natural and engineered processes that sustain life and drive innovation. Embrace this knowledge, and let it empower you to make informed decisions in both your academic pursuits and practical life.
Additional Resources
Online Educational Platforms
- Khan Academy – Osmosis – Detailed video lessons and practice exercises.
- MIT OpenCourseWare – Offers courses in biology, chemistry, and engineering that explore osmosis in depth.
Books and Academic Texts
- Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences by Gerald Karp – Provides an in-depth look at cellular processes, including osmosis.
- Water and Life by Felix Ehrat – Explores the role of water in biological systems, discussing osmosis among other topics.
- Principles of Membrane Biophysics – For a deeper dive into how semi-permeable membranes work in osmosis and related processes.
Research Journals and Articles
- Journal of Membrane Science – For the latest research on membrane technology and osmosis.
- PubMed – Search for scholarly articles on osmosis in medical and biological contexts.
Interactive Tools and Simulations
- PhET Interactive Simulations – Offers simulations on osmosis and diffusion to help visualize the process.
- Apps and Software: Tools like MATLAB or Python (with libraries such as NumPy and SciPy) can be used to model osmotic processes and analyze data.
Community and Discussion Forums
- Reddit’s r/biology – Engage with enthusiasts and experts about osmosis and related topics.
- Stack Exchange: Biology – Ask questions and share insights about biological processes like osmosis.
By leveraging these resources, you can continue your exploration into the fascinating realm of osmosis, deepen your understanding, and stay current with the latest scientific advancements.